Content
In favorable conditions with sufficient moisture and fertilizer, tomatoes grow actively and form a large number of shoots. Such intensive development thickens plantings and reduces crop yields. That is why experienced gardeners recommend shaping tomatoes, which involves pinching and pinching the plants. These activities must be carried out competently, so as not to harm the tomatoes, but to help them bear fruit successfully.
How to form tomato bushes of various types
Farmers divide all varieties of tomatoes into indeterminate And determinant. Sometimes on packages of seeds you can see exaggerated synonyms of these concepts, that is, “tall” and “short" tomatoes. This rough classification allows the buyer to select varieties with certain agrotechnical characteristics. Caring for indeterminate and determinate tomatoes is fundamentally different. When purchasing this or that type of tomato, you should take into account the peculiarities of cultivation, including the rules bush formation.
Determinate tomatoes
It is not for nothing that the division of all tomatoes into indeterminate and determinate varieties is called a rough classification. The thing is that each of these species has its own subspecies. In general, determinate tomatoes are plants that independently regulate their growth. As a rule, determinate tomatoes do not form more than five fruiting clusters on one shoot, including the main one.
Superdeterminate varieties
Superdeterminate varieties limit their growth quite early. The fruits of such plants ripen quickly in mid-summer. Superdeterminate tomatoes do not form large stepsons, so caring for the crop is quite simple and involves removing only the lower leaves. There is no need to pinch or pincher the plants.
Determinate varieties
"Simple" determinate tomatoes are sometimes called medium-growing tomatoes. During the growing process, they must be shaped by removing the stepsons. Otherwise, the tomatoes will actively grow green mass, and their fruits will set in small quantities and ripen slowly. When growing determinate tomatoes, usually leave 2-3 additional side shoots on which they will form ovaries after growth of the main stem stops.
Standard varieties
Standard tomatoes are an excellent option for lazy gardeners. The advantage of standard tomatoes is their independent growth regulation and slow growth of stepchildren. Caring for such tomatoes is very simple, because they do not need to be shaped by pinching and pinching, you just need to periodically remove the lower leaves of the tomatoes.
All types of determinate tomatoes form the first fruit cluster above the 5-7 leaf.Next, the formation of inflorescences occurs after 1-2 leaves. It is recommended to grow such tomatoes in open areas of soil, however, in the northern regions, planting determinate plants in protected soil is quite justified. During the growing process, superdeterminate and determinate tomatoes need staking. Gartering of standard varieties is carried out as needed.
For a determinate type of plant, you can watch a video of the formation of a tomato bush:
Indeterminate tomatoes
More often Indeterminate tomatoes are the choice of professional farmers. They are able to grow and bear fruit unlimitedly throughout the warm period. More often they are grown in greenhouses or heated greenhouses. If the latter are available, tomatoes can be harvested from indeterminate plants all year round.
Indeterminate tomatoes can grow up to 3 m in height. In the absence of bush formation, stepsons form in large numbers and thicken the planting, robbing the plants of the strength to form and ripen fruits. The first inflorescence of such tomatoes appears above the 9th leaf. All higher located inflorescences are tied through 3 leaves. Over the entire life cycle, indeterminate tomatoes can form up to 50 fruiting clusters. Such tomatoes require tying to a stable support and carefully forming the bushes into one stem.
A video of the formation of an indeterminate tomato bush can be seen in the video:
Thus, when purchasing tomato seeds, it is necessary to pay attention to the agrotechnical characteristics of the variety. Having chosen “simple” determinate, semi-determinate and indeterminate tomatoes, you need to be prepared for the fact that you will need to form the bushes in a certain way, using the methods of pinching and pinching tomatoes. Superdeterminate and standard tomatoes will not require special care, however, their yield will be comparatively lower.
