Content
Tomatoes are plants from the nightshade family. Their homeland is South America. Shitomatl, as the Indians called it, is still found there in the wild. The weight of such a tomato is only 1 g. Like any other plant, the main goal of a tomato is procreation, i.e. flowering and fruiting. To do this, the bushes must be strong and accumulate a lot of green mass. There may be few fruits. For centuries, breeders have been working to ensure that tomatoes produce a large harvest, and not to increase the leaf apparatus. But it is not easy to change the nature of a plant. So the tomatoes grow with stepchildren, and gardeners tirelessly shape the plants, setting them up for harvest.
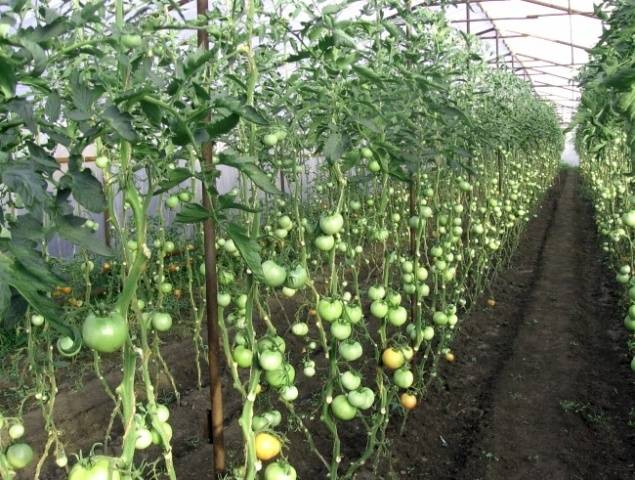
The photo shows a wild tomato harvest.
If you don't carry out stepsoning and let the tomatoes grow as they please, you end up with continuous thickets, in which it’s not easy to find tomatoes. So, wild tomatoes grow in their homeland. Climatic conditions allow them to produce a good harvest even in the absence of care and formation. But the size of their fruits is tiny. They are more reminiscent of currants.And disease resistance in wild tomatoes is inherent at the genetic level. Cultivated varieties without proper care and pinching will inevitably develop late blight, and then there will be no harvest.
There are a great many varieties of tomato. Each gardener grows his favorite and repeatedly proven ones. The care for different groups of varieties is different, as is the formation.
Characteristics of tomatoes
Based on their growth strength, tomatoes are divided into tall, medium-sized and low-growing.
Based on the type of growth, the following groups of tomatoes can be distinguished:
- Indeterminate - their growth is not limited, they grow and form flower clusters one after another as long as weather conditions allow. The first flower raceme can be seen above the 7-9 leaves. The next ones are every 2 or 3 sheets. Ripening dates are usually medium or late.
- Semi-determinant. This is an intermediate type between indeterminate and determinate varieties. There are up to 10 brushes on the main stem. They form many stepsons. Most often they are planted in a greenhouse.
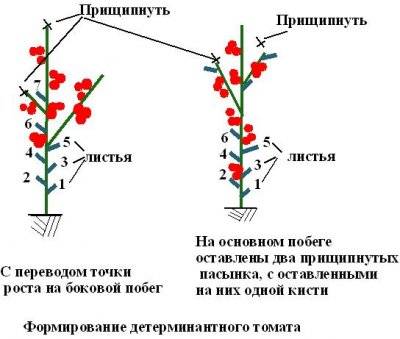
- Determinate - can form a certain number of clusters, usually from 5 to 7 on the main stem; further growth of the central shoot ends and the rest of the crop is formed on the stepsons, which also limit growth. The flower brush starts from the seventh leaf and then after 1 or 2 leaves. The ripening period can be any.
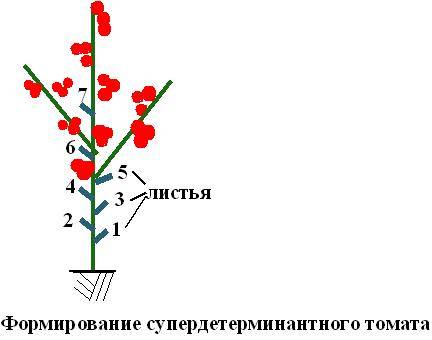
- Superdeterminate and standard varieties are the most compact. There are no more than 3 racemes on the main stem, its growth ends quickly, and the number of stepsons is limited. Flower clusters are laid very early, sometimes already behind the 4th leaf. These varieties are distinguished by a strong stem, they are not tall and usually do not produce large fruits. In terms of ripening time, they are early ripening and ultra-early.
Such tomatoes are more hardy and resist diseases well.
The only exceptions are the southern regions, in which, with appropriate garter in open ground Indeterminate tomatoes are also successfully grown.
The method of formation depends on the type of growth of the tomato and consists of several operations:
- tomatoes are growing;
- The bush is clarified, that is, the leaves are torn off in a certain order;
- shoots are pinched.
