Content
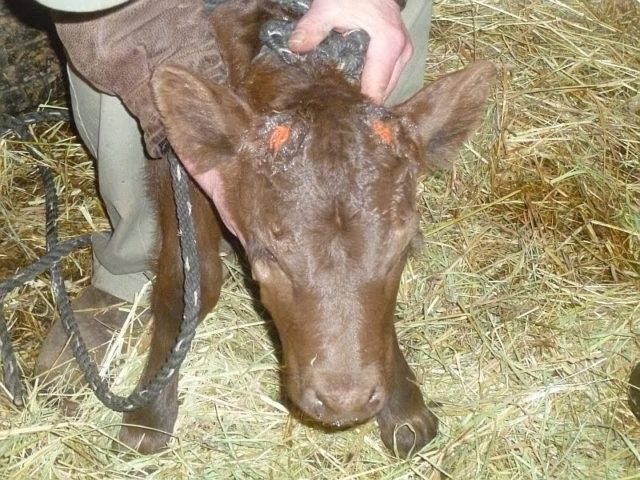
Cattle owners often find themselves in a situation where a cow breaks its horn. Such injuries can be prevented, but if this does happen, then the necessary measures should be taken immediately to help the animal.
What are the dangers of horn injuries in cattle?
Horns are a kind of derivative of skin, along with nails, claws and hair. Their formation occurs from the transformation of the epidermis. It grows from the base, and after final formation it does not change until the end of its life.
The section shows that the organ is represented by a keratinized upper layer, a kind of cover - the epidermis, as well as the dermis. Its main function is to connect to the frontal bone. In addition, blood capillaries and vessels, nerve endings pass through it, which feed the capsule and ensure its active growth.
Under the dermis there is connective tissue, which is covered with a mucous membrane. The horn inside is empty.
A cow's horn is usually divided into three main parts:
- apex;
- body – middle part;
- the basis of the organ is the root.
The base is connected to the soft part - the wax, which, in turn, connects it to the skin.
Blood vessels, capillaries, and nerves are found in the two lower layers of the cow's horn, and the top is the keratinized epidermis.This way the part can be removed without causing pain or bleeding to the cow.
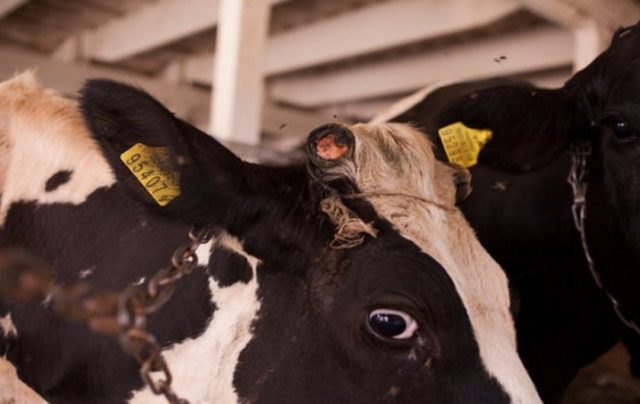
Often a broken horn in a cow leads to complications. Especially if the lower areas are damaged. In this case, a bleeding wound appears on the head, and the base of the horn also bleeds. As a rule, if help is not provided in time, microorganisms that cause blood poisoning get into the wound. The local temperature is elevated and the cow becomes anxious when touched. All this indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process. After some time, suppuration of the wound surface begins. The cover becomes movable and can be removed.
Veterinarians classify injuries as mild, moderate, and severe based on severity.
The injury is considered minor if the very tip is broken, since there are no blood vessels there.
Moderate cracks include small cracks. This causes bleeding, but the prognosis is usually favorable.
A fracture in the middle part is already a severe case. The animal experiences severe pain. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into an open wound, which contributes to the development of inflammation in the frontal sinus, oral and nasal cavities. The animal lowers its head and tilts it to the injured side. Sometimes the infection also spreads to the brain. This type is characterized by mobility of the broken organ and unilateral nosebleeds. Blood enters the nasal passage through the frontal sinus.
The most severe type of injury is detachment of the cover and fracture at the base. This is very dangerous and painful for cattle.
What to do if a cow breaks its horn
Therapy for cracks is aimed at cleansing dirt, restoring the skin and epidermis.
First of all, if the horn is broken, you should:
- wash the wound with a syringe with a solution of manganese or hydrogen peroxide;
- lubricate with iodine or brilliant green;
- apply a bandage as tight as possible with antibacterial ointment and change it every day;
- If the temperature rises significantly, antibiotic treatment should be prescribed.
In case of a closed fracture, if the sheath is not damaged, a splint is installed on the broken horn. You should also apply a very tight figure-of-eight bandage between the two horns. The cow should be kept in a separate room and walked away from the herd.
If the horn is broken in the middle part, therapy consists of stopping the bleeding, treating the wound with antiseptics, and then resorting to surgery using anesthesia, since the broken horn cannot be restored.
Prevention of horn injuries in cows
Prevention should be aimed at eliminating the main causes of fractures. Cows must be kept in free stalls in accordance with animal hygiene standards. In the premises where cows are kept, equipment should not be stored, as well as anything that could cause injury. The herd's exercise should not take place near overgrown gardens or windbreaks. It is not recommended to use non-standard harness options. When transporting cows, it is necessary to properly secure the cows with a special bridle.
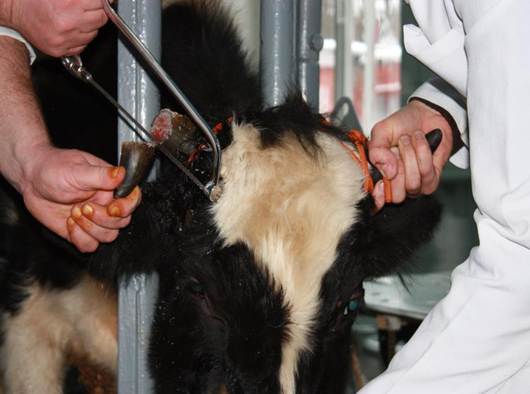
However, the most reliable way to avoid injury is the dehorning procedure (decornuation) of the entire livestock. The procedure is carried out at a young age, when the horns are not fully formed. There are several options for this:
- sawing, in which only the top is removed;
- chemical removal is carried out under the influence of certain active substances;
- electrical removal, the essence of which is to cauterize the emerging horns.
The decoruation method prevents future horn injuries.
Conclusion
If a cow breaks a horn, the reasons can be varied. The owner is able to eliminate them and provide assistance to the animal. More and more experts are coming to the conclusion that cows do not need horns at home. Their purpose is protection. So for domestic cows kept in a herd, they are a kind of atavism.