Content
- 1 Why is boric acid used in gardening and gardening?
- 2 Benefits of boric acid for plants
- 3 Methods of using boric acid for the garden or vegetable garden
- 4 Feeding plants with boric acid in the garden or vegetable garden
- 5 Is it possible to water flowers with boric acid?
- 6 The use of boric acid in pest control
- 7 How to treat plants with boric acid against late blight
- 8 Signs of boron overdose in plants
- 9 Conclusion
The use of boric acid in the garden is very popular. Inexpensive fertilizer promotes rapid growth of crops and also protects them from pests.
Why is boric acid used in gardening and gardening?
It is difficult to provide ideal conditions for vegetable and garden crops on the site. Due to the lack of nutrients, plants begin to suffer from diseases and stop developing.
Using a solution of boric acid in the garden helps:
- strengthen the immunity of garden crops;
- promote abundant formation of ovaries;
- ensure a good harvest even in dry seasons;
- improve the taste of berries and vegetables.
Regular boric acid powder is suitable for use in the garden.
Unlike many industrial fertilizers, the product is very inexpensive.
Benefits of boric acid for plants
Using boric acid in the garden is especially useful on poor soil - brown forest, gray, sandy, soddy-podzolic. When used correctly, fertilizing gives the following results:
- stimulates the formation of new roots;
- improves chlorophyll production;
- increases the number of ovaries;
- increases sugar levels in fruits.
With a sufficient amount of boron, garden crops are much less likely to suffer from diseases. In particular, the use of fertilizing helps prevent the development of bacteriosis and rot, and also repels dangerous garden pests.
Signs of boron deficiency
It is necessary to add boron to the soil urgently if:
- garden crops grow poorly and produce scanty ovaries;
- on young leaves the veins turn pale and yellow spots appear;
- The bark on the shoots dries and dies.
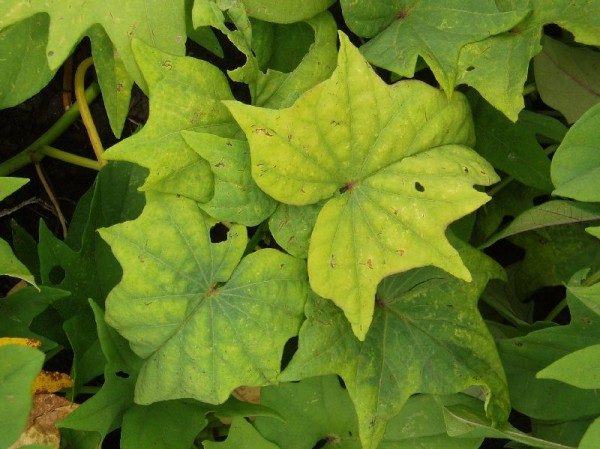

Yellowing leaves indicate a lack of boron
With boron deficiency, the fruits of vegetable and garden crops are often deformed.
Methods of using boric acid for the garden or vegetable garden
There are several main options for using boron powder.
- Soaking seeds.To make the planting material germinate faster, it can be kept in a boron solution before transferring it to the ground. In this case, only 2 g of acid is diluted in a liter of water.
Tomato and beet seeds are kept in boric acid for about a day; cucumbers and zucchini need 12 hours.
- Soil cultivation. Shortly before planting garden crops, you can water the beds with boron solution. The preparation proportions remain the same - 2 g of substance per liter.
After using boron to water the beds, they must be thoroughly loosened
- Spraying. For developing plants, foliar feeding is most often used; the dosage per liter of water is equal to 1 g of acid. It is recommended to cultivate the garden and garden three times - before flowering, during it and during the fruiting period.
Foliar spraying is the most effective method of applying boron fertilizing
- Watering at the root. Depending on how severe the boron deficiency is, take 1-2 g of the product per liter of liquid.
Root irrigation is rarely used, only when there is a clear lack of boron
Feeding plants with boric acid in the garden or vegetable garden
Any garden crops respond positively to moderate use of boron. But some plants need more minerals, while others need less.
What plants can be sprayed with boric acid
Vegetable and fruit crops can be divided into 3 groups depending on how much boron they need:
- Increased need: beets, cabbage and pome trees.For these plants, fertilizing is carried out up to 3 times during the season - on swelling buds, on the ovary and during fruiting.
- Average need: berry bushes, greens, most vegetable crops and stone fruit trees. Feeding is carried out twice, at the beginning of flowering and at its height.
- Minor requirements - potatoes, strawberries, legumes and herbs. Typically, the use of boric acid solutions is indicated only for symptoms of deficiency.
For crops with a low need for boron, fertilizer can be applied to the soil once before sowing.
How to dilute boric acid for spraying plants
Boric acid has a peculiarity - it cannot be dissolved in cold water. To mix the solution, the liquid is heated to a temperature of about 80 °C.