Stepchildren and stepchildren
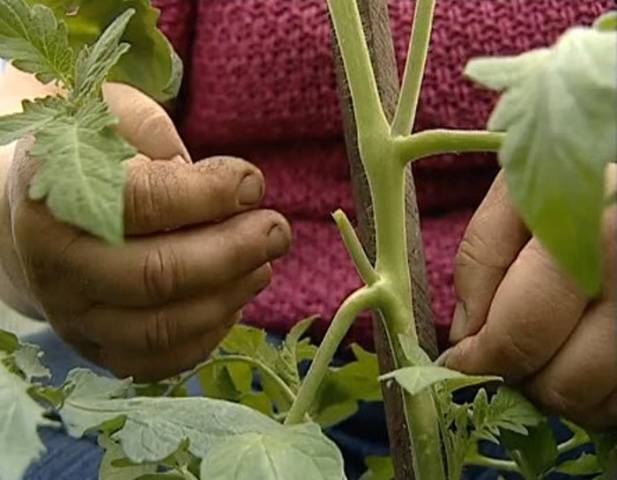
Stepchildren grow in the axil of the tomato leaf and are its generative organ.
The stepson requires food. If you do not plan to leave it for crop formation, removal must be carried out necessarily and in a timely manner. When is it better to remove stepchildren? The best time is when their size is no less than 4 cm and no more than 6 cm.
Why can't I delete it earlier or later? If removed earlier, it will not be possible to leave a stump of approximately 3 cm. It is needed in order to prevent the growth of a new stepson from this sinus. With later removal, the bush is weakened, since the growth of the unnecessary part consumes the nutrition necessary for the formation of fruits. The plant is under stress.
Stepson rules
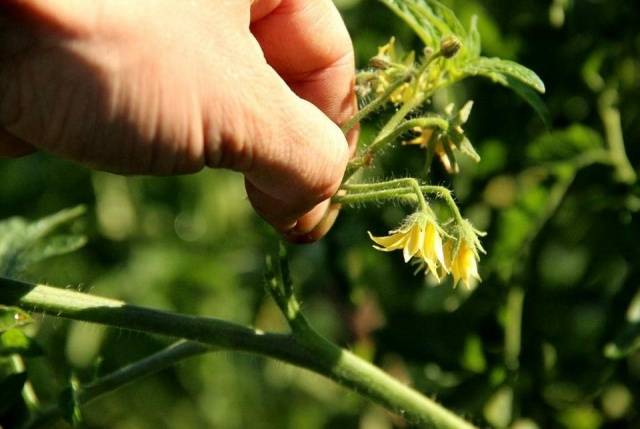
- Remove the shoots in the morning so that the wounds have time to dry before evening.
- Break them off with your hands without touching the injured part of the tomato to avoid infection.When working with scissors, disinfect them by dipping them in a dark solution of potassium permanganate after each removal so as not to transmit a hidden infection from tomato to tomato.
- Do not carry out stepsoning a few days before and after the full moon. On a waxing moon, the above-ground part of the plant is most saturated with juices. Losing even a small part of the plant will be difficult for a tomato and will take a lot of effort.
- Do not process tomatoes after working with potato plants. So, it is very easy to infect tomatoes with late blight.
- After removal, a stump must remain, preventing the growth of a new stepson from the sinus.
- Carry out stepsoning regularly, as stepsons grow very quickly.
The plant must be absolutely dry, otherwise late blight cannot be avoided.
How to lighten tomato bushes correctly
The rules for removing excess leaves are the same as for pinching. The timing will be indicated by the complete formation of the hand and the first signs of its ripeness.
Tomatoes after removing leaves.
Pinching shoots
This event is necessary to remove brushes that do not have time to mature. When pinching plants, leave 2 leaves above each cluster. The rules for working with tomatoes are the same as for planting.
Formation of tomatoes in open ground
What determines the method of forming low-growing tomatoes in open ground? There are several factors here.
- Tomato growth type.
- Tomato variety.
- Growing conditions: care, soil fertility.
- Weather.
Features of pinching different types of tomatoes
The choice of tomato type depends on how quickly the gardener wants to get ripe fruits and what kind of harvest he expects.All standard varieties are characterized by early ripening, they produce an early harvest, but since the bush itself does not grow for long, this early harvest ends quickly.
But then you will have to grow more seedlings.
Standard varieties
The formation of a standard bush is carried out only when there is a desire to try tomatoes very early. In all other cases, these tomatoes do not need to be shaped.
The gain in ripening time can be up to 14 days.
Superdeterminants
Superdeterminate tomatoes are grown without stepsoning, but they will have to be tied up. The maximum that can be done with them is to remove a couple of lower stepsons, if any have formed. A few lower leaves are also removed.
