Inveterate vegetable growers have had to deal with tomato diseases more than once. Sometimes weather conditions are to blame for the onset of the disease. However, as practice shows, most often the crop suffers from mistakes made by the gardeners themselves. Usually serious illnesses end in the death of a culture. But some diseases tomato seedlings are treatable if the necessary measures are taken in time.
Causes and methods of curing culture at home
On many forums, the most common question is how to save tomato seedlings from death, because at stake is the work of a whole month, a lot of wasted nerves and money. Some complain that after picking the seedlings, most of them are gone, and the surviving plants are so weak that it is better to throw them away.
Growing tomato seedlings at home is not an easy task, because this tasty vegetable is loved not only by people, but also by many parasitic microorganisms. There are two ways to get healthy tomato seedlings:
- The simplest and easiest way to get good tomato seedlings is to buy plants that are ready for planting.However, this method does not guarantee complete protection against diseases, because no one saw the conditions in which the plants were grown. Many dishonest entrepreneurs feed seedlings before selling. As a result, after planting, the purchased succulent and beautiful plants begin to wither, get sick, and some even die.
- The second way to get a rich harvest of tomatoes is to grow seedlings yourself. Here you will have to be patient, learn to independently identify the ailments of tomatoes, treat them, and also take preventive measures.
When growing tomato seedlings, it is advisable to adhere to one important rule: before spraying the plants with chemicals, you must accurately determine the causative agent of the crop disease. In addition to the fact that an incorrectly selected drug is useless, the harmful substances in its composition will accumulate over time. Now we will try to consider photo of tomato seedling disease, let’s figure out why they arise and what methods of struggle exist.
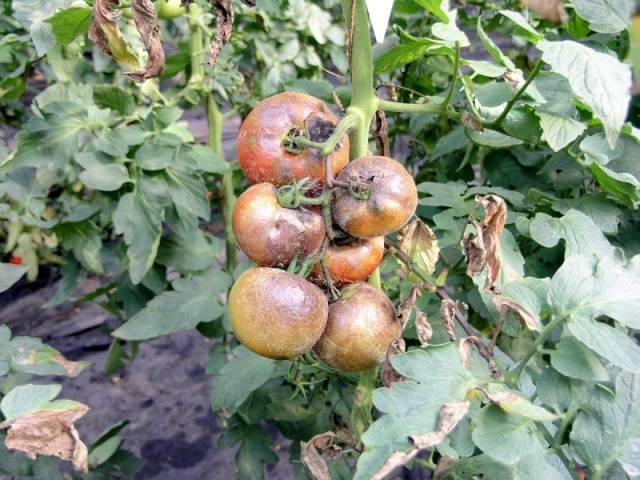
Late blight
This tomato disease is usually called late blight. The disease is nothing more than a fungus. Where do fungal spores develop best? Of course, where there is dampness, temperature changes, and large plant density. Almost all tomato plantings suffer from late blight in the rainy, hot summer. Initially, the disease manifests itself on tomato leaves with the formation of black areas followed by drying. Further, these symptoms are transmitted to the fetuses.
The video talks about late blight:
They begin to fight late blight on the twentieth day after planting tomatoes in the ground. The first time you need to spray the seedlings with Zaslon. 20 days after the first treatment, the tomato seedlings must be sprayed again, but with a different preparation - “Barrier”. After the third inflorescence appears on the plants, the tomatoes are treated with a solution prepared from 10 liters of water, 1 g potassium permanganate and 1 cup of garlic heads twisted in a meat grinder. Approximate solution consumption when spraying – 0.5 l/m2. Instead of these ingredients, a solution can be prepared from 10 liters of water and two tablets of the drug "Oxychom".
Mosaic
A very dangerous viral disease is accompanied by the loss of fruits and the plants themselves. Mosaic is often transmitted by seeds. That is why it is necessary to pickle tomato grains in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. The disease is characterized by pale spots on the leaves and fruits. In this case, a change in leaf shape is observed, the ovary stops, the plant turns yellow and gradually dries out.
It is useless to treat mosaic. The affected tomato is removed from the garden and then immediately burned. For prevention, tomato seedlings are watered with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate twice a day with an interval of three weeks. Spraying with low-fat milk - skim milk with the addition of 1 tsp per 1 liter of liquid helps a lot. urea. Tomatoes are processed every 10 days.
