Content
The frame is the main structure of any greenhouse. It is to this that the covering material is attached, be it film, polycarbonate or glass. The durability of the structure depends on the material used for the construction of the frame. Frames are made from metal and plastic pipes, wooden blocks, and corners. However, galvanized profiles that meet all construction requirements are considered more popular for greenhouses.
Pros and cons of using galvanized profiles in greenhouse construction
Like any other building material, galvanized profiles have their advantages and disadvantages. Most of all, the material receives positive feedback from summer residents. In particular, this is justified by the following points:
- Any amateur without construction experience can assemble a greenhouse frame from a profile. The only tools you need are a jigsaw, an electric drill and a screwdriver. Most of this can be found in every owner's utility room. As a last resort, you can cut parts from the profile with a regular metal file.
- The big advantage is that galvanization is less susceptible to corrosion; it does not need to be painted or treated with an anti-corrosion compound.
- The greenhouse frame made from the profile is lightweight. If necessary, the entire assembled structure can be moved to another location.
- The cost of a galvanized profile is several times less than a metal pipe, which is very beneficial for any summer resident.
On sale now there are ready-made greenhouses made of galvanized profiles in disassembled form. It is enough to buy such a construction set and assemble all the parts according to the diagram.
Typically, the greenhouse frame is secured to the foundation with dowels. If there is no concrete base, the frame is fixed to pieces of reinforcement driven into the ground at 1 m intervals.
The disadvantage of a galvanized profile can be considered its low load-bearing capacity relative to a metal pipe. The bearing capacity of the profile frame is maximum 20 kg/m2. That is, if more than 5 cm of wet snow accumulates on the roof, the structure will not support such weight. That is why most often the profile frames of greenhouses are made not with a pitched roof, but with a gable or arched one. This form retains less precipitation.
As for the absence of corrosion, this concept is also relative. The profile does not rust quickly, like a regular metal pipe, as long as the galvanization remains intact. In those areas where the galvanized coating was accidentally damaged, over time the metal will corrode and will have to be painted.
What is an omega profile
Recently, galvanized “omega” profiles have been used for greenhouses.It got its name from its bizarre shape, reminiscent of the Latin letter “Ω”. The Omega profile consists of five shelves. Many companies produce it in different sizes according to the individual order of the consumer. Omega is often used in the construction of ventilated facades and roof structures. Due to the simple installation of the profile with your own hands and increased strength, it began to be used in the manufacture of greenhouse frames.
Thanks to its shape, "omega" can withstand more weight than a regular profile. This increases the load-bearing capacity of the entire greenhouse frame. Among builders, "omega" received another nickname - a hat profile. To produce Omega, metal with a thickness of 0.9 to 2 mm is used. The most popular are products with wall thicknesses of 1.2 mm and 1.5 mm. The first option is used in the construction of weak, and the second - reinforced structures.
Assembling the greenhouse profile frame
Having decided to improve your home plot with a greenhouse made of galvanized profile, it is, of course, better to give preference to “omega”. Before purchasing the material, you must make an accurate drawing of all the design details and the diagram of the greenhouse itself. This will simplify the process of future construction and allow you to calculate the required amount of profile.
Manufacturing of end walls
It should be noted right away that if an “omega” profile is chosen for the greenhouse frame, then it is better to make the roof gable. It is difficult to bend arched structures on your own; moreover, the “omega” breaks when bent.
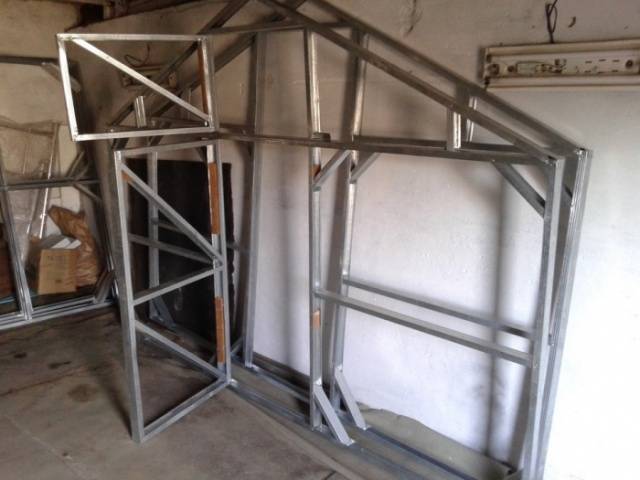
The end walls set the shape of the entire frame. To ensure they have the correct shape, all the parts are laid out on a flat area.Any flaw in the design will entail a distortion of the entire frame, to which it will be impossible to attach the polycarbonate.
