Content
Acidosis in cows is a common disease that reduces the productivity of the animal. It is harmless if recognized in time. Otherwise, death is not far away. That is why anyone who deals with cattle should know the symptoms and treatment of acidosis in cows.
Acidosis in cows: what is it?
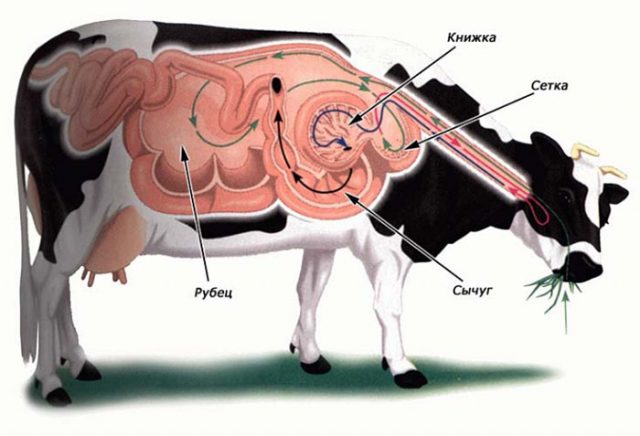
Acidosis is a disease of the rumen in cows due to impaired metabolism. As a result, lactic acid accumulates in the animal’s stomach and the pH is disrupted. As the disease progresses, lactic acid enters the bloodstream, causing destructive processes in the cow's liver. If acidosis is not treated, the cattle will die.
The disease cannot occur without symptoms. The passage of food is disrupted, characteristic pain occurs, the animal becomes susceptible to other diseases, as immunity decreases. A cow suffering from acidosis becomes lethargic, eats poorly or refuses food altogether, and the amount of milk decreases sharply.
Acidosis is especially dangerous for a pregnant cow, as the development of the placenta is disrupted. All harmful products reach the fetus, as a result of which its immune system does not function as expected. Calves are born sick and die in the first days.If they survive, they are noticeably behind other cows in development. As a rule, they are sent to slaughter.
It is important to understand that the disease is not contagious, but it affects several individuals or the entire herd at once, since food is given to the entire herd.
Form of acidosis
Acidosis in cows is closely related to the animal's digestive system, so its symptoms can be confused with another gastrointestinal disease. To prevent this from happening, you need to know that in veterinary medicine there are 3 handicaps, each of them manifests itself in its own way and requires specific treatment.
Acute
The acute stage of the disease cannot be missed. It's the easiest to define. Symptoms appear within 2-6 hours after eating low-quality food. Acute acidosis is characterized by:
- sudden lethargy of the cow;
- difficulty breathing;
- refusal to eat;
- presence of compaction in the scar area;
- trembling throughout the body;
- loose and frequent stools;
- convulsions.
Treatment of acidosis with such symptoms should begin immediately. If a sick animal lies motionless, stops chewing, grinds its teeth and later falls into a coma, then death occurs within a day.
Subacute
Subclinical or subacute acidosis is not so dangerous, but it cannot be ignored. This form occurs in cows after calving, when the animal’s diet is changed. If the changes occurred abruptly, then the microflora in the rumen did not have time to rebuild. As a result, acidosis begins.
The symptoms of the subacute form are similar to the acute course of the disease, but they develop slowly.The cow's weight gradually decreases, muscles weaken, and mastitis may develop.
Chronic
The advanced form of acidosis enters the chronic stage. Complications associated with the disease:
- hoof diseases;
- disorders in the reproductive organs;
- inflammation of the scar mucosa;
- liver abscess;
- heart problems.
The cow becomes apathetic, does not respond to external stimuli, and does not eat food well. She develops anemia.
The danger lies in the fact that for a long time the chronic form of acidosis does not manifest itself in any way, there are no pronounced symptoms. You can suspect an illness by the appearance of the cow - she gets tired quickly. In addition, the milk from a sick animal is low in fat.
Causes of acidosis in cows
Acidosis appears only through the fault of the herd owner. This is caused by illiterate or improper nutrition of cattle. You cannot suddenly change the diet of cows or the ratio of its components. The main reasons that lead to acidosis:
- poor quality silage;
- finely ground feed;
- excess quickly digestible carbohydrates;
- food too wet;
- disturbance of microflora in the rumen.
These include an abundance of:
- apples;
- beets;
- potatoes;
- grains or vegetable waste.
The cow should not be allowed to eat just anything. Food should not be constantly available.
One of the causes of acidosis is a lack of roughage. This cannot be allowed. Such food causes an abundance of saliva, without which normal digestion cannot exist.Too soft and crushed feeds lead to decreased salivation. As a result, the food in the cow's stomach turns sour, causing indigestion and loose stools.