Cladosporiosis
This fungal disease is also called brown spot or leaf mold. Most often, the disease spreads to tomatoes growing under film cover. The first damage occurs on the back side of tomato leaves, which is expressed by the formation of brown spots with a rough coating. Over time, a leaf with a plant dry up, and the matured fungal spores are transferred to a healthy tomato.
Cladosporiosis develops if the greenhouse is cold and too humid at night. The gardener himself can contribute to the disease of tomatoes by watering the plantings with ice water. These factors must be taken into account and taken as measures to get rid of the disease. For prevention, seedlings are sprayed with the preparation “Barrier” or “Barrier”. Before planting tomatoes, the greenhouse is disinfected with copper sulfate.
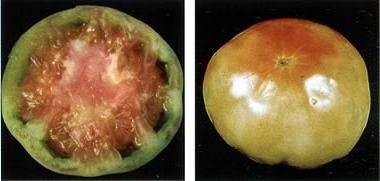
Fomoz
The fungal disease is also called brown rot. Only fruits suffer from the disease. A small spot forms on the back of the tomato around the stem. It grows in size only after the entire tomato inside has already rotted. This is why many vegetable growers begin to notice this disease late.
It will not be possible to cure diseased tomatoes; you can only prevent the spread of the fungus. First, you need to get rid of excess moisture. Secondly, avoid applying fresh manure under the plants. For disinfection, tomatoes are sprayed foundationazole or the drug "Zaslon". All tomatoes that show rot should be picked and burned immediately.
Apical rot
You can notice blossom end rot on green tomatoes. The fruit becomes covered with a spot, slightly pressed into the flesh.Moreover, the affected area can be dry or damp, and also have a different color: from black to light brown. The cause of the disease is a lack of moisture or calcium, as well as an excess of nitrogen.
You can prevent the development of blossom end rot by regularly watering your tomatoes. For spraying, prepare a solution of 10 liters of water with the addition of 1 tbsp. l. calcium nitrate.
Gray rot
This fungus is the most offensive to the vegetable grower. The disease affects ripening fruits, but green tomatoes can also become infected. This usually happens when the crop finishes fruiting in the fall in cold and rainy weather. Round small spots appear on the tomato, gradually developing into large watery rot. Based on its external signs, gray rot is often mistaken for late blight. In addition to the fruits themselves, the entire plant is affected over time.
To effectively combat the disease, only removal of the entire plant is acceptable. The soil where the tomato grew is disinfected, and healthy tomatoes are sprayed with antifungal drugs.
Alternaria blight
If brown areas appear on the back of a tomato leaf, you should sound the alarm. Over time, the entire tomato leaves turn brown, dry out and fall to the ground. Plant stems begin to rot next.
Only chemicals will help get rid of dry rot. Fugicides have proven themselves best. Spraying is carried out after the first signs of the disease appear, and then repeated after 2 weeks.
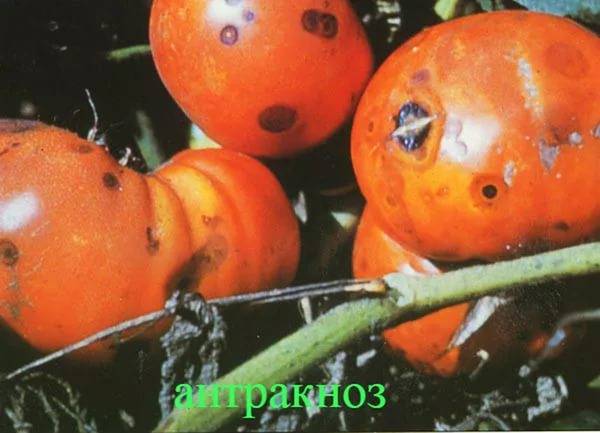
Anthracnose
The disease affects all parts of the tomato plant. The weakest point is the root system and the fruit. Moreover, the already ripe tomato gets sick, which is a shame.Initially, small rotten spots appear, increasing in size over time.
It is impossible to cure an affected tomato, but you can prevent the development of the disease by spraying it with Polyram or Novosil.
Stem rot
If we take the tomato as a whole, then this rot most often affects the stems of the plant. This is where the name of the disease comes from. Typically, the affected areas appear as brown depressions at the base of the stem. As the rot spreads throughout the tomato stem, the leaves begin to turn yellow and fall off. The result is that the tomato dries out.
The development of the disease can only be prevented by spraying tomatoes with preparations containing copper.
