Content
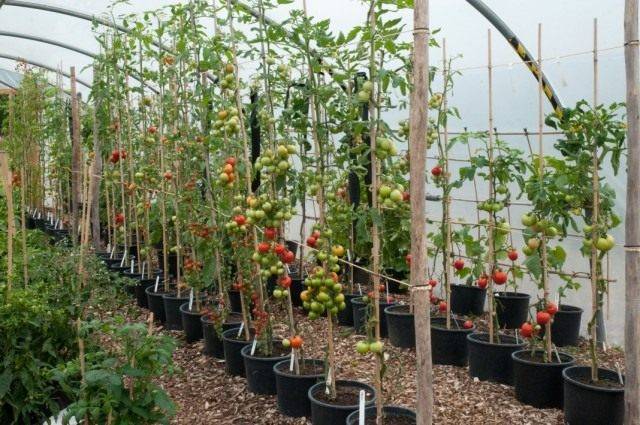
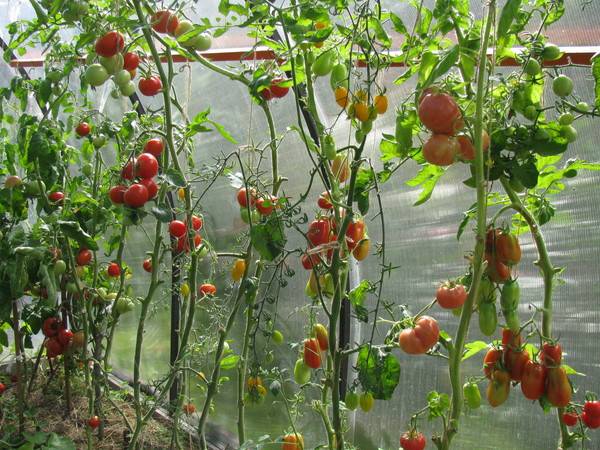
Often in the beds you can see very bare tomato bushes, on which there are practically no leaves, but at the same time there are a huge number of tomatoes. What's the matter? Why do gardeners “peel” tomatoes so mercilessly? But the reason for this is not hatred of plants, but, on the contrary, the desire to help vegetable crops bear fruit in large quantities with minimal energy expenditure. This “exposure” is the result of the formation of a bush, in which the lateral stepsons and lower leaves are removed. Formation of tomatoes single stem is the most commonly used crop growing scheme. It is suitable for tall, medium-sized and even standard tomatoes. We will talk about how to properly carry out such formation without harming the plants in the article below.
Why shape plants
Many gardeners, growing tomatoes for the first time, do not even think about the need to control plant growth and form tomato bushes. As a result, they get lush, quite beautiful bushes with a small number of tomatoes on the branches, which are still green at the end of the season.How does this happen? Why, if you follow all the rules of watering and fertilizing, can you not get a good harvest of vegetables?
And the whole point is that throughout the growing season the plants spent their energy not on the formation of flowering clusters, ripening and filling tomatoes, but on growing greenery in the form of stepsons and leaves. As a result of such incorrect redistribution of nutrients and moisture, the farmer receives low yields, but simply a beautiful plant in the garden.
To prevent this situation, farmers have developed a method for forming tomato bushes. It involves pinching, stepsons and removing some leaves. Depending on the agrotechnical characteristics of the plant, farmers use methods of forming into one, two or three main stems. At the same time, the formation of tomato bushes into one stem is an excellent technology for both tall indeterminate and short determinate tomato varieties.
The technology for forming tomato bushes allows you to improve the process of growing the crop, namely:
- increase the yield of vegetables, make them larger and fuller;
- speed up the harvesting process;
- accelerate the process of fruit ripening with the onset of autumn;
- correctly redistribute the load on the bush from the resulting greens and vegetables;
- make plantings less dense, thereby preventing the development of viral and fungal diseases, improving air circulation;
- make it easier to care for plants;
- extend the fruiting period of tomatoes with limited growth.
Thus, a simple procedure for forming bushes allows the plant to develop correctly, devoting all its strength to increasing productivity. However, you should not mindlessly break off the shoots and leaves on tomato bushes, because the process of plant formation should be gradual and methodical. It must be carried out with knowledge of the matter and compliance with certain rules.
