Content
- 1 What is leukemia in cattle?
- 2 The causative agent of leukemia in cattle
- 3 How is bovine leukemia transmitted?
- 4 Symptoms of leukemia in cattle
- 5 Stages of bovine leukemia
- 6 Methods for diagnosing bovine leukemia
- 7 Treatment of leukemia in cattle
- 8 Instructions for the prevention of leukemia in cattle
- 9 Pathological changes in leukemia in cattle
- 10 Conclusion
Bovine viral leukemia has become widespread not only in Russia, but also in European countries, Great Britain, and South Africa. Leukemia causes irreparable damage to the cattle industry. This is due to increased culling of the herd, waste disposal, treatment, and other measures. The disease is developing more intensively in the dairy industry.
What is leukemia in cattle?
The causative agent of the disease is an infectious pathology containing an oncogenic virus. It is similar to leukemia in other animal breeds. There is another option that sheep and goats are tolerant of. Leukemia is associated with malignant proliferation of hematopoietic tissue cells and is of a tumor nature. The virus may remain latent for a long time and not manifest itself. Rapid development begins with a decrease in immunity. During the course of the disease, the immune system is completely destroyed, so the animal is susceptible to recurrent leukemia even after recovery.Lack of immunity leads to an increase and duration of other diseases.
The causative agent of leukemia in cattle
The causative agent is a specific leukemia virus. It is extremely unstable in the external environment and dies at 76 degrees in 16 seconds. Boiling water kills him instantly. Destroyed by various disinfectants:
- 2-3% sodium hydroxide solution;
- 3% formaldehyde;
- 2% chlorine solution.
Also deactivated under ultraviolet light in 30 minutes. In direct sunlight - within 4 hours. Sensitive to various types of solvents - acetone, ether, chloroform.
The bovine leukemia virus has a spherical structure, up to 90 nm in size. Consists of a cubic core surrounded by a lipoprotein shell. Contains a genome with two helical RNA molecules.
Antigenically, bovine leukemia viruses are related but different from retroviruses. Based on similarities and differences, it can be classified into a special group - type E.
How is bovine leukemia transmitted?
The main reason for the pathogenesis of bovine leukemia is neglect of livestock, lack of disinfection of premises, and ignorance of preventive measures.
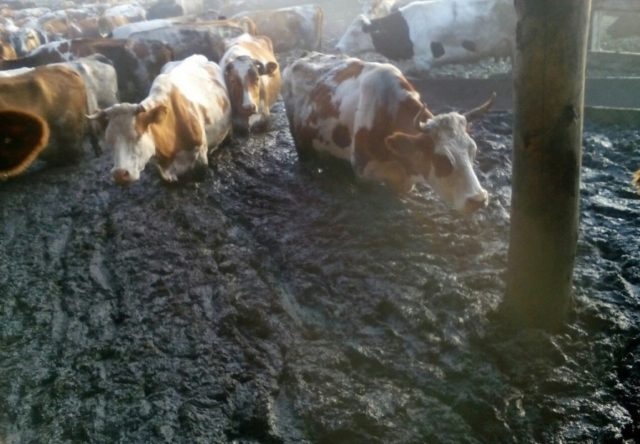

Unsanitary conditions in the barn
Transmitted:
- With direct contact between animals through biological fluids - blood, milk, sperm. Calves are already born infected or acquire the disease through their mother's milk. The herd can become infected even in the absence of an inseminating bull. Animals jump on each other, damaging the skin. If one animal is infected, it can transmit the virus through injuries.
- Through the bites of blood-sucking insects. Anything that feeds on blood is dangerous.No methods of control have been found.
- Through non-sterile veterinary instruments during mass examinations and vaccinations. Symptoms of the disease do not appear immediately. During this time, most of the herd may become infected.
There are 2 forms of leukemia - sporadic and enzootic. The first is very rare and develops only in young animals. The second has a latent period of more than 3 months. Affects adults.
Symptoms of leukemia in cattle
The initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic. Only in the later stages are health problems noted. After changes in blood composition, the signs become more noticeable:
- Animal weakness.
- Increased breathing.
- Weight loss.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Swelling of the dewlap, udder, abdomen.