Determinants
For determinants, formation is carried out depending on the variety, the vigor of the bush, and even whether it will be warm and sunny in the summer. There are many low-growing varieties bred by breeders for lazy or very busy gardeners, they no pinning required.
One can name a whole series of non-grafting varieties of Ural selection: non-branching scarlet, pink, round, crimson, plum-shaped, cylindrical, amber. All these tomatoes are low-growing and early. The Explosion varieties do not take steps too, Danko, Foreign exchange, Siberian trump card, Parsley the Gardener, Watercolor, Supermodel, Eldorado, Skorospelka, Golden Stream.
Carefully read everything written on the package when choosing a tomato variety.
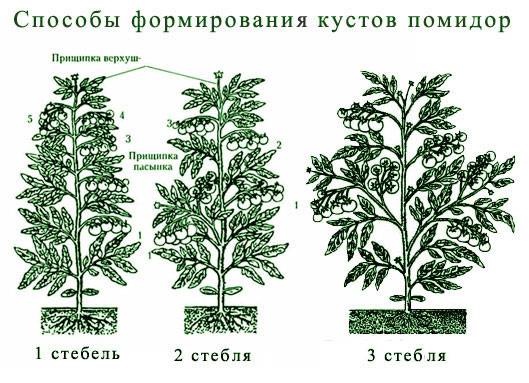
However, most determinate varieties need formation. There are two main ways to grow determinants: in 1 and in 2 stems. In the first method, one main stem is left on the tomato, removing all the stepsons. With the second method, the crop will be formed on the central shoot and on one stepson; it should be located directly under the lower flower brush.
They are distinguished by their great growth force and take away a lot of nutrition from the plant, slowing down the formation and ripening of the crop.
All the brushes are left on the central shoot, and only two on the stepson. It needs to be pinched 2 sheets after the second brush.
There is another way pinching low-growing tomatoes for open ground. The central stem is pinched when 3 brushes are formed, leaving 2 leaves; the stepson will continue to grow, emerging from the axil above the first flower brush; after 2 brushes are formed on it, pinching is carried out over the second leaf and another stepson is grown, which comes after the first flower brush on first. This method is called one escape with continuation. Here are other ways to form determinants.
There are exceptions to every rule.Provided that the soil is sufficiently fertile, care is carried out according to all the rules, and the summer pleases with warm and sunny days, you can leave additional stepsons on the tomato.
The point of pinching is not only to standardize the yield in accordance with the capabilities of the tomato, but also to create the best conditions for the rapid ripening of fruits. And this is only possible with the least shading.
For the same purpose, another agrotechnical technique is carried out, which is part of the process of plant formation: tearing off leaves on a tomato. It begins only when the lower cluster is fully formed and the fruits begin to ripen.
This procedure gives a double benefit - the tomatoes on the lower cluster are more illuminated by the sun and ripen faster, and the bush is better ventilated, which reduces the likelihood of late blight, because there is no contact of the leaves with the soil.
The last operation that is carried out to form tomato plants is pinching the tops. They do it in the third decade of July, cutting off all the extra clusters that will no longer have time to bear fruit, but will slow down the ripening of the rest of the crop.
The video shows how a professional tomato grower shapes tomatoes:
Formation of low-growing varieties in a greenhouse
Low growing tomatoes quite good for a greenhouse. Determinants will give an excellent harvest in it, since their development takes longer. Of course, the yield of determinate varieties cannot be compared with that of indets, but there is much less hassle with them.
The formation of low-growing tomatoes in a greenhouse is no more difficult than that of determinate varieties in open ground and is not much different.Unless you can leave more flower clusters, they will all have time to form fruits and produce a harvest. Some gardeners, in general, do without pinching tomatoes in the greenhouse, but even if the tomato doesn’t stalk, it is still necessary to lighten the bushes, since late blight does not sleep.
Valery Medvedev will talk about how to form determinate varieties in a greenhouse in a video:
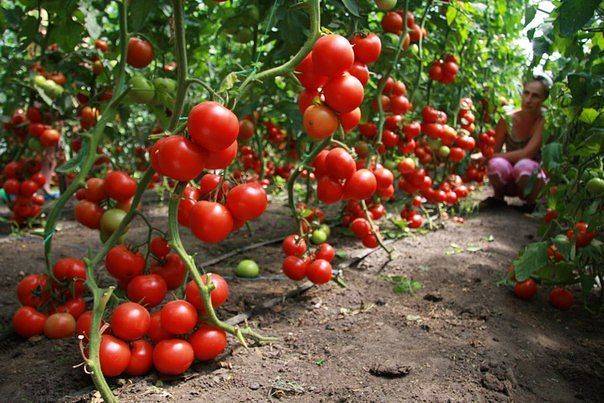
Properly formed tomatoes, taking into account the variety, type of growth and growing conditions, will give a good harvest in any summer.