Rules for forming a bush
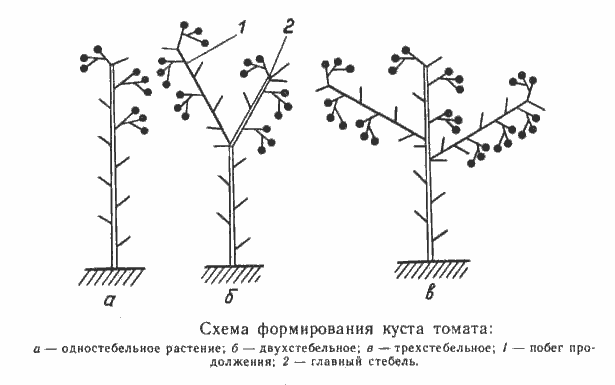
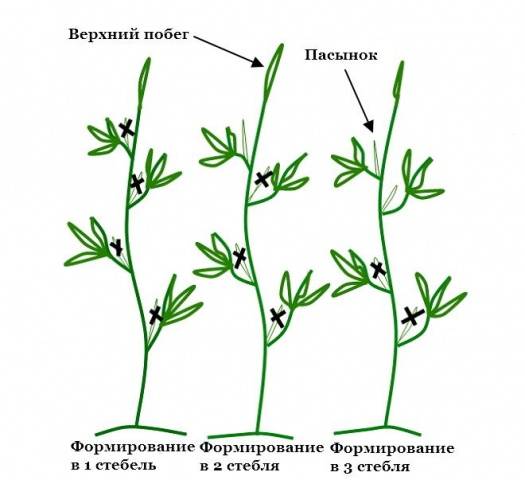
As has already become clear, various types of tomato bushes form one, two or several stems. At the same time, pinching and pinching tomatoes perform very specific functions, and the activities must be carried out in compliance with clear rules.
Stepping procedure
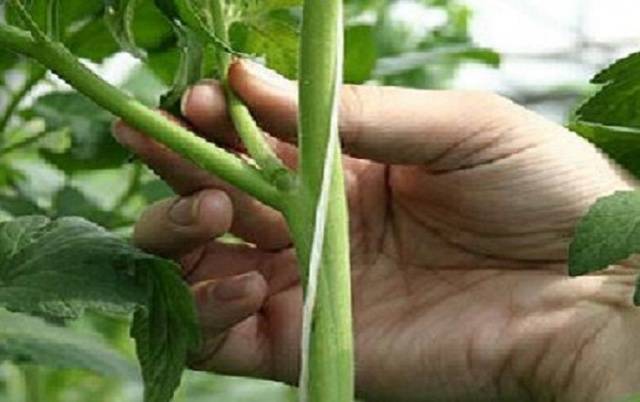
Proper formation of a tomato always includes a pinching procedure. For beginning farmers, identifying and removing stepchildren can cause some difficulties, so we will try to talk about this in more detail.
What is a stepson
The stepson is a side shoot formed in the axil of a tomato leaf. During the growth process, green leaves and fruit clusters are formed en masse on the stepsons, as well as on the main stem. Such active growth of stepsons requires a large amount of nutrients, which can provoke the formation of smaller fruits on the main stem and slow down their ripening period. If you do not remove the lateral stepsons, the plantings become very thick. The lack of normal air circulation between the bushes causes the development of diseases and rotting of the fruits.
Proper pinching of tomatoes allows you to harmoniously form the plant, regulating the ratio of green mass and the number of fruits.As a result of pinching, the plants do not experience severe stress and can safely bear fruit until the end of the growing season. By watching a video of tomato planting, you can appreciate the importance and necessity of this procedure.
How to properly plant tomatoes
It is necessary to plant tomatoes 10-15 days after planting the seedlings in the ground. The size of the stepsons should be approximately 5 cm. After the initial pinching, it is necessary to regularly carefully inspect the plants and carry out additional pinching of the tomatoes every 2 weeks.
A video of pinching tomatoes will allow you to avoid some mistakes and clearly see the implementation of the event:
At bush formation All the resulting stepsons are removed into one stem. This pinching of tomatoes is carried out for indeterminate, tall varieties. If we are talking about stepsoning tomatoes of the semi-determinate type, then in the process of removing shoots it is necessary to leave one of the strongest stepsons. This will allow the plant to form fruit clusters on the stepson at a time when the growth of the main stem has already stopped. At pinching tomatoes with a determinate type The bush leaves two, and sometimes more, side shoots. The scheme for pinching tomatoes into one, two or more stems is shown below.