- Lameness in hind legs.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Noticeable tumors.
- Bug-eyed. Rarely appears.
Exhaustion and weakness appear as a result of poor absorption of useful elements from feed. Milk output decreases.
Stages of bovine leukemia
Any cattle is susceptible to leukemia. There are 3 stages:
- Incubation. The latent period is up to 3 months. It starts from the moment of a virus attack. Outwardly it does not appear at all. In cows with strong immunity, it may take longer.
- Hematological. Characterized by changes in blood composition with a rapid increase in white blood cells - leukocytes. White blood is analyzed by composition. At this moment, the first disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract begin.
- Tumor development in hematopoietic organs. This can happen 4-7 years after infection.
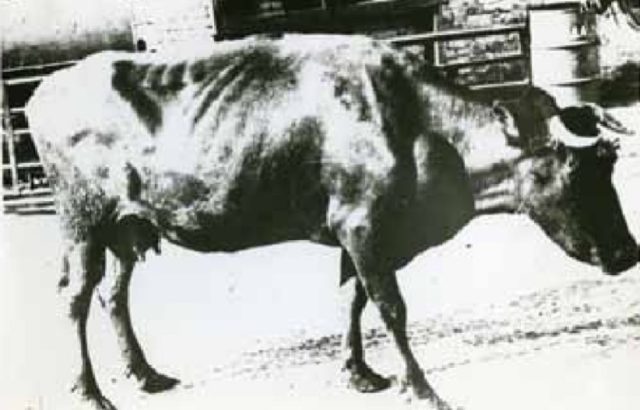

Enlarged prescapular lymph node in bovine leukemia
Early stages of the disease can be detected in milk tests. Therefore, it is extremely important to take it to the laboratory periodically. This will help isolate infected individuals and avoid mortality.
Methods for diagnosing bovine leukemia
The first case of leukemia with white blood cells in an enlarged spleen was described in 1858. Since the end of the 19th century, for almost 100 years, scientists have been trying to find the causative agent of the bovine leukemia virus. It was only opened in 1969. Leukemia came to our country with the import of breeding cattle.
Several diagnostic methods are known - primary, serological, differential. The primary method is used on farms. The basis for it is a pathological examination of dead animals, blood tests, and the study of epizootological and serological data. A histological sample must be taken.
Signs of leukemia during primary diagnosis:
- Clinical.
- Hematological changes - increased number of leukocytes and atypical cells of hematopoietic organs.
- Pathological changes in the organs of dead cattle.
- Positive result of histological studies.
For bovine leukemia, laboratory diagnosis is the most reliable way to determine the disease.
Leukocytes are counted in a Goryaev chamber or under a microscope. Leukocytes and lymphocytes are compared with the data in the “leukemia key” table. Based on the number of cells and the morphology of the blood, a conclusion is made about the disease - a healthy animal is at risk or is already sick.
Serological tests identify antibodies to the bovine leukemia virus antigen. They appear 2 months after the patient is infected - much earlier than noticeable hematological changes. Then they persist throughout life. The immunodiffusion reaction (IDR) is the main research method in Russia and other countries. Animals with positive RID results are considered infected. Such clinical results or blood tests immediately place cattle in the category of sick.
Differential diagnosis of bovine leukemia determines the disease based on a number of chronic infectious and non-infectious diseases.

Diagnosis of bovine leukemia
These are tuberculosis, actinomyosis, brucellosis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, nephritis and other diseases of the liver, lungs, and bones. These diseases are accompanied by leukemia-like changes - leukemoid reactions.
Treatment of leukemia in cattle
To date, no effective treatment option has been found. Attempts were made to eliminate bovine leukemia with a vaccine, but they were unsuccessful. The main therapy is related to the culling of cows and their slaughter. It is recommended to slaughter the animal at an early stage of the disease, so as not to suffer and not lose profit on treatment. Milk from leukemic cows is prohibited by law. The same ban has been introduced on the consumption of meat from sick animals. Milk from virus carriers is subject to mandatory pasteurization. After which they are disinfected and used without restrictions.
According to veterinary rules, in case of bovine leukemia, farms engaged in dairy farming are forced to slaughter their entire livestock. Treatment takes a long time and can last for years.