Further work is performed in the following order:
- A square or rectangle is laid out from profile sections on a flat area. The choice of figure depends on the size of the greenhouse. You must immediately mark where the bottom and top of the resulting frame will be.Attention! Before fastening the parts into one frame, use a tape measure to measure the distance between opposite corners. For a regular square or rectangle, the difference in the lengths of the diagonals should not exceed 5 mm.
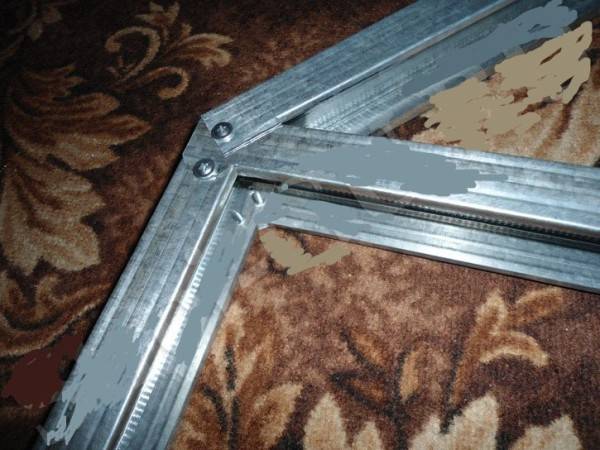
- Galvanization is quite soft and does not require additional drilling to tighten the screws. The ends of the frame parts are inserted into each other and simply tightened with at least two screws at each corner. If the frame is wobbly, the connections are additionally reinforced with self-tapping screws.
- From the center of the top element of the frame, mark a perpendicular line, indicating the ridge of the roof. You immediately need to measure the distance from the top, that is, the ridge, to the adjacent corners of the frame. It should be the same. Next, these two distances are summed up and the length of the profile is measured based on the result obtained, after which it is sawed off with a hacksaw or jigsaw. In the resulting workpiece, the side flanges are cut strictly in the center and the profile is bent in the same place, giving it the shape of a gable roof.
- The resulting roof is fixed to the frame with self-tapping screws. To strengthen the structure, the corners of the frame are reinforced diagonally with stiffening ribs, that is, sections of the profile are screwed obliquely. The rear end wall is ready. Using the same principle, a front end wall of identical size is made, only it is supplemented with two vertical posts that form a doorway.Advice! The door frame is assembled using the same principle from a profile, but it is better to do this after making the doorway to avoid errors in dimensions.
- Having finished working with the end walls, cut pieces of the profile and, having cut in the center, bend additional skates of the same size as they did for the end walls. Here you need to accurately calculate the number of skates. The width of the polycarbonate is 2.1 m, but such spans will sag and snow will fall through them. It is optimal to install skates in increments of 1.05 m. It is easy to calculate their number along the length of the greenhouse.
The last thing you need to prepare before assembling the frame is 4 pieces of profile the size of the length of the greenhouse. They are needed to fasten the end walls together.
Assembling the greenhouse profile frame
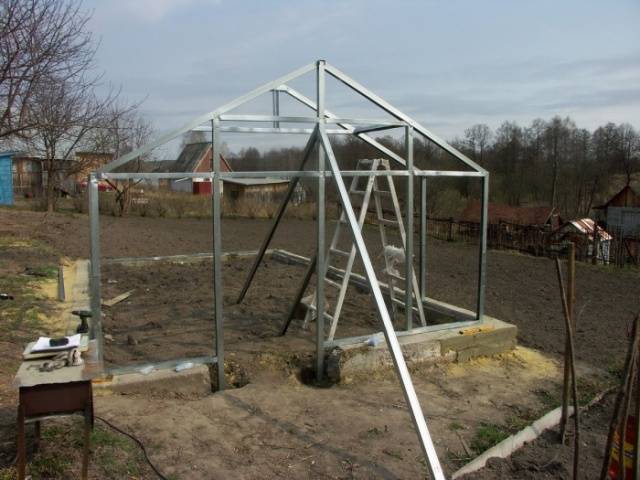
Assembly of the frame begins with the installation of both end walls in their permanent place. To prevent them from falling, they are supported with temporary supports. Prepared 4 long profiles connect the end walls. The upper corners of the opposite walls are fastened with two horizontal blanks, and the same is done with two other blanks, only at the bottom of the structure. The result is a still fragile greenhouse frame.
