Content
Planting a seed in a peat pellet makes germination much easier. Growing seedlings also really like peat tablets. Reduced labor costs and increased germination are understandable reasons for the increased popularity of planting in peat tablets.
What it is
Tablets before and after moisturizing
Seedling tablets are essentially compressed circles of peat or peat mixture. Mostly high-moss (often called sphagnum) moss is used - almost not decomposed, with a small content of minerals. But it is distinguished by durability and excellent filtering capabilities.
The peat is selected to be finely dispersed, after pressing it is dehydrated and covered with a fine mesh that can withstand significant swelling.
In the center there is a small depression for the seed. A moistened tablet increases in volume up to 7 times.
Types of tablets used
Since they are used for seeds and seedlings of very different sizes, their height/diameter also differs significantly: from 8/24 mm to 30/100. The size is influenced by two more factors - the rate of seed germination and the time until transshipment. Taking these factors into account, peat tablets of different diameters are used as follows:
- < 3 centimeters – for small seeds;
- 3-4 cm – for medium seedlings, seeds of asters, marigolds, lavender;
- > 4 cm – for seeds of tomatoes, peppers, eggplants.
Depending on the quality of peat and the additives used, there are 4 classes of tablets:
- Conventional ones are made of sphagnum peat with mineral additives, covered with cellulose.
- Peat-humus substrate - in addition to mineral and other growth additives, includes antibacterial components (against root rotting).
- The highest class of peat - vitamin and mineral growth stimulants are added to the premium class substrate.
- Peat with fungicides – impregnation with fungicides protects against fungi, viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens.

Cups

Briquettes
Benefits of seedling tablets
- the best way to germinate crops with small seeds;
- complex nutrition in a tablet makes seedlings more resistant, with immunity to diseases;
- the best method for plants that do not tolerate transplantation;
- provide high germination;
- freeing up space;
- do not require additional power;
- do not absorb moisture more than necessary;
- maximum simplification of the gardener’s work;
- allow cassette and mini-greenhouse growing of seedlings;
- unlimited shelf life.

Plastic mini-greenhouses
Growing seedlings in peat tablets
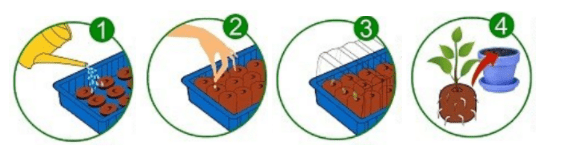
First, the area for planting is prepared. It is convenient to use pallets or containers for this. The tablets are placed in them with the indentations facing up. During watering: either 2 tablespoons per tablet, or the entire tray - since the peat will not become more wet than necessary.After 15-20 minutes (until the tablet swells completely), excess water is drained from the pan.
At the 2nd stage, 1-2 seeds are inserted into the tablet recesses - to a depth of two seed lengths. Sprinkle the seeds with a thin layer of humus.
It is better to lay the bottom of the container/pallet with coarse sand or small pebbles to ensure normal humidity conditions in it.
At the third stage, the pallet is covered with plastic film or clean glass, forming a mini-greenhouse. Place the greenhouse in a warm place, but not in direct sunlight and so that it is convenient to approach. It needs to be ventilated from time to time.
And finally, after the planting material is ready (determined by the roots entangling the entire cylinder), it must be transplanted to a permanent place. Two days before this, harden it by taking it out into the fresh air, or opening a window next to the mini-greenhouse. It's enough.
Where there were two seeds, either the weak sprout of the plant is removed, or the strong second one is planted in a separate pot with a nutritious soil mixture, like the first.
It is not necessary to remove the shell from the cylinder.
Growing seeds and seedlings in peat tablets is grateful to housewives and agricultural technicians - simplicity, cleanliness, increased germination and immunity compared to traditional sowing in a box.