Content
Udder dermatitis in cows is an inflammatory process that forms in the deep layers of the skin. It can be either acute or chronic. This article will provide detailed information about the types of udder dermatitis, causes, its signs, as well as the rules for providing assistance to the animal.
Types of udder dermatitis
Cows may have one of the following types of dermatitis:
- traumatic, which is caused by mechanical damage to the skin;
- medicinal due to the use of medications or ointments;
- verrucous (warty), which becomes a consequence of advanced drug or traumatic dermatitis, has a chronic form;
- gangrenous - when the causative agent of necrobacteriosis - necrosis sticks - enters through skin lesions;
- nodular - due to viruses of the nitling group.
Causes of udder dermatitis in cows
Udder dermatitis can be caused by:
- prolonged hypothermia of the animal;
- chapping of a wet udder;
- the use of sharp ointments to treat various diseases in the udder area;
- failure to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards and animal care rules.
In some cases, dermatitis may be a consequence of impaired metabolic processes in a cow or occur against the background of damage to other areas and organs by the disease. This is typical for food intoxication, which is divided into potato, buckwheat, bard and clover exanthema.
Symptoms of the disease
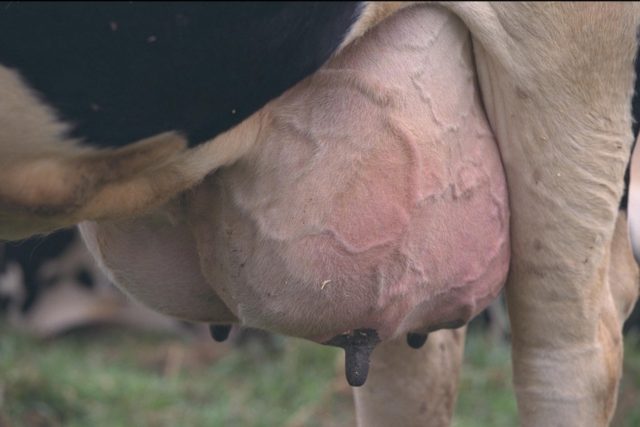
The disease is easy to identify by external clinical signs. They can be of varying degrees of severity - from small foci of pale red inflammation to serious purulent lesions of the udder. The most severe degree is usually localized in the middle of the left and right thickening of the udder, but can spread throughout the entire area.
Painful ulcers are formed from cracks, from which ichor mixed with pus is constantly released. With insufficient care or untimely detection, these cracks become covered with a thin crust or, when mixed with dirt and dust, form a mass with a characteristic unpleasant odor, which sticks the fur together and causes even more discomfort to the animal. In addition to the formation of cracks and ulcers on the skin, purulent foci of various sizes begin to appear throughout the udder - from barely noticeable to large ones - the size of a walnut. If the skin lesion affects the nipples and parapapillary area, daily milking causes severe pain and severe anxiety in the animal.
Diagnostics
In most cases, a general clinical examination is sufficient to diagnose dermatitis, which helps to make an accurate diagnosis. This is due to the fact that the symptoms of the disease appear almost immediately. To determine nodular dermatitis, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests of saliva, as well as secretions from the mucous membranes. Be sure to examine the affected areas of the udder separately. The incubation period for nodular dermatitis can last a month, however, the first signs begin to appear already in the second week after infection.
How to treat udder dermatitis in cows
The outcome of udder dermatitis in cows with properly selected treatment is positive. Non-infectious forms of the disease are the easiest to treat. For them, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease (adjust temperature conditions, maintain care, maintain cleanliness in the room). Then the dermatitis will go away on its own.
But if the disease is of infectious origin, complex treatment using various medications, rubs and solutions may be necessary. Treatment occurs in several stages:
- Eliminating the cause. With dermatitis, the animal suffers from severe constant itching, so it constantly scratches. Constant exposure to irritated skin causes inflammation and injury in the form of cracks and wounds. Therefore, the first step is to remove the cause that causes irritation of the skin. For example, if dermatitis appears while taking certain medications, you should limit their use and look at the results. To identify the cause, you should know the types of dermatitis and what causes them. Information on this can be found in one of the previous sections.
- Trimming affected areas. In areas with sores, cracks and irritation, all hair should be removed. This will make subsequent treatment easier, allow the skin to breathe freely and prevent dirt and sweat from accumulating in the affected areas. And in the summer, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, the skin will recover and dry faster.
- Cleaning wounds with soap and water. In the affected areas, ichor and cracks quickly form. To prevent dirt and infection from getting into them, they must be constantly washed with plain clean water and antibacterial soap. After sanitizing the skin, be sure to wipe it with a dry cloth. Under no circumstances should you leave your skin wet.
- Selection of complex drug treatment. It is advisable that medications and other therapeutic measures be prescribed by a qualified veterinarian. However, it is not always possible to resort to his services, so first you should correctly determine the type of dermatitis and organize treatment depending on its origin and clinical manifestations.
If dermatitis was caused by taking antibiotics or mechanical damage to the skin, it is recommended to treat the udder with alcohol solutions with added antiseptics. Pyoctanine is very popular for these purposes. Also, to prevent further spread of the disease, it is recommended to use ointments and gels for disinfection, for example, balsamic liniment, zinc or streptocide ointments.
In some cases, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for therapy, as well as a novocaine blockade. To treat warty dermatitis, various cauterizing solutions made from turpentine, formalin or potassium permanganate are used.In advanced stages of the disease, surgical operations with the application of a dense plaster cast cannot be avoided.
Antibiotics - Tetracycline and Oleandomycin - are used as therapeutic measures against nodular dermatitis. To support the animal’s condition, a course of vitamins is prescribed, and proper nutrition and adequate rest are monitored.
Prevention
Preventive measures help prevent the occurrence of dermatitis. These include:
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards when keeping animals. The room should be warm and dry. There must be a thick and clean pad on the floor so that the animal does not sleep on a hard and dry floor. It is necessary to regularly monitor the hygiene of cows - wash and dry the udder once every 1-2 days. When treating the skin, it should be constantly diagnosed for the appearance of mechanical damage and irritation for their timely elimination. If the formation of cracks is associated with the use of specific drugs, treatment should be stopped immediately and the cow should be monitored until symptoms disappear completely.
- Vaccination. Such a preventive measure is needed solely to prevent the occurrence of infectious dermatitis. If an animal has already suffered this disease once, it develops a stable immunity to it. Therefore, such a preventive measure is considered the most effective way.
- Quarantine. If a new animal arrives in the barn, it must be kept separately for the first month, using individual care items. You should also refrain from importing animals from unfavorable areas, for example, from India, where almost all cows are infected with one or another infectious disease.It is recommended to do all tests immediately after admission. And only after receiving the results can the cow be transferred to a common room.
Conclusion
If diagnosed early, udder dermatitis in cows can be easily treated. To prevent it, it is necessary to follow preventive measures, vaccinate animals and responsibly treat the import of new cows into a common barn.