Content
After completing the construction of the greenhouse, one cannot yet talk about its readiness for growing vegetables. The structure must be equipped inside, and the convenience of growing crops, as well as the yield indicator, depends on how this is done. Now we will look at how to arrange a greenhouse inside polycarbonatein order to rationally use space and at the same time get a good harvest.
Important nuances of the internal arrangement of a greenhouse
When the question of how to properly arrange the internal greenhouse space becomes relevant, you immediately need to decide on the method of growing crops. The layout of the entire room depends on where the plants will grow in the garden bed or shelving.
There are several main points that require attention at the initial stage of arranging a greenhouse:
- Watering – this is the first thing that plants cannot do without. Internal watering should begin at the initial stage of arrangement. First of all, water intake points are prepared. Usually 1 point is enough, but if the greenhouse area is large, it is wise to make several of them. It is important to immediately decide on the future irrigation system.Drip irrigation is considered the most effective.
- When equipping a greenhouse, it is important to take care of ventilation. Without access to fresh air, not a single plant can develop normally. In a polycarbonate greenhouse, it is very easy to make sections that can be opened for ventilation. The location of the vents is determined even before the greenhouse frame is sheathed with polycarbonate.
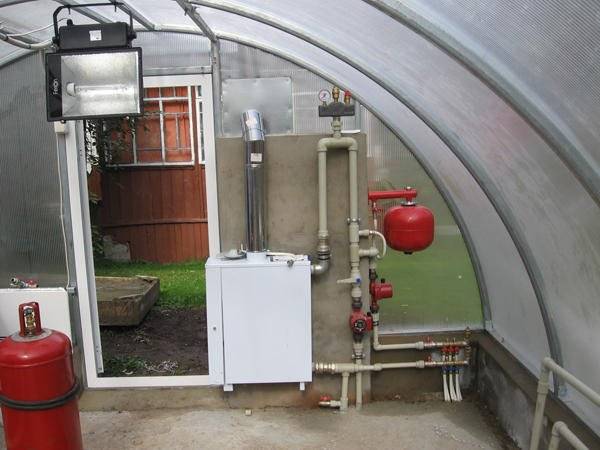
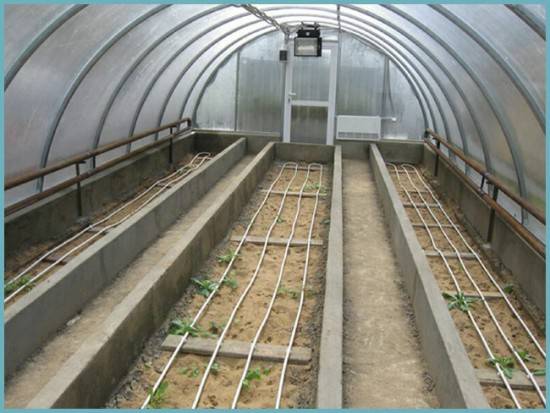
- Next attention needs to be paid heating. Polycarbonate greenhouses can be used for winter growing of vegetables. You can set up a heating system in different ways: from the simplest installation of a potbelly stove, heat gun, or infrared heater to the complex installation of water heating or heated floors. When choosing one of the heating systems, it is necessary to take into account that almost all of them are aimed at heating the air, and only a warm floor can warm up the greenhouse soil. Laying of heated floors is carried out under all beds and drainage. It is imperative to put thermal insulation under the thermal circuit. It would be better if it had a foil reflector. This layer prevents the passage of heat into the soil and directs it upward to heat the soil in the garden bed.
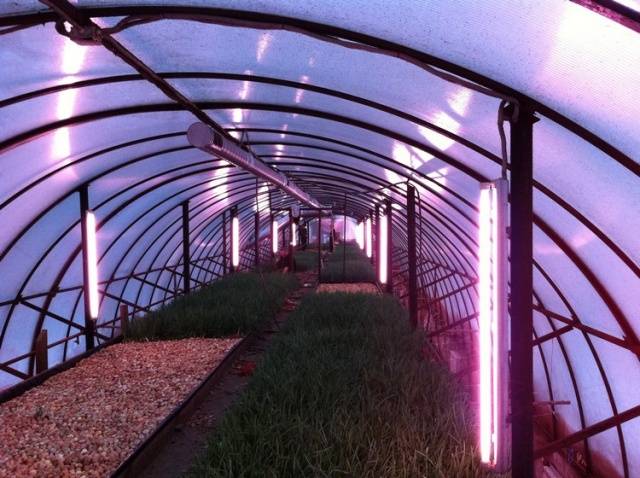
- A greenhouse with lighting from ordinary incandescent lamps represents an ordinary equipped barn. Plants will develop poorly in this light due to the lack of blue light in the spectrum. It is optimal to use LED, gas-discharge or fluorescent lamps for lighting polycarbonate greenhouses.