Basic principles of forming tomatoes into one stem
It is necessary to begin the process of forming tomatoes 1-2 weeks after the plants have been planted in the ground. Plants are formed in the greenhouse and in the open ground, observing the same rules, adhering to the same principles.
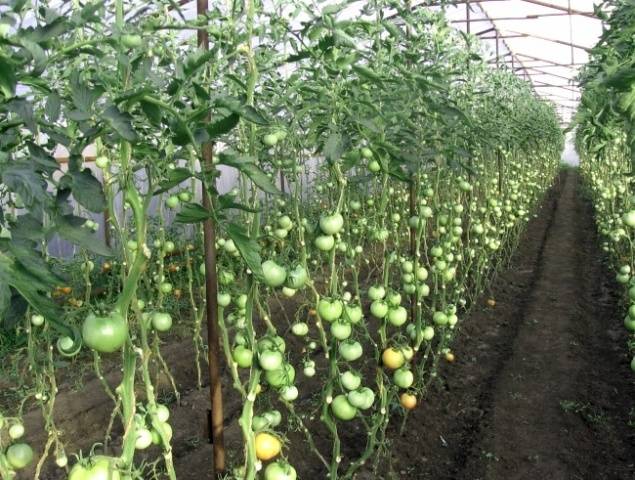
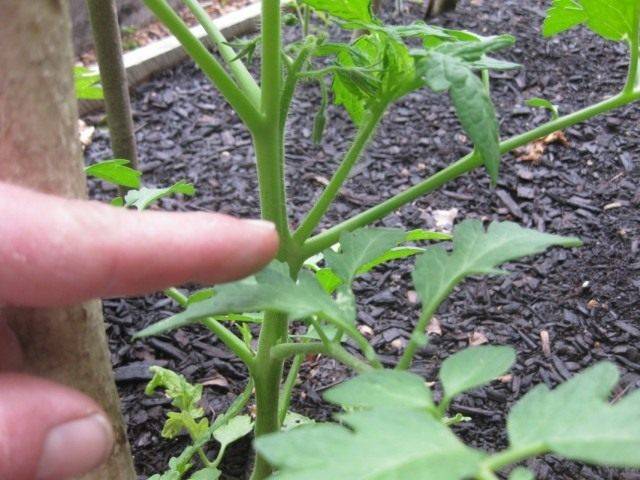
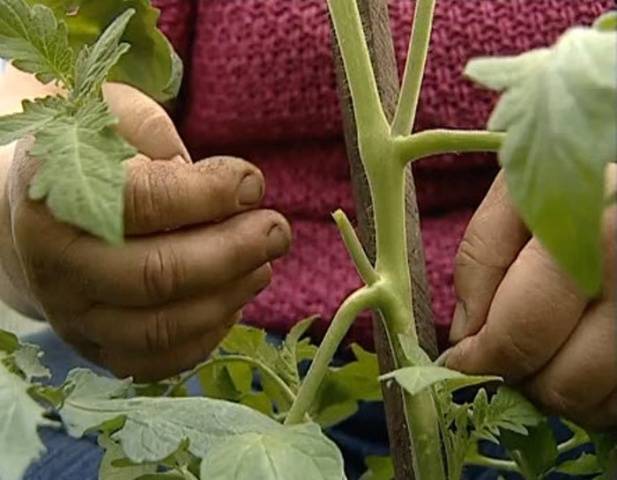
The formation of tomatoes is based on the technology of removing stepsons. Stepchildren are called shoots that form in the axils of tomato leaves. On tomato seedlings, stepchildren are unlikely to be seen, since these shoots, as a rule, develop only after the formation of 5-6 true leaves. Tomatoes are especially active in growing side shoots when there is sufficient moisture and micronutrients in the soil. Plants transfer a large amount of nutrients from the root to the stepsons, thereby taking away resources from the fruits formed on the main stem. That is why gardeners try to remove stepsons at an early stage of their development.
The situation with tomato leaves is approximately the same. Nutrients rise from the root along the stem of the plant, which are used, among other things, to ensure the vital activity of the leaves. To save energy, the lower leaves of tomatoes can be removed during the formation of the bush. However, the leaves at the top of the tomato plant should always be preserved.They are a kind of pump for raising nutrients from the root up the trunk.
Pinching the top of the plant is recommended at the end of the growing season to accelerate the ripening of existing fruits. After pinching, the plant stops its growth, but at the same time strives to form as many stepsons as possible. They must be removed regularly to redirect nutrients to the fruits of the plant.
