Content
Cucumbers are a widespread crop and must be grown in every garden. It is impossible to imagine a summer menu without cucumbers; the vegetable is included in many recipes for winter preservation. Many winter dishes are prepared using pickled and pickled cucumbers. Growing cucumbers that are tasty and beautiful in appearance is the task of every gardener.
The crop grows well in fertile soils. That is, those that are provided with a high level of nutrients. The soil in summer cottages is constantly exploited; the cultivated plants carry out the necessary nutrients. Therefore, they need to be constantly replenished by applying fertilizers.
The role of nitrogen in growing cucumbers
Nitrogen is the most demanded element in plant nutrition. For cucumbers, nitrogen is relevant at all stages growth: first for increasing green mass, then for flowering and laying the crop, then during the fruiting period and its extension.
Nitrogen in nature is found in humus, in the top fertile layer of soil. Organic matter under the influence of microorganisms becomes available for absorption by plants. The natural reserves of nitrogen for cultivated plants may not be sufficient.Then plant growers are obliged to replenish the deficiency of the element by applying nitrogen fertilizers.
However, the following situation may arise: the gardener regularly applies fertilizer, but the cucumbers do not grow. Then the reason lies in the soil itself.
Thus, when the temperature is too low or the soil is highly acidic, nitrogen is in a form that is inaccessible for absorption by cucumbers. Then the addition of nitrate nitrogen (ammonium nitrate or sodium nitrate) is required.
And if the soils are slightly alkaline or neutral, then it is better to add ammonia nitrogen (ammonium sulfate, sodium ammonium sulfate).
Overfeeding cucumbers with nitrogen is harmful. Plants actively increase leaf mass to the detriment of flowers and fruits. And if the fruits grow, they have an unmarketable appearance: bent and twisted. Everything is good in moderation, and the application of nitrogen fertilizers should be under special control, since if they are in excess, the substance accumulates in cucumbers in the form of nitrates.
Watch a useful video about nitrogen and nitrogen fertilizers:
Types of Nitrogen Fertilizers
Organic
Nitrogen fertilizers for cucumbers - all types of organic fertilizers (manure of any animals, bird droppings, peat). These fertilizers have been used by humans in crop production for a long time. For organic matter to work, it must go into a form convenient for absorption by plants, and this takes time. It is not for nothing that it is recommended to apply fresh manure in the fall. The autumn-winter period is just the right time. Apply 40 kg of organic matter per 1 sq.m of land, followed by digging up the soil.
Fresh manure releases enormous amounts of heat as it decomposes. Therefore, plants can simply “burn out.”However, this property of fresh manure is used by gardeners to prepare “warm beds”.
To feed plants in the summer, use an infusion of fresh manure or litter. 1 volume of organic matter is filled with 5 volumes of water and left for a week. The finished nitrogen fertilizer concentrate is diluted and feeding cucumbers. For 10 parts water, take 1 part infusion.
Gardeners have a twofold attitude towards peat as a nitrogen fertilizer. Peat contains nitrogen, but in a form that is poorly suited for absorption by plants. Peat is much more suitable for improving the quality and composition of heavy soils, which in its presence become air- and moisture-permeable. Peat can be used together with other fertilizers. However, you can increase the value of peat by making peat compost from it.
Sawdust is placed in the base, which is covered with a layer of soil and peat, then a significant layer of grass, tops, and plant residues is laid out, on top of which a layer of soil and peat is laid. The entire structure is spilled with infusion of slurry. The height of the structure is about a meter, the preparation time is 2 years. The criterion for the readiness of compost is its crumbly structure and pleasant earthy smell.