The video talks about lamps for lighting greenhouses:
When all these important points have been thought through, you can proceed to the next stage of arrangement. This means making shelves, shelving, partitions and other structures.
Methods for insulating a greenhouse
It is very good to make heating in a greenhouse, but its effectiveness depends on how well the insulation of the building itself is done. After all, a large loss of heat will cost the owner a pretty penny, plus during severe frosts the heating system may not be able to cope with heating the greenhouse and the plants will simply die.
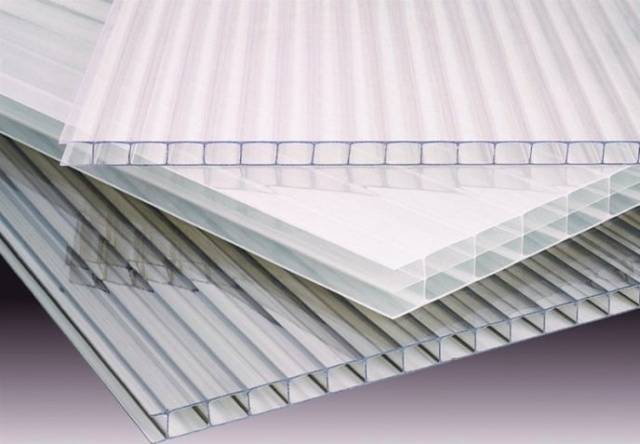
Since polycarbonate cladding has been chosen for the greenhouse, this is already the first step in preserving heat. Transparent sheet plastic with a cellular structure has minimal heat loss compared to polyethylene film. However, when attaching polycarbonate, you cannot skimp on rubber seals. Thanks to them, the possibility of heat escaping through the cracks of the joints is eliminated.
It is necessary to take care of heat conservation at the initial stage of greenhouse construction. First of all, you need to insulate the foundation itself. The foundation is laid no shallower than the depth of soil freezing. For the construction of foundations, adobe blocks treated with concrete mortar and polymer mastic have proven themselves to be excellent. The upper part of the foundation is covered with roofing felt, and the inside is insulated with foam plastic and a 400 mm layer of sand.
Heat in the soil itself can only be retained in a properly made bed. It must be raised by at least 400 mm. An electric heating cable buried along the rows has a good effect.
The video talks about insulating a polycarbonate greenhouse:
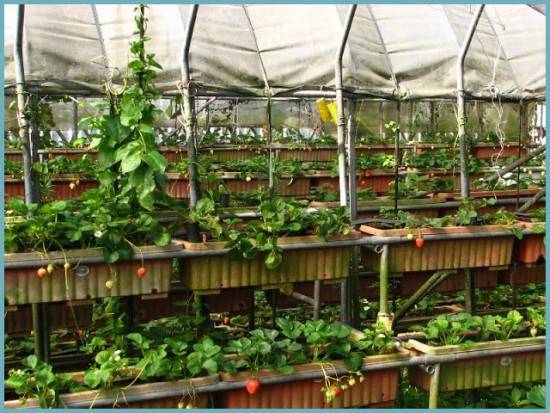
Arranging a greenhouse with shelving
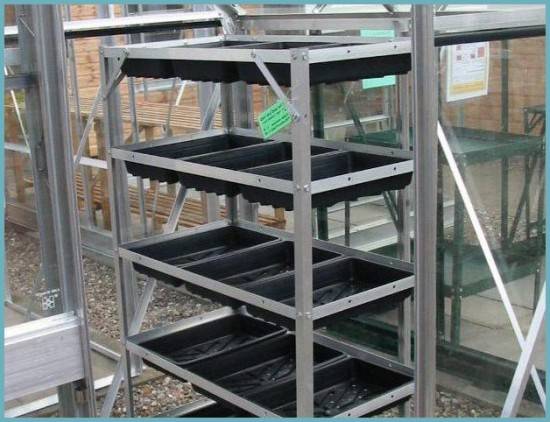
A polycarbonate greenhouse allows you to grow some crops on shelves. This is very convenient, since double space saving allows you to get more harvest. Racks, regardless of the material from which they are made, have an impressive weight. After all, there are many containers with soil on the shelves. Only a concrete floor can ensure the stability of the structure. For small ones racks for growing seedlings It will be enough to lay the floor with old bricks or slabs.