Usually a so-called “mother solution” is made from boric acid, and only then it is added with clean water.
For simplicity, the following algorithm is used. Just a liter of water is heated to the desired temperature. Boric acid is thoroughly stirred and the product is allowed to cool, and then simply added with water to the standard 10 liters.
For convenience, when selecting a dosage, you can use the table for using boric acid for plants:
Garden culture | Volume of boric acid per bucket (for spraying on leaves) |
Cabbage | 10 g |
Potato | 10 g (for treating tubers before planting) |
5 g | |
Beetroot and tomatoes | 10 g |
Strawberries, currants, gooseberries | 5 g |
Cherry, apple, pear | From 10 to 20 g |
It is not customary to use an alcohol solution of boric acid in the garden. But in extreme cases, you can dilute the product with water 1 to 20, in which case it will become safe.
Fertilizing plants with boric acid
Recommendations for the use of boron for vegetable and fruit crops are very similar.But plant requirements may vary slightly.
How to use boric acid to feed seedlings
Plants can be fertilized with boric acid already at the seedling stage during the period of active growth. Tomatoes that are sensitive to lack of substances especially need such feeding.
A solution for use on seedlings is prepared as follows: stir 1 g of boron powder in a liter of hot water. The cooled liquid is sprayed onto the leaves of the seedlings.
Tomatoes and cucumbers
Tomatoes and cucumbers especially need boron. The first time you need to feed the crops is before flowering, then when the ovaries form, and again during the ripening of the fruits.
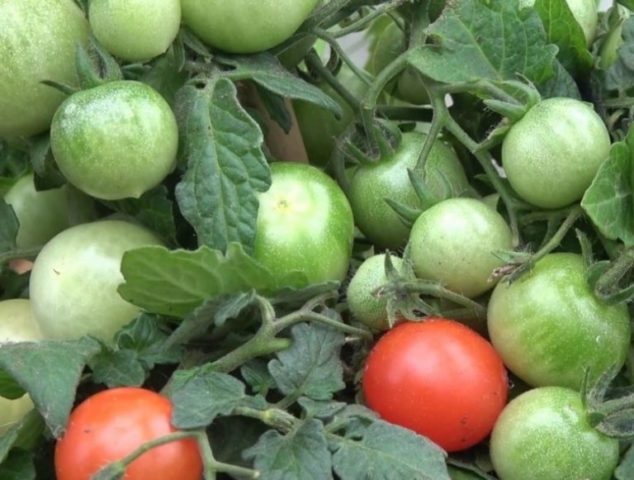

Tomatoes are in great need of boron fertilization
For tomatoes, about 10 g of acid is dissolved in a bucket, for cucumbers - only 5 g.
Potato
With a lack of mineral matter, the tops of the crop turn yellow, the petioles become brittle and turn red, the root crops grow more slowly and are more likely to suffer from fungi.
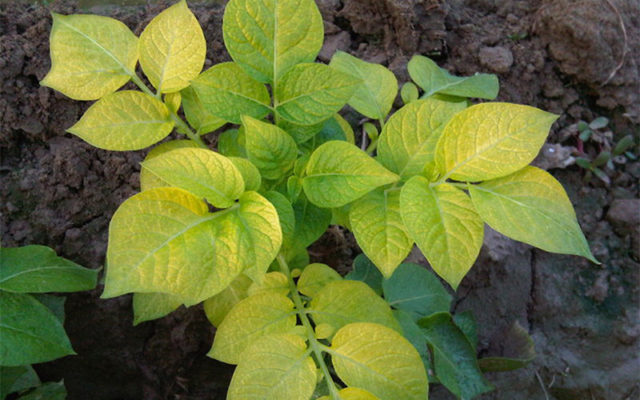