Urea
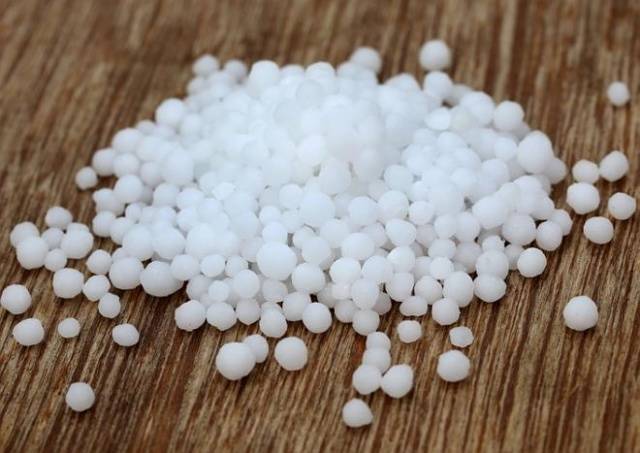
Urea is an organic nitrogen fertilizer for cucumbers, which is produced artificially. The fertilizer is familiar to all gardeners due to its effectiveness (nitrogen content 47%) and low cost. After application under the influence of microorganisms urea transforms into a form convenient for absorption by cucumbers. The only requirement when using urea is to embed the granules deep into the soil, since decomposition produces a gas that can evaporate, resulting in a loss of nitrogen.
The most effective way to feed cucumbers with urea is to use its solution. Dissolve 45-55 g of urea in 10 liters of clean water. Urea is also suitable for foliar feeding cucumbers, applying the solution to the leaves and stems through spraying. In this way, you can very quickly eliminate nitrogen deficiency in cucumbers.
Ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate or ammonium nitrate (ammonium nitrate) is an equally popular nitrogen (34% nitrogen) fertilizer for cucumbers among gardeners. It is produced in the form of white or gray powder or granules, highly soluble in water. Can be used on any soil. Suitable for feeding cucumbers at any stage of development. Dissolve ammonium nitrate (3 tablespoons) in a 10-liter bucket of water and water the plants. You can also use the root method of applying fertilizer. Next to the cucumber plantings, grooves are made into which saltpeter is distributed, based on the norm of 5 g of ammonium nitrate per 1 square meter. m of soil.
Ammonium sulfate
Another name is ammonium sulfate. Nitrogen fertilizer works in any weather. Therefore, it can be added to the soil when digging it in early spring or autumn. A special feature of ammonium sulfate is that the nitrogen in the fertilizer is contained in ammonium form, which is very convenient for absorption by plants. Ammonium sulfate for cucumbers can be applied in any form: dry, with abundant watering, or in the form of a solution. Consumption rate: 40 g for 1 sq. m of cucumber plantings. To prevent acidification of the soil, add ammonium sulfate together with chalk (1:1).
Calcium nitrate
Other names are also used calcium fertilizers nitrate or calcium nitrate.Nitrogen fertilizer is more suitable for feeding cucumbers on acidic soils, especially when grown in protected soil. It is the presence of calcium that helps plants fully absorb nitrogen.
The fertilizer dissolves well and absorbs moisture during storage, causing it to cake. For cucumbers, it is recommended to mostly feed them “on the leaf” with calcium nitrate from the beginning to the end of the growing season every 2 weeks. Nitrogen fertilizer solution for spraying: dissolve fertilizer (20 g) / 10 liters of water and spray the leaves and stems of cucumbers.
Fertilizer increases plant resistance to various diseases and temperature changes. Forms a good harvest of high quality.
Sodium nitrate
Or sodium nitrate, or sodium nitrate. The use of this nitrogen fertilizer is indicated on acidic soils. Nitrogen content is only 15%.
Everyone chooses their own nitrogen fertilizer for cucumbers, however, it is worth having a small theoretical base so that, firstly, not to harm the plants, and secondly, not to waste money. Since not all nitrogen fertilizers are universal. Be sure to consider the acidity of the soil in your garden to get the maximum benefit from applying nitrogen fertilizers.
Fertilizers for cucumbers
During the entire growing season, cucumbers usually require 3-4 fertilizing with fertilizers. However, if the plants look healthy, set ovaries and bear fruit abundantly, reduce fertilizing to a minimum.Cucumbers, like other plants, require not only nitrogen, but also potassium and phosphorus.
Potash fertilizers
In case of shortage potassium, cucumber leaves turn yellow at the edges and curl inward. Then they die off. The fruits are pear-shaped and have a watery, bitter taste. Plants cannot withstand temperature changes, attacks from bacteria and insect pests. Cucumbers bloom, but do not form an ovary. Fertilizing with potassium fertilizers is especially important for cucumbers at the stage of crop formation:
- Potassium chloride has a high potassium content - 60%. However, due to the chlorine content, which does not have the best effect on the growth and fruiting of cucumbers, the use of this fertilizer directly during the growing season becomes impossible. However, it can be applied in the fall when preparing the soil. Use 20 g of potassium chloride for 1 sq. m;
- Potassium sulfate – potassium sulfate has a high potassium content, suitable for use in greenhouses and open ground. Does not contain chlorine, which is especially important when feeding cucumbers. When digging up soil for cucumbers in the spring, apply 15 g of fertilizer per square meter. m. During current fertilizing, the use of a solution is indicated. Take potassium sulfate (30-40 g), dissolve in a bucket of water (10 liters of water), water the plants. Bring in potassium sulfate together with superphosphate. They work very well together.