For the manufacture of the racks themselves, wooden blanks treated with an antiseptic, as well as metal pipes, profiles, and corners are suitable. The dimensions of the structure are determined individually according to needs. It is reasonable to select the height of the rack in relation to the height of the owner. The top shelf should be at eye level so that the grower can reach the plant without a stand. It is possible to manufacture high shelves for storing various equipment.
The number of shelves on a rack in a standard greenhouse 2 m high depends on its purpose. For growing crops, 3 or 4 shelves are usually left. Here you need to be guided by the height of the plants so that their tops do not rest against the shelf above. A rack equipped for growing seedlings can consist of 6 shelves.
Plants growing on shelves should receive maximum light; for this purpose, racks are placed along the walls. If they stand in rows, then it is necessary to maintain a minimum passage width of 500 mm. Racks on wheels have proven themselves to be quite good. They allow you to periodically turn the plants with different sides to the transparent wall of the greenhouse.
Installation of partitions in a greenhouse
A partition is not an essential design, but its use is justified when growing poorly adjacent crops. To make the partition, they usually take the same material that was used to cover the frame of the greenhouse - polycarbonate. To have access to both parts of the greenhouse and to ventilate it, a door is made in the partition. If the building is a walk-through building, that is, with doors at both ends, the partition can be made blank. In this case, you can simply stretch the PET film.
Arrangement of the pantry
If the dimensions of the greenhouse allow you to set aside a small room for a storage room, do not neglect this. After all, you always need a tool to work. Carrying shovels, hoes, and watering cans from the barn every time is not very convenient, but by placing them in the pantry, the necessary tool will always be at hand. It is enough to fence off a small room to install a wooden rack with shelves and cells in it.
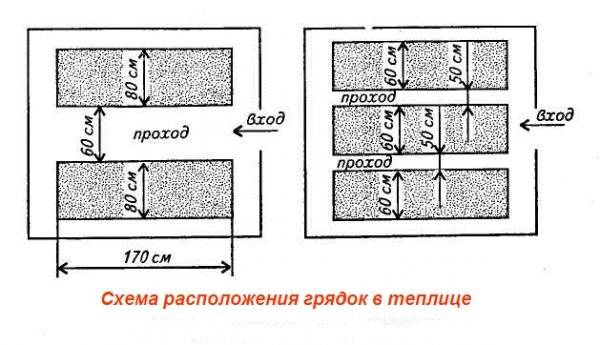
Beds and paths in a greenhouse
To access the ridges, you need to take care of the paths. Their number and arrangement depend on the shape and dimensions of the greenhouse. For example, for a rectangular building measuring 2x6 m, 1 path 400 mm wide in the center between the beds is sufficient. Then the width of the beds on both sides of the path will be 800 mm. These dimensions make it convenient to care for plants.
In large greenhouses there may be 2, 3 or more paths between the beds. Typically, paths are paved with any hard material: brick, crushed stone, tiles, etc. The hard surface will not become limp from moisture and will not slip.
The standard height of the beds from the level of the path is 300–400 mm.Fences made of boards secured with wooden stakes will help keep the edges of the beds from spilling soil onto the path. Instead of boards, the beds are fenced with curbs, bricks or any other available material.
Arranging the beds begins with laying the film. It will serve as a water barrier, save heat and retain moisture in the soil. A drainage layer is poured on top of the film, and only then does it reach the soil. The soil is chosen to be fertile and suitable in composition for growing a particular crop. In the future, the soil will have to be fed with mineral and organic fertilizers.
The video tells about the arrangement of the greenhouse:
Here, in general, are all the main stages of arranging a polycarbonate greenhouse. Each vegetable grower has the right to equip the building at his own discretion, the main thing is that growing crops is comfortable and gives a positive result.