Potatoes begin to experience boron deficiency in acidic soils
If alarming symptoms appear, the use of boric acid is recommended; 6 g of powder is dissolved in a bucket. For prevention, tubers can be treated at the seedling stage - the potatoes are sprayed with a strong solution, and as much as 15 g of the substance is poured into a bucket of water. About 50 ml of solution should be used for 1 kg of planting material.
Grape
Due to a lack of boron in the soil, grapes develop worse. Yellowish spots appear on its leaves, and the berries become smaller and resemble peas.
In case of mineral deficiency, treatment with boron for grapes is carried out during the budding period. About 5 g of powder is diluted in a bucket of water.
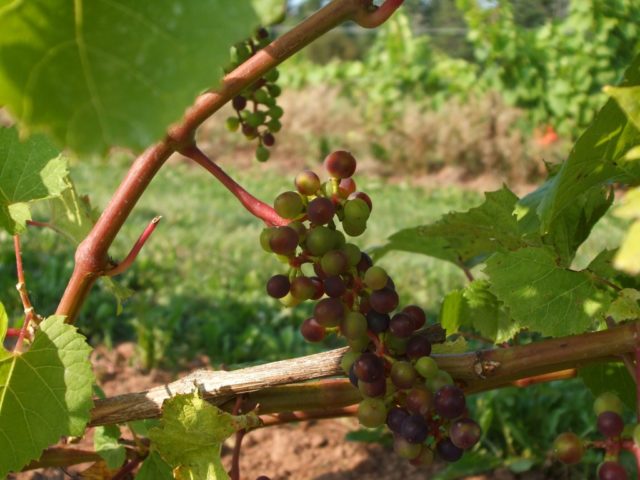

Timely fertilizing with boron prevents grapes from peas
Beet
With insufficient use of boron, beets suffer from phomosis.First, brown spots with black specks in the center appear on the leaves of the crop, and then the root crop rots from the inside.
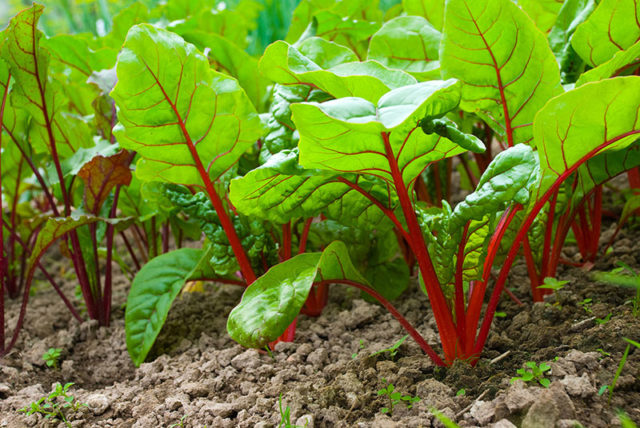

For beets, the use of boron is justified both before planting and at the growth stage
Beet seeds are soaked in boric acid for 10 hours before planting; only 1 g of the substance is diluted in a liter of liquid. After transfer to the soil, foliar fertilizing with boric acid is carried out at the fifth leaf stage; the usual concentration is used, about 5 g for a bucket of water.
Cabbage
Cabbage reacts to a lack of boron by the appearance of glassy inflorescences and hollow heads of cabbage. The fruits become deformed and acquire a bitter taste. The treatment is carried out in 3 stages - the plantings are sprayed during budding, during flowering at the stage of the fifth leaf and during the period of ripening of heads of cabbage.
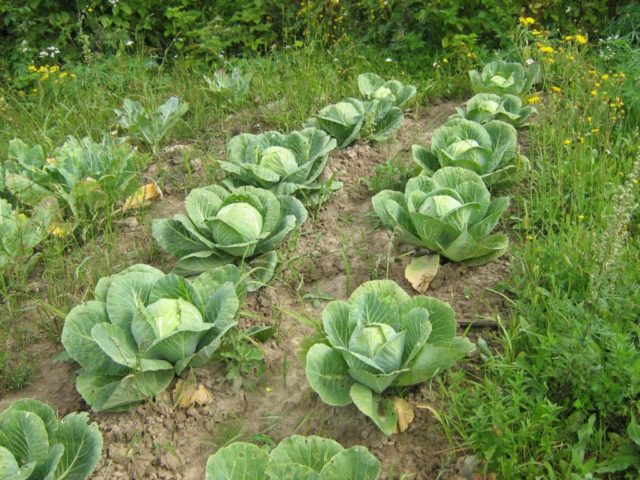