It is worth noting that the lower stepsons on plants are always removed. The same applies to shoots growing from the root of the plant.
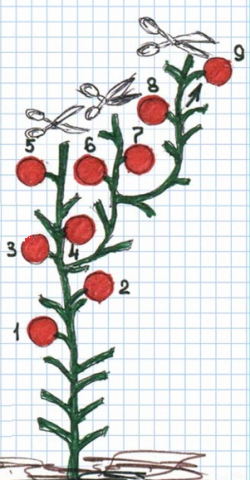
For determinate tomatoes, in addition to the proposed scheme for forming plants into two and three stems, you can use a stepwise pinching scheme. So, under the first fruiting brush of a short or medium-sized plant, a stepson is left. This side shoot develops safely and also forms fruiting clusters. Under the first of them it is also necessary to leave one stepson. After its growth, the stepwise stepsoning procedure is repeated. This allows low-growing and medium-growing tomatoes to form into one stem, while new stepsons will constantly bear fruit, replacing the main stem, which has stopped growing. This pinching of tomatoes can be seen in the diagram below.
It is important for every farmer to remember that pinching and staking tomatoes should be carried out simultaneously. This will relieve the plants of the load from the resulting fruits and leaves.
A video on how to properly tie tomatoes can be seen here:
Pinching tomatoes
Pinching of tomatoes is carried out only when growing tall, indeterminate or semi-determinate varieties. This allows you to stop the growth of the plant and direct all its forces to the ripening of existing fruits. Pinching tomatoes is carried out in the fall, a month before the expected end of the growing season.
Important! Determinate tomatoes are also sometimes pinched to speed up the ripening of the fruit.
When growing tomatoes in a stepwise pattern, you can also use pinching of the main shoots.
The pinching procedure for tomatoes in open areas of land and in greenhouses is carried out in the same way.To do this, remove the top of the main stem to the height of two leaves. Leaving the top leaves of the tomato plant will act as a “pump,” drawing micronutrients from the soil and moving them up the stem. After pinching, the tomatoes begin to actively grow side shoots, however, they also need to be removed by pinching. If you do not remove the lateral stepsons, then the procedure of pinching the tops of tomatoes will be meaningless.
You can see the procedure for pinching tall tomatoes and hear comments from an experienced farmer in the video:
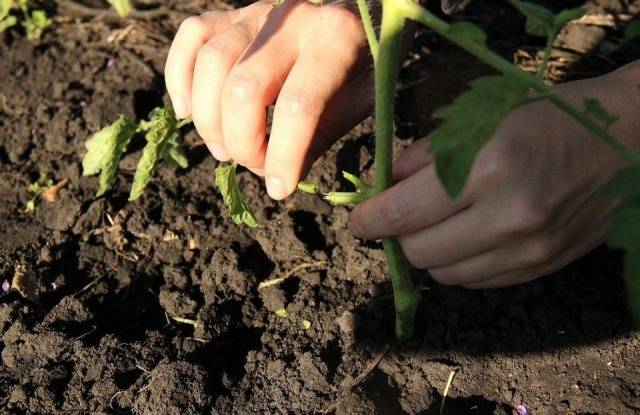
Removing leaves
Experienced gardeners and professional farmers know that by removing leaves you can also speed up the ripening process of tomatoes. This thinning of foliage on tomatoes is carried out starting in early June. Regularly, every week, it is recommended to remove 1-3 leaves located under the lowest fruiting brush. This allows the plant to supply all its nutrients directly to the fruits without wasting energy supplying the leaves.
Leaves must be removed carefully so as not to damage the skin of the plant. To remove leaves, you can use pruning shears or break them off by hand by bending them to the side.
Conclusion
Thus, when growing tomatoes in open areas of the ground and in a greenhouse, it is very important to properly plant the tomatoes, pinch the plants in a timely manner, tie them up and remove the lower leaves. A set of such measures will remove excessive load from plants, speed up the process of fruit ripening, and prevent the development of viral and fungal diseases.Growing and pinching tomatoes must be carried out in compliance with the described rules, adhering to the chosen scheme. If you violate the rules for forming a bush, you can reduce the crop yield, slow down the growth of plants, or even destroy them.