Schemes for forming tomatoes into one stem
In practice, farmers use two different methods of forming tomatoes into one stem: classic and stepped. The classic method of forming tomatoes into one stem is used when growing indeterminate tomatoes in the greenhouse and in the open ground. Step formation of tomatoes is suitable for indeterminate and determinate plants. When used for tall bushes, the method allows you to reduce the length of the shoot without shortening the duration of fruiting. For low-growing determinate tomatoes, including standard varieties, the technology can significantly extend the fruiting period after the main shoot has been independently established.
Classic scheme
The classic scheme for forming tomatoes with 1 stem is only suitable for indeterminate tall tomatoes. It is most often used in a greenhouse, where it is convenient to tie plants to the frame of a stationary structure.
To implement the technology, it is necessary to remove all the lateral stepsons that form at an early stage of crop cultivation. This is done at a time when the length of the side shoot is slightly more than 5 cm. Such a shoot has already developed leaves and is easy to distinguish from the fruiting brush of the plant. When all side shoots are removed, only one main stem develops, on which inflorescences will form, and subsequently the fruits themselves.
Removal of the lower tomato leaves must be carried out in parallel with pinching. Only the lower leaves, in the axils of which there are no fruiting brushes, should be removed. At one time, 3 sheets can be removed at once, but no more.
In this case, only one main fruit-bearing shoot will actively grow. Closer to autumn, it needs to be pinched in order to speed up the ripening process of the vegetables on the trunk. Pinching involves removing the upper part of the stem so that at the top of the plant there remain 2-3 leaves without inflorescences above the outermost fruiting raceme. This will help maintain the circulation of nutrients in the plant trunk.
How to properly pinch the main stem of indeterminate tomatoes is shown in detail in the video:
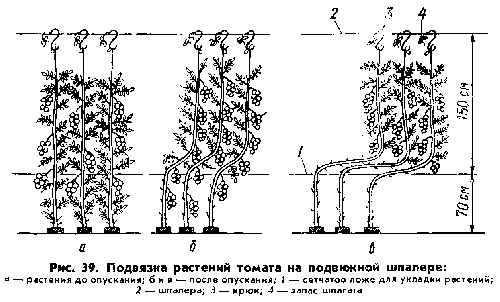
It is convenient to tie tall tomatoes, formed into one stem in a greenhouse, with twine. It is a kind of movable trellis. When the height of the shoots reaches the ceiling of the greenhouse, the ropes can be lowered, providing additional space for the tomato to grow. A diagram of such a garter can be seen below.
When forming indeterminate tomatoes into one stem, you can also tie the main long shoot to vertical supports located along the ceiling of the greenhouse. Some farmers suggest bending the plant stem downwards when it reaches a height equal to the height of the greenhouse ceiling for reverse growth.
As a result of forming a tomato bush into one stem, you can get those bare plant trunks with a large number of tomatoes. The yield of such tomatoes is very high and will certainly please even an experienced gardener.
Scheme with partial abandonment of stepchildren
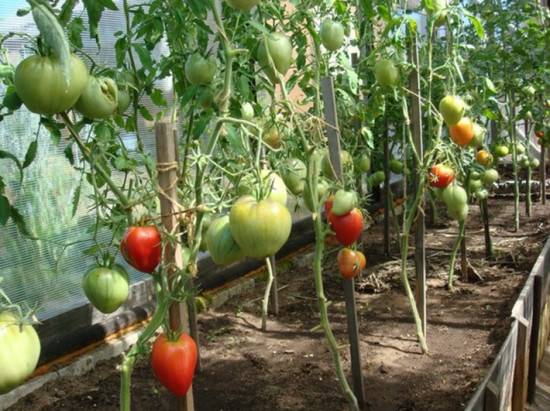
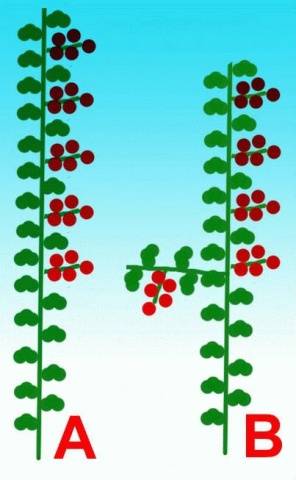
Stepchildren on tomatoes can also perform a very specific task. On them, as well as on the main stem, ovaries are formed, which can help increase crop yield. Some gardeners use this property by leaving several shoots on the tomatoes until the first ovaries appear. After this, the stepsons are pinched so that they do not build up excess green mass and do not consume the valuable energy of indeterminate tomatoes. The diagram of the formation of plants into one stem with partial leaving of stepsons is shown below in Figure “B”. For comparison, Figure “A” shows the classic diagram of the formation of a tomato bush into one stem.