Cabbage is sprayed with boric acid three times from budding to fruiting.
To use the solution, add 2.5 g of the substance to a bucket of water.
Pepper, eggplant
If there is not enough boron in the soil, peppers and eggplants produce small, deformed leaves, stop growing and may drop flowers and ovaries. Fertilize crops three times during the growing season:
- during the formation of buds;
- after 10 days, during flowering;
- at the maturation stage.
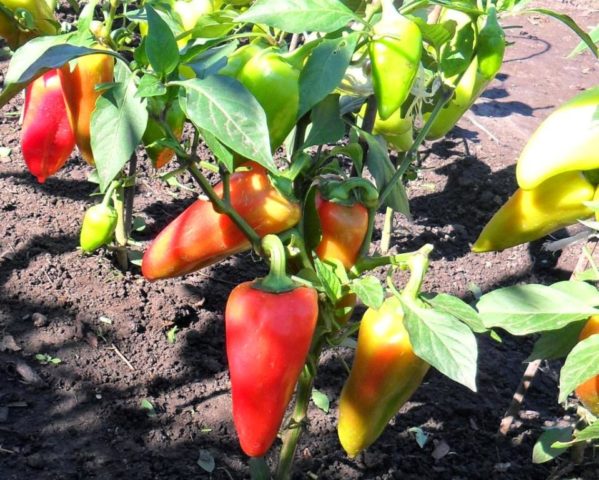

Peppers, like eggplants, are sprayed with boron three times per season.
Mix no more than 1 g of powder in a liter of water; the solution is suitable for both root application and spraying. It is best to process plantings by leaves.
Pears and apple trees
You can understand that fruit trees do not have enough boron by the following signs:
- leaves become deformed and thicken;
- the veins darken and become “corky”;
- At the ends of the shoots, peculiar rosettes of small leaves appear;
- The tops of the trees begin to die.
The use of boric acid in gardening increases not only the quantity, but also the quality of fruits, in particular, prolongs their shelf life.

With a normal level of boron, the fruits of pears and apple trees grow large and without spots
In a pear, due to a lack of boron, pits and crust-like spots may appear on the fruit; in an apple tree, brown areas inside the pulp, similar in structure to a cork. To eliminate mineral deficiency, 2 feedings are carried out for fruit trees:
- at the beginning of flowering;
- 10 days after the first spray.
Boric acid is diluted in increased volumes, up to 20 g per bucket, and the crowns are evenly treated in the evening. Productivity after this increases to 30%.
Strawberry
The use of boron solutions increases strawberry yields and improves the quality of berries. The treatment is carried out twice - the strawberry beds are watered in early spring, dissolving only 1 g of the substance in a bucket of water, and the plant is sprayed before flowering. In the latter case, 2 g of the substance must be mixed in 10 liters.

Strawberries require boron treatments twice a season.
Treatment of plants with boric acid for fruit set
Particular attention should be paid to fertilizing at the ovary stage. The best results are obtained by spraying; watering at the root is less effective. For processing, a pure boron solution is used without adding other components; the proportions are 1 g of the substance per liter.
During the procedure, you need to process the entire plant from all sides to cover the leaves, flowers and the developing ovary. The temperature of the solution should be about 20 ° C; plantings can be sprayed only in the morning or evening, in the absence of bright sun.
Is it possible to water flowers with boric acid?
The use of boron solution is useful not only for garden crops and fruit trees.The product can be used to fertilize flowers in a flower bed; this will have a good effect on the size of the buds and prolong the decorative period.
What flowers love boric acid?
Boron is an indispensable element for any plants. However, roses, dahlias, gladioli and garden violets respond best to it.
How to dilute boric acid for flowers
You can fertilize garden beds by spraying or applying a solution at the root. In the first case, the concentration is 0.5 g per bucket, in the second - up to 2 g per similar amount of liquid.

Any garden flowers respond well to the use of boron
As always, boron powder for use is dissolved in preheated water. The procedure itself is carried out after the liquid has cooled.
How to feed flowers with boric acid
On average, fertilizing with boron for flowers is carried out twice, during the period when the buds are gaining color, and during active flowering. They use a foliar application method, spraying is carried out in the evening so that there are no sun burns on the leaves. If fertilizing is carried out at the root, then the soil is pre-moistened; it is impossible to water dry soil with boric acid, this is dangerous for the plants.
How to spray roses with boric acid
For lush flowering of roses, it is enough to feed with boron 2 times - during the formation of buds and a week later, when the bushes bloom. The recipe for fertilizing with boric acid is standard - the substance is diluted in hot water (10 g per bucket), treatment is carried out in the morning or evening.