- Potassium (potassium) nitrate or potassium nitrate - a popular potash fertilizer containing nitrogen and potassium - the most necessary elements for cucumbers. At the same time, there is less nitrogen. Therefore, the use of potassium nitrate is indicated at the stage of crop formation, when cucumbers do not need to grow green leafy mass. Does not contain chlorine.To feed plants with a solution, take potassium nitrate (20 g) and dissolve in 10 liters of water;
- Kalimagnesia ("Kalimag") differs in that in addition to potassium, it also contains magnesium, which improves the taste of cucumbers and prevents nitrates from accumulating. Together, the 2 elements are absorbed by cucumbers with maximum benefit. Feed plants at any time, diluted or in granular form. Dissolve 20 g of potassium magnesia in a 10-liter bucket of water and pour over the cucumbers. If you use it dry, then measure 40 g per 1 square meter. m of soil.
Potassium is important for plants, it accelerates photosynthesis processes, strengthens the immunity of cucumbers, improves the taste of the fruit and the amount of ovary formation.
Phosphorus fertilizers
Without phosphorus, cucumber seeds will not sprout, the roots and above-ground parts of the plant will not develop, cucumbers will not bloom, and there will be no harvest. Phosphorus is called the growth energy of cucumbers, how important the element is for nutrition. The peculiarity of phosphorus is that plants themselves regulate its amount during absorption. Therefore, gardeners cannot overfeed or underfeed cucumbers.
Plants signal to you by their appearance that there is not enough phosphorus. If cucumber leaves are pale green, there are spots or uncharacteristic colors on the lower leaves, flowers and ovaries of cucumbers fall off - then these are signs of phosphorus deficiency. Use fertilizers with a high phosphorus content to quickly help your plants:
- Superphosphate – produced in the form of granules, phosphorus content – 26% in a convenient form for absorption by plants. Apply superphosphate in the fall when digging the soil, for each square. m use 40 g of fertilizer. When regularly feeding cucumbers, make a solution: dissolve 60 g in 10 liters of water. Another method for preparing the solution: superphosphate (10 tbsp.l) pour 1 liter of hot water, stir well and let it brew for a day, stirring occasionally. Dilute 0.5 cups of the resulting concentrate in water (10 l);
- Phosphorite flour works great on acidic soils. It must be applied in the fall, however, the effect should not be expected immediately. Only after 2 years will there be a visible result. Add flour (30-40 g) per 1 square meter. m of soil. On slightly acidic soils, you can add 3 times more flour; it does not dissolve in water. The effect lasts for several years, especially with the joint application of nitrogen fertilizers;
- Diammofos – is distinguished by its versatility, suitable for any crop, soil and application time. Apply fertilizer (30 g) per 1 square. m of soil during autumn or spring digging, 40 g of diammophos during scheduled fertilizing per 1 sq. m landings;
- Potassium monophosphate contains 50% phosphorus and 26% potassium. When using it, you can extend the period of obtaining cucumbers, protect them from temperature changes and diseases. To prepare the solution, take 10 g of fertilizer/10 liters of water. Cucumbers respond well to foliar feeding with potassium monophosphate: dissolve 5 g/10 l of water and spray the plants.
Phosphorus increases the number of ovaries on cucumbers. Therefore, using fertilizers with a high phosphorus content, you will provide yourself with high yields.
Conclusion
Modern crop production is impossible without the application of fertilizers. You can spend all your energy on planting, watering and weeding, however, you will not get a harvest at all or get it of very dubious quality. But only because the plants did not receive all the necessary nutrients in a timely manner.Any type of activity requires a certain set of not only skills, but also knowledge. Crop farming is no exception. Plant life rests on “three pillars” - phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen. The first task of a gardener is to provide food for his wards.