Farms with a small number of sick people - up to 10% of the livestock - separate leukemic cows and hand them over for slaughter. Serological tests are carried out once every 2 months.
If the number of cases is more than 30%, not only serological studies are carried out, but also hematological studies after 6 months. Cattle are divided into groups that have successfully passed the study and virus carriers. Sick people are separated for slaughter.
Instructions for the prevention of leukemia in cattle
Farms with this disease are brought under control and declared unsafe. According to the rules for combating bovine leukemia, a number of restrictions are imposed on them to reduce the spread of infection. Quarantine measures do not allow:
- Driving livestock within populated areas without the permission of a veterinarian.
- Free mating of cows with stud bulls.
- Use of contaminated instruments when treating animals and premises.
- Keeping healthy and sick people together.
- Free import and export of animals.
Measures for bovine leukemia involve quarantine of all newly arrived livestock. The sale of meat and dairy products is carried out only with the permission of the veterinary station.
During the quarantine period, premises for keeping livestock and animal care items are regularly disinfected.
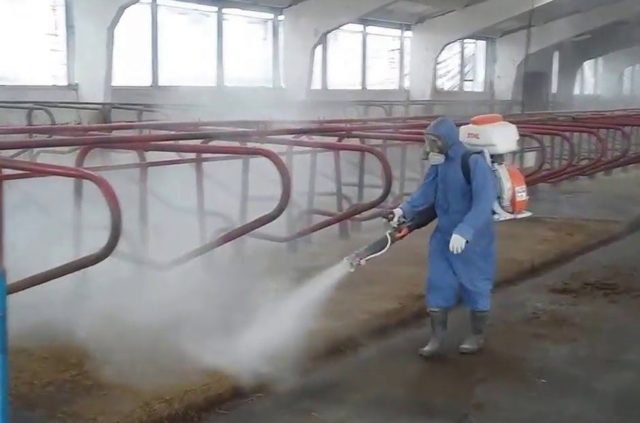

Disinfection of premises for leukemia
All cattle waste products are disposed of.
To restore the livestock, replacement young animals are raised. He is kept in other premises and grazed on separate pastures. Upon reaching the age of 6 months, serological tests are carried out and then repeated every six months. According to the instructions for bovine leukemia, infected young animals are separated and fattened away from healthy ones. Then they score.
Pathological changes in leukemia in cattle
Autopsies of dead animals are carried out periodically to study the course of the disease, causes of death, and the effect on individual organs and systems as a whole. Bovine leukosis leads to the elimination of diseased livestock. An autopsy shows diffuse or focal infiltration into different parts of the body at different stages of leukemia development:
- hematopoietic organs;
- serous covers;
- digestive system;
- heart;
- lungs;
- uterus
The main forms of the disease are leukemia and reticulosis. Changes in leukemia:
- greatly enlarged spleen - up to 1 m;
- enlargement of follicles;
- rupture of capsules with hemorrhage into the peritoneum;
- enlargement of the superior lymph nodes in the tumor stage up to 10*20 cm;
- the smooth capsule is easily removed, the tissue pattern of the lymph nodes is smoothed;
- the liver, heart, kidneys sprout as diffuse or focal neoplasms from gray-white to gray-pink;
- pathology of other organs manifests itself at later stages of the disease.
Changes with reticulosis:
- uneven enlargement of lymph nodes;
- the capsule is not smooth, but rough;
- fusion of the capsule with adjacent organs and tissues;
- tumors of various sizes - from a pea to 30 kg;
- tumor color is gray-white;
- a dense tumor is covered with foci of necrosis and hemorrhage;
- dystrophic changes are noticeable in the liver, spleen, endocrine glands, and brain;
- Metastases to the abomasum, heart, and other organs are possible.
Conclusion
The bacteria that cause bovine leukemia cannot tolerate heat treatment. But the infection in the early stages is asymptomatic.If diagnostics are carried out in a timely manner, young animals and infected animals are isolated, antiseptic treatment is carried out, and sick animals are slaughtered, the likelihood of recovery of farms from bovine leukemia will be higher. It is better to stop infected cattle in time than to lose the entire livestock.