Content
- 1 Where does the Packham pear grow?
- 2 Description of the Packham pear variety
- 3 Fruit characteristics
- 4 Pros and cons of the variety
- 5 Optimal growing conditions
- 6 Planting and caring for Packham pear
- 7 Pollination
- 8 Productivity
- 9 Calorie content of Packham pear
- 10 Diseases and pests
- 11 Reviews of Packham pear
- 12 Conclusion
Packham pear appeared on the Russian market relatively recently. This variety grows in South America and Australia. Many gardeners love the fruits for their excellent taste. The pulp is quite dense, but at the same time juicy, tastes sweet with a slight presence of sourness. After harvesting, Packham pears can be stored in a cool, well-ventilated place.
Where does the Packham pear grow?
The Packham pear is a variety of the Bartlett variety. The breeder Ch. Packham began breeding the hybrid in the 19th century, after which the tree received the appropriate name.
Fruits were brought to Russia from Chile, Argentina and South Africa. Planting material is suitable for propagation in places with a temperate climate, so it is necessary to take into account that seedlings need shelter for the winter.
Description of the Packham pear variety
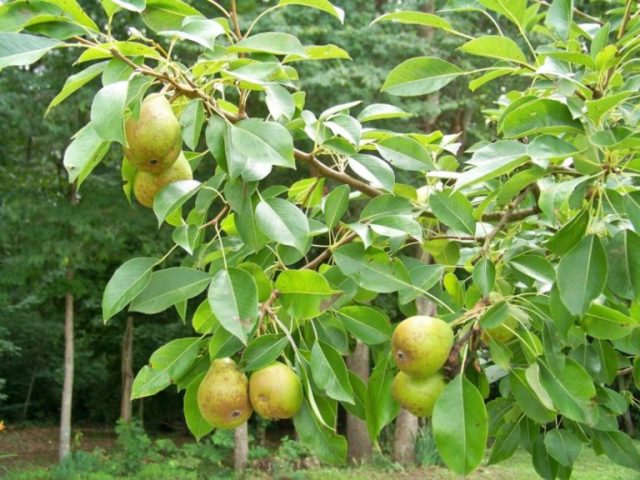
Ripe fruits of the Packham variety are oblong and irregular in shape, usually with small tubercles. The average weight of the fruit is 200 g. The peel is rough, rich green in color, with inclusions.At the moment of ripening, the color changes to yellow or cream.
Young seedlings look like pyramids with a spreading crown. The leaves are medium in size; there are a small number of them on the tree. As the fruits begin to ripen, the branches droop toward the ground, making the tree's shape irregular. When mature, the tree can grow up to 3 m in height. Flowering and fruiting are quite late; the tree can produce a harvest for about 80 years.
Fruit characteristics
At the moment of ripening, the fruits become yellow, after which the pears become creamy. The pulp is juicy and sweet, crunchy when eaten.
Ripe fruits are low in calories, while pears contain a large amount of vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Eating pear varieties Pakham, toxic components can be removed from the body. If you provide optimal storage conditions, the harvested crop will last in the basement for about 2 months.
Pros and cons of the variety
When studying the benefits of the Pakham pear, it is necessary to highlight:
- high level of productivity;
- excellent taste;
- long shelf life of the crop.
According to gardeners, significant disadvantages are:
- rather low level of frost resistance;
- susceptibility to diseases and attacks by insect pests.
Before choosing a particular pear variety, it is recommended to study the available features.
Optimal growing conditions
If we take into account the description of the Packham pear variety and reviews from gardeners, we can conclude that the seedling is suitable for growing in any region where moderate climatic conditions are observed. The only drawback is the low level of frost resistance and the need for shelter for the winter. Without covering work, the root system may freeze, which will lead to the death of the entire tree.
Planting and caring for Packham pear
To achieve high yields, it is necessary to provide the Pakham pear with proper care. To keep trees healthy, it is necessary to carry out preventive work to combat pests and diseases.
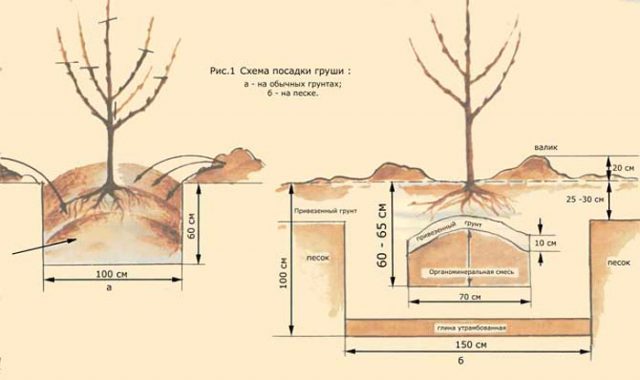
Landing rules
For planting, select seedlings up to 2 years old and up to 1.5 m high. The branches of a young tree must be flexible and the root system strong. Before planting the Pakham pear in open ground, you should keep the roots in a growth stimulator (for example, Kornevin or Heteroauxin) for 12 hours, which will allow the seedling to take root much better. After completing the work, the pear trees should be watered; each root requires about 20 liters of water.
Watering and fertilizing
Fertilizers are applied throughout the year:
- In spring, liquid fertilizers are used under the roots, in summer - preparations containing nitrogen;
- in July it is recommended to apply mineral and nitrogen fertilizers; if necessary, phosphorus can be added;
- in September they use nitrogen substances;
- before the onset of winter, potassium and superphosphates are added.