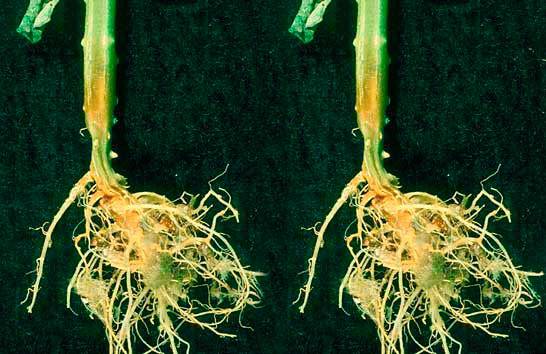
Root rot
Greenhouse tomatoes most often suffer from the disease. It is impossible to immediately see a rotting root, but the first signs can be identified by the withering aerial part of the tomato. This disease is typical for both tomatoes and cucumbers. It is undesirable to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse where cucumbers grew in the garden last year or vice versa.
You can try to save the affected tomato by watering it with Zaslon. But it’s better to remove the tomato and etch the soil with a solution copper sulfate. The best option is to replace the top layer of soil, plus etching with copper sulfate.
Mottling
A bacterial disease destroys tomato leaves. Brown dots appear on the surface, increasing over time into oblong yellow spots. After the entire surface is affected, the leaf dies and falls to the ground.
Tomato plantings can be saved by spraying with appropriate preparations. “Fitolavin” has proven itself quite well.
spotting
The same bacterial disease as mottling. The disease on tomato appears as brown dots of different shades. Moreover, not only leaves, but also fruits can be covered with dots.
You can fight spotting by spraying tomato plantings, for example, with the same “Fitolavin”.
Withering
Bacterial infection begins with the leaves of the lower tier of the plant. Moreover, yellowness is completely absent. The leaves of the lower part of the bush become limp, after which the entire tomato takes on a similar appearance. Over time, the entire tomato dries out.
You can try to save the plants by spraying them with Copper Humate. As an option to prevent the disease, tomato seeds are treated with the same drug before sowing.
Bacterial cancer
A very dangerous disease of tomatoes that destroys tomato blood vessels. Sores appear throughout the plant, including the fruits, and the crop gradually dies.
You can save yourself from this trouble by treating the seed material with formaldehyde immediately before sowing. If such a tomato is found in the garden bed, the plant must be immediately removed, even the soil where it grew must be replaced.
Browning of tomato pulp
The initial stage of this disease can be determined even on green fruits. By touching with your hands you can feel peculiar compactions in the tomato pulp. Over time, they increase in size, and the tubercles become gray-yellow in color. The disease leads to uneven ripeness of the pulp.
This disease can be avoided if zoned varieties for a particular region were selected for planting tomatoes.
Wet rot
This disease affects fruits and can manifest itself in several ways:
- Pythium rot spots appear on ripe and green tomatoes in the form of wet mucus. The fruit quickly becomes watery and becomes covered with a white coating.
- The formation of black mold begins near the stalk. Black rot appears on the surface of the tomato, which eventually affects the entire pulp.
- Hard rot is called rhizoctonia rot. On ripe tomatoes, compactions first appear, which over time turn into watery formations.
- Soft rot can be identified by watery areas of the tomato. This fruit gives off the smell of fermentation.
- Green tomatoes may suffer from sour rot. Infection begins from the stalk, gradually spreading throughout the fruit, followed by cracking of the skin.
This fungal disease of tomatoes occurs during hot and humid summers. Plants need to be provided with better ventilation; thickening is not allowed. Tomatoes are sprayed with fugicides for disinfection.
Powdery mildew
The appearance of the disease is determined by the front side of the tomato leaves. A white powdery coating of fungus appears on them, after which the leaf gradually wrinkles and becomes yellow-brown.
Spraying with fungicides helps combat tomato disease.
Phytoplasmosis
The second name for the tomato disease is stolbur. The disease affects the inflorescences, making them infertile. If there is already an ovary on the plant, then the fruits acquire a yellow-orange color. Such tomatoes are not eaten.
The spread of the disease is weeds. They must be carefully removed from the garden bed.
The video will share a solution to problems with tomato seedlings:
We looked at the most common diseases of tomato seedlings found in everyday life.This delicate crop is susceptible to many other diseases, and in order not to be left without a harvest, you need to select the right varieties, plus comply with all the conditions of the agricultural technology of the crop.