Pathogenesis of acidosis in cows
In the first section of the cow's stomach - the rumen - up to 70% of all feed consumed is accumulated and digested. If its quality leaves much to be desired, then a lot of lactic acid is released, which should speed up the breakdown of food. Gradually, lactic acid becomes abundant and the pH of the stomach decreases. Instead, acidity increases. An imbalance of substances occurs. It is this condition of the animal that leads to acidosis.
Symptoms
In order to start treatment on time, it is important to know the general symptoms of bovine acidosis. In the first hours of the disease, the animal's breathing increases sharply. After which it is restored after 10-15 minutes. This is observed throughout the day. In severe cases, rapid breathing remains.
In addition, symptoms of acidosis include:
- Abrupt refusal of the animal to feed. This condition can last 2-5 days.
- Change in color of the surface of the tongue. It takes on a dirty yellow tint.
- Saliva becomes cloudy.
- When examined, the scar area is painful and filled with gases. This symptom can be noticed within a day from the onset of the disease.
- Feces change color and consistency. By the end of the first day, they become liquid, dirty gray in color, and contain remnants of undigested food. The smell of feces is sour.
- The cow lies motionless.
- The animal begins to have conjunctivitis, and purulent or serous contents are released from the eyes.
If you start treating a cow in time, then with a mild course of the disease the animal will return to normal life in 4-5 days. In advanced forms of acidosis, recovery will take more than 10 days.
Diagnosis of acidosis in cows
The owner alone will not be able to accurately diagnose the cow, since acidosis can easily be confused with other diseases whose symptoms are similar. To do this, you will need to consult an experienced veterinarian who will conduct a series of studies and prescribe treatment.
To make an accurate diagnosis, an analysis of the contents of the animal’s rumen, blood and urine is performed. A sick cow's urine is acidic and contains protein, which is especially characteristic of a severe course of the disease. Residues of lactic acid can be detected in the blood.
In addition to the procedures described, the veterinarian may prescribe an electrocardiogram. Tachycardia is observed in 80% of sick cattle. The heart rate reaches 136 beats per minute. This condition lasts 12-15 days.
Treatment of rumen acidosis in cows
The key factor in the recovery of livestock is timely diagnosis and timely treatment of rumen acidosis in cows. To begin with, the scar should be thoroughly rinsed using a special probe. The contents are removed, after which alkali is introduced. It is allowed to use a 15% solution of baking soda. If simple treatment does not help, then opening the scar is indispensable. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The contents of the proventriculus are cleaned surgically, followed by the administration of medication. You can introduce alkali 8 times per day.
In addition to the treatment described above, the veterinarian will prescribe blood substitutes or sodium bicarbonate. It is necessary to restore the water balance in the body. It is useful to give a sick animal water and salt up to 7 times a day.
In case of severe fever and muscle cramps, it is necessary to instill B vitamins or give an anti-shock drug approved in veterinary medicine, for example, Prednisolone.
Before the veterinarian arrives, you should try to alleviate the cow’s condition yourself. To do this, it won’t hurt to give her 1 liter of vegetable oil to loosen her stool. The animal's head must be kept tilted.
If acidosis has already become chronic, then deaths are practically excluded. The treatment will be different:
- Gastric lavage.
- Feed replacement.
- A course of enzymes that regulate the production of lactic acid and normalize digestion. It is designed for 2 months.
In addition, vitamin supplements and strict control over the components of the mash will be required.
There are also traditional methods for treating cow acidosis, but they are suitable for the subacute and chronic stages of the disease, when there is no threat to the life of the cattle:
- Gastric lavage with soda.
- Massage.
- Yeasting of feed.
At the first symptoms of acidosis, the cow is forcibly given a solution of soda to drink, after which vegetable oil is poured in to induce vomiting and thus cleanse the cattle’s stomach.
After cleansing, massage is performed if the stomach is not very swollen. This will help start the process of digesting food. Do it with soft pressing movements.
In case of chronic disease, it is useful to give the cow 100 g of mineral yeast per day. This promotes food digestion, improves gastric permeability, and prevents feed from souring.
Prevention
Cow acidosis is a disease that is easy to prevent; it is enough to monitor the quality of feed and correctly prepare the animal’s diet:
- Eliminate spoiled, rotten or rotten silage from the diet.
- Add coarse feed so that there is more than half of it.
- Control the humidity of the mash, which should be at the level of 45-55%.
- Reduce consumption of molasses and fodder beets. Their share in the mash is 7% of the dry matter.
- Reduce the amount of wheat, add corn to 50% of all components.
In addition, it is necessary to deprive the animal of the opportunity to eat food selectively. All components are thoroughly mixed and distributed in the form of a wet mash.
Conclusion
Symptoms and treatment of acidosis in cows help to cope with the disease in a short time. It is important to adhere to all the veterinarian’s recommendations and subsequently review the cattle’s diet, otherwise the chronic form of the disease is not far away.