Seedlings recently planted in open ground are regularly watered. After watering, the soil is loosened, which helps prevent the appearance of an earthen crust. To ensure that water evaporates slowly, the ground around the pear tree is mulched, covered with manure or dry leaves.
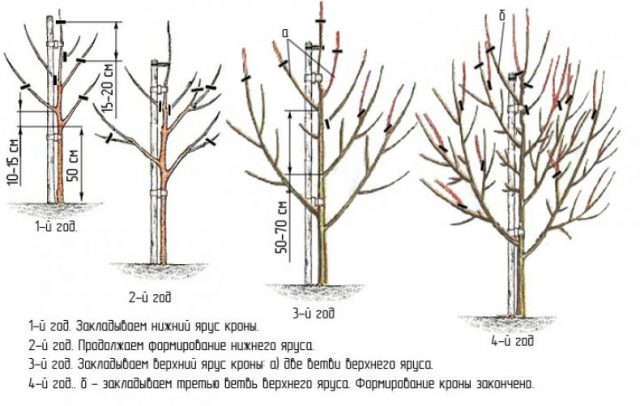
Trimming
The formation of young trees begins in the spring, before the onset of the growing season. To do this, weak side shoots are removed completely, as a result of which stronger branches unimpededly strengthen the base of the tree.
Mature pear trees are pruned 2 times throughout the year:
- in early spring;
- late autumn, when the movement of juices slows down. In this case, it is necessary to remove old branches and thin out the crown.
Whitewash
The Packham pear needs whitewashing so that during the growth process the trunk is not susceptible to frostbite and sunburn. Otherwise, cracks appear on the tree bark, into which pests and fungal spores penetrate and the process of infection of the fruit tree begins. You can purchase a ready-made solution in a specialized store or prepare it yourself.
Preparing for winter
The root system of the Packham pear needs shelter for the winter. The work algorithm looks like this:
- The trunk is wrapped with paper, cardboard or straw.
- Around the planting hole, remove existing weeds.
- Before sending the tree to winter, it is watered abundantly.
- Fertilizers can be added if necessary.
In order for the pear tree to better tolerate low temperatures, it is necessary to pre-treat the plant with an Ecobin or Zircon solution.
Pollination
When growing pears, take into account that there are varieties capable of self-pollination, but most pear trees, including the Packham variety, are self-sterile. If the pollination process occurs naturally, then there will be no result and the fruits will not set. Forest Beauty, Olivier de Serre, and Clapp's Favorite are used as pollinators for this variety.
If necessary, you can pollinate fruit trees yourself. To do this, purchase a special preparation in the store and, according to the attached instructions, pollinate the Packham pear.
Productivity
Before you start planting planting material, it is recommended to first study the advantages, disadvantages and features of the Packham pear variety. As a rule, planting should be done in groups; trees should not be planted individually, as there is a high probability that the seedling will die.
As a rule, fruiting is abundant. You can start harvesting the finished crop 4 years after the tree was planted in open ground. The period of active fruiting occurs in the seventh year of the tree’s life. As experienced gardeners have noticed, from each specimen you can collect from 80 to 150 kg of ripe fruits.
Calorie content of Packham pear
The calorie content of Packham pear is 42 kcal per 100 grams; in addition, it contains:
- proteins – 0.7 g;
- fats – 0.2 g;
- carbohydrates – 10.9 g;
- acidity is moderate.
The fruits contain useful substances, but they can negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract, so it is not recommended:
- wash down fruit with water;
- eat on an empty stomach;
- combine with meat and curd products.
If you follow these recommendations, then Packham pears will bring significant benefits to the body.
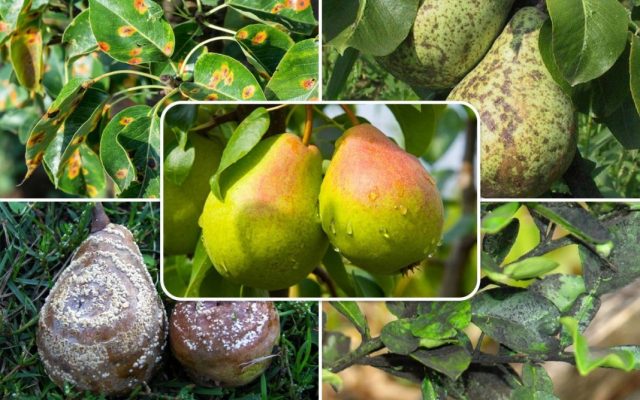
Diseases and pests
Most often, the Packham pear is affected by rot, fungus and insects. By carrying out preventive measures and timely treatment, you can maintain the health of the tree. Among the common problems gardeners note are the following:
- scab – the fruits of the infected tree begin to crack and become woody;
- rot – a disease brought by birds, resulting in growths appearing on fruits;
- black cancer – the tree itself becomes infected, the bark begins to deform.
To prevent diseases, you can use traditional methods or insecticides.
Reviews of Packham pear
Conclusion
The Packham pear is valued by many gardeners for its high yield.From 80 to 150 kg of ripe fruits are collected from each tree; up to 40 tons of pears are obtained from 1 hectare. The fruits have a large number of advantages: excellent taste, juiciness, long-term storage. Pears of this variety contain many vitamins, so they are recommended for children and adults.