Step formation scheme
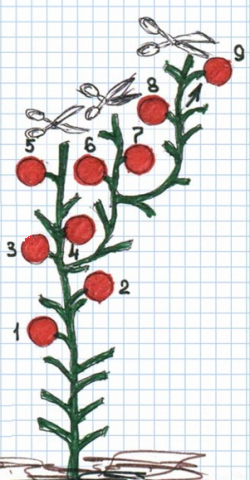
Stepped formation of tomato allows you to solve the problem of tying a long main shoot of an indeterminate bush. During stepwise formation, farmers repeatedly use pinching. So, tall bushes are formed according to the classical principle described above.However, approximately in the middle of the main trunk, one strongest side shoot (stepchild) is left. It develops and grows parallel to the main stem, but as soon as fruits appear on it, the main long shoot is pinched. It is worth noting that caring for such a shoot is similar to caring for the main stem. It also needs to be pinched and the lower leaves on its surface removed.
If the growth of the abandoned shoot is active and by the end of the growing season its height is expected to exceed the height of the ceiling in the greenhouse, then the operation of leaving the side shoot can be repeated. Only this time the stepson needs to be left on the new main shoot. Conventionally, such a diagram is shown in the picture below.
Using this scheme, you can not only reduce the length of the main shoot of an indeterminate tomato, but also extend the fruiting period of determinate plants. Their peculiarity lies in the ability to climb independently, limiting their growth. So, depending on the variety, the plant can form from 6 to 9 flowering clusters on one shoot. In order to increase the volume of fruiting, they use the method of stepwise formation of a bush into one stem. In this case, all stepchildren are also removed except for one. The main fruit-bearing stem can be pinched or left to grow on its own. After the formation of fruits, another stepson should be left on the additional shoot. This scheme allows you to repeatedly increase the number of tomatoes on low-growing and medium-growing tomatoes.The technology is especially relevant when growing determinate tomatoes in greenhouse conditions, where favorable conditions for fruiting are maintained for a long period of time.
Thus, when purchasing tomato seeds, it is necessary to pay attention to the agrotechnical properties of the variety and evaluate its tallness. After all, the care of plants and the method of forming their bushes will depend on this criterion.
When forming tomatoes, you need to remember!
The formation of a bush must be carried out in compliance with certain rules. So, it is best to remove the stepsons and leaves of the plant in the morning, when there is an increased filling of the vegetative organs. In this case, during the day, the resulting wounds will heal and will not allow harmful microorganisms to penetrate inside the trunk. This is especially true when planting bushes in the second half of summer and autumn, as well as during cold spells and rains, when there is a threat of late blight infection.
When pinching, it is important to leave a small part of the shoot in the leaf axil. This will prevent the formation of a new side shoot in this place. The size of the left stump can be 1-3 cm.
When removing leaves and shoots, special care must be taken so as not to damage the delicate skin of the tomato. To do this, experienced gardeners advise not to break out excess greenery, but to remove it using scissors or a blade. The instruments used should be disinfected, for example, with a manganese solution. This will prevent the spread of possible infection between plants.The same measure to prevent the spread of infection should be taken when breaking out shoots manually. It is recommended to do this with gloves, which must be treated with potassium permanganate when moving from one plant to another.
Conclusion
Following these simple recommendations for working with tomatoes will allow you to properly form the bushes without harming them or infecting them with infectious diseases. In general, caring for tomatoes under any growing conditions should consist not only of fertilizing and watering, but also of forming bushes. By removing unnecessary greenery, you can intelligently redistribute the flow of nutrients and moisture in the plant trunk, thereby increasing the yield and facilitating the process of fruiting for the crop. The method of forming into one stem can be used for tomatoes with different agrotechnical characteristics. In this case, the technique will have different effects, but in each case it will only contribute to improving the plant growing process.