On the lower and upper newly installed horizontal profiles, marks are made every 1.05 m. In these places, the rack-mount stiffeners of the frame are attached. Prepared skates are fixed to the same racks. The last to be installed is the ridge element at the very top along the length of the entire greenhouse.
Reinforcement of the frame with additional stiffening ribs
The finished frame is strong enough to withstand average gusts of wind and precipitation. If desired, it can be further reinforced with stiffeners.Spacers are made from profile pieces, after which they are fixed diagonally, reinforcing each corner of the frame.
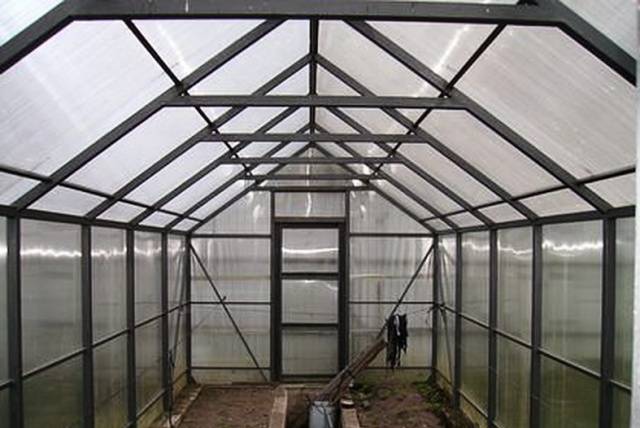
Polycarbonate sheathing
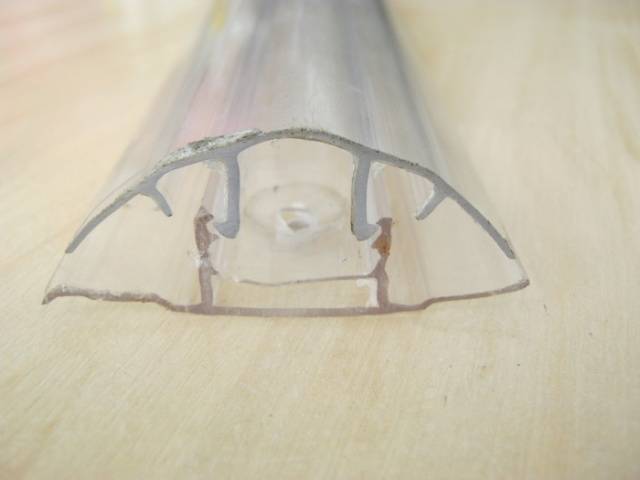
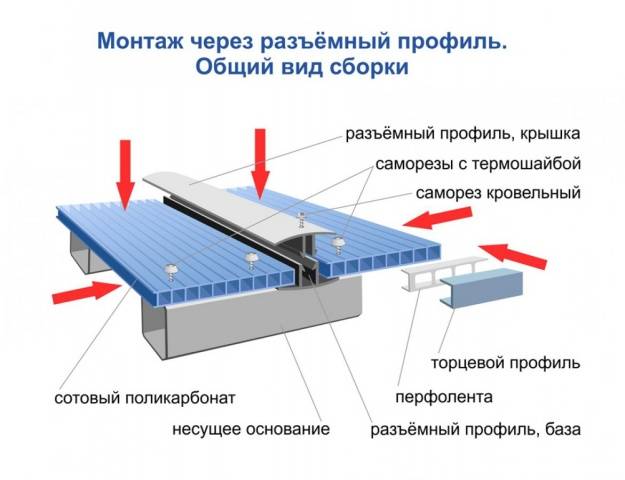
Covering the frame with polycarbonate begins with attaching the lock to the profile at the joints of the sheets. The lock is simply screwed on with self-tapping screws and rubber gaskets.
It is optimal to start laying polycarbonate from the roof. The sheets are inserted into the grooves of the lock and screwed to the profile with self-tapping screws and plastic washers.
All polycarbonate sheets must be evenly pressed against the frame with self-tapping screws. It is important not to overdo it so that the sheet does not crack.
After fixing all the sheets, all that remains is to snap the top cover of the lock and remove the protective film from the polycarbonate.
The video shows the production of a greenhouse frame from a profile:
The greenhouse is completely ready, all that remains is to do the interior arrangement and you can grow your favorite crops.