Content
Taking blood from cattle is considered a rather difficult and traumatic procedure. Due to various types of diseases, this procedure is done quite often. Today, blood is taken from cows from the tail, jugular and mammary veins. To simplify the work, vacuum syringes have been developed, thanks to which the procedure for taking blood from the tail vein becomes completely safe.
Preparing for blood collection from cattle
As a rule, blood is drawn from cows from the jugular vein, located in the upper third of the neck. The volume of material obtained for research should not be less than 5 ml with an anticoagulant of 0.5 M EDTA.
Before starting the procedure, the needles used should be pre-sterilized using boiling for this purpose. It is important to consider that sampling from each cow must be done with a new needle.
The collection site must be disinfected. For disinfection, use alcohol or a 5% iodine solution. During sampling, the animal must be securely restrained - the head is tied.
After the material for the study has been taken, it is worth tightly closing the tube and turning it over several times so that mixing with the anticoagulant occurs. In this case, shaking is not allowed. Each test tube is numbered according to the inventory.
The most effective way is to take blood from the subcaudal vein. In this case, it is not necessary to restrain the cow. It is recommended to further store the tubes at a temperature range from +4°C to +8°C. A refrigerator is perfect for these purposes. Do not use the freezer. If clots appear in the sample taken, it is unsuitable for further research.
Methods for collecting blood from cows
Today, there are several methods for collecting blood from cattle. It is taken from the following veins:
- jugular;
- dairy;
- tail vein.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is recommended to first secure the animal, which will prevent injury. In this state, the cow will also not be able to knock over the test tube. Before the procedure, you will need to disinfect the blood collection site using a solution of phenol, alcohol or iodine.
Taking a sample from the jugular vein is one of the most popular methods. As a rule, the procedure is carried out early in the morning or before the cow receives food. To carry out the procedure, the animal's head is tied and fixed in a motionless state. The needle must be inserted at an acute angle, with the tip directed towards the head.
It is allowed to draw blood from the mammary vein for research only from an adult. The milk veins are located on the side of the udder and extend down the abdominal area. Through them, the mammary glands are supplied with blood and nutrients. It is worth noting that the better developed the milk veins, the more milk can be obtained from the cow.
It is safest to take samples for testing from the tail vein. The injection site, as in other cases, must be disinfected. If you choose the injection site at the level of 2 to 5 vertebrae, the procedure will go more smoothly.
Taking blood from cows from the tail vein
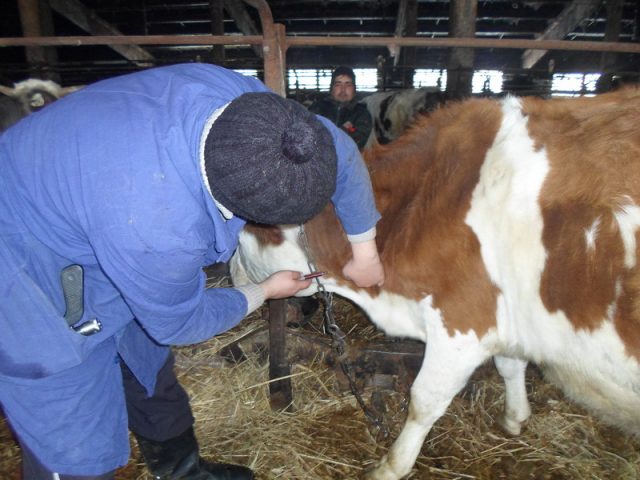
As practice shows, taking blood from the tail vein for research is the safest option. For these purposes, you can use a regular needle or use a special vacuum system. Such systems already include special tubes that contain an anticoagulant and the required pressure, which allows blood from the tail vein to flow smoothly into the container.
Before taking a sample from the tail vein, it is necessary to disinfect the injection site with alcohol or iodine solution. After this, the cow’s tail is lifted and held by the middle third. In this case, the needle must be inserted smoothly into the tail vein, the angle of inclination should be 90 degrees. The needle is usually inserted all the way.
This method of collection has many advantages:
- the sample taken is completely sterile;
- practically no clots form in the test tube, as a result of which all samples are suitable for research;
- This procedure does not require much time.An experienced veterinarian can call samples from 200 animals in 60 minutes;
- when using this method, there are no side effects, and the chance of injury to cattle is minimized;
- contact with blood is minimal;
- the animal does not experience stress, the usual level of milk yield is maintained.
This method is most often used on large farms where it is necessary to take a large number of samples in a short period of time.
Taking blood from cattle from the jugular vein
If it is necessary to draw blood from the jugular vein, it is recommended to insert a needle at the border where the upper third of the neck transitions to the middle third. The first step is to induce a sufficient level of filling of the vein and minimize its mobility. For these purposes, it is recommended to compress the vein using a rubber band or fingers.
During the puncture, you will need to hold the syringe with the needle in your hand so that the direction of the needle coincides with the line of the vein being punctured. It is necessary to ensure that the cut of the needle is directed upward, towards the head. The needle should be inserted at an angle of 20 to 30 degrees. If the needle gets into a vein, blood will begin to flow out of it.
Before removing the needle from the cow's jugular vein, you should first remove the rubber tourniquet and pinch the vein with your fingers. It is necessary to pinch just above the place where the needle is located. The needle is gradually removed, and it is recommended to compress the injection site with a cotton swab for a while, which will prevent the formation of hematomas on the animal’s body. At the end of the procedure, the venipuncture site is disinfected with alcohol or tincture of iodine and treated with Collodion solution.
Taking blood from the mammary vein
In this case, it is necessary to take into account that blood sampling from the mammary gland can only be done in adults. The required vein can be found on the side of the udder.
Before taking a sample, it is recommended to first secure the animal. As a rule, the procedure will require the presence of several people. The first step is to shave or cut off the hair from the place where you plan to puncture with a needle. After this, the prepared area is disinfected using alcohol or iodine solution.
There should be a kind of small tubercle in good visibility, where it is recommended to insert the needle. Since it is quite easy to harm a cow, the needle is inserted as carefully as possible. It must be inserted at an angle, parallel to the course of the vein, until the needle precisely hits it and dark-colored venous blood appears.
This method has some advantages:
- reasonable cost of materials required for research;
- It does not take much time to collect samples;
- minimal blood spatter.
Despite this, there are also significant disadvantages:
- the risk of injury to the cow is quite high;
- will have to come into contact with the blood of the animal;
- during blood sampling, the animal experiences severe stress, as the needle is inserted into the most tender place on the body;
- This procedure is quite difficult to carry out.
Thanks to new technologies, this method has become outdated and is practically not used in research.
Features of vacuum blood sampling
The use of vacuum systems has a significant advantage, since after collection the blood immediately goes into a special tube, resulting in no contact between veterinary personnel and the sample taken.
Such systems consist of a vacuum syringe, which serves as a container, and a special needle. The connection with the anticoagulant is carried out inside a vacuum container.
If we consider the advantages of vacuum blood sampling, we can highlight the following:
- within 2 hours it is possible to collect samples for research from 200 animals;
- it is not necessary to fix the animal in a motionless state before starting the procedure;
- at all stages of collection there is no direct contact of the veterinarian with the blood;
- since blood does not come into contact with objects from the environment, the risk of spreading infection is reduced to zero;
- the animal experiences virtually no stress during the procedure.
As a result of the fact that cattle do not experience stress, cows' milk yield does not decrease.
Conclusion
Taking blood from cows from the tail vein is the most popular and painless method for the animal. As practice shows, this sampling method does not require much time, as a result of which a large number of samples can be taken from cattle in a short period of time.