Boric acid ensures abundant and bright flowering of rose bushes
You can protect roses from fungal diseases and strengthen their endurance even before planting. Shrub cuttings are soaked for several minutes in a concentrated boron solution, 20 g per 10 liters, and then transferred to the ground.
The use of boric acid in pest control
Beneficial boric acid promotes plant health, but is poisonous to most insects. Therefore, its use is recommended, including for pest control.
From ants
Baits are used to get rid of ants. For example, you can add 5 g of boron powder to a glass of sugar syrup and pour the product on the beds and near insect nests. Treatment should be carried out in mid-spring; strawberries, carrots and garden flowers need special protection.

Sweet baits containing boric acid are used to kill ants.
From woodlice
Small woodlice actively reproduce in moist, acidic soils and poorly harvested areas. The use of boric acid in gardening helps to get rid of them; you need to dilute 10 g of powder in 500 ml of water and spray the passages between the beds. The procedure is carried out in early and mid-summer, when woodlice is especially active.

The use of boric acid against woodlice is especially justified in humid, warm weather.
Plantings of potatoes, beets and tomatoes, as well as fruit bushes, can be treated against woodlice. Spraying should be carried out on moist soil so that the roots of the plants do not get burned.
From the bear
It is quite difficult to remove mole crickets from the garden, but boric acid gives a good effect. It is necessary to make a special bait - 1 kg of steamed grain is mixed with 2 small spoons of the substance and spilled with any oil in a small amount.To use, the boron mixture is embedded directly into the ground or placed in the passages left by the mole cricket.

To remove mole crickets, bait made from boric acid and grain is used.
The use of baits is allowed to protect any plants, especially potatoes and beets. You can spread homemade poison for the pest on the beds immediately after planting the crops, since the mole cricket wakes up already at 12 °C.
From aphids
Removing aphids using boric acid can be difficult. The fact is that the pest feeds only on plant juices and does not pay attention to bait. But spraying has a positive effect - 2 g of powder is poured into a liter of liquid, mixed and the plantings are generously treated with leaves, buds and ovaries.

When treating aphids, it is important to spray the leaves both above and below
The procedure is carried out from the end of May, when aphids begin to attack plantings in warm weather, and is repeated as necessary until the fall, but not more than once a month. When using a boron solution, cabbage and tomatoes, beets and eggplants, as well as flowers, grapes, gooseberries, currants and other crops can be protected from pests.
How to treat plants with boric acid against late blight
The late blight fungus can affect any crops in the garden, but potatoes and tomatoes are especially often affected by it. Under the influence of the disease, dark spots appear on the leaves and fruits, and underground tubers undergo dry rot.
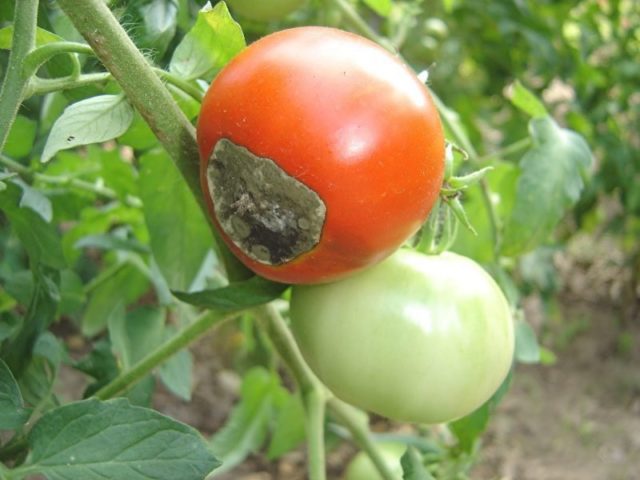

Tomatoes are treated against late blight during the period of active growth and fruiting.
To eliminate the fungus, you need to dilute 1 small spoon of boron powder in a bucket of water and spray the plantings, as well as carry out root feeding. The use of the substance is indicated for noticeable symptoms of the disease; treatment should be carried out in the evening and morning. If tomatoes and potatoes grow nearby on a plot, both crops must be sprayed with boric acid.
Signs of boron overdose in plants
Excessive use of the substance poses a danger to plants. You can understand that there is too much boron in the soil by the following signs:
- leaves of garden and garden crops have become unnaturally glossy;
- the edges of the leaf plates were bent inward, and the middle protruded upward;
- the greenery in the lower parts of the plants closer to the ground began to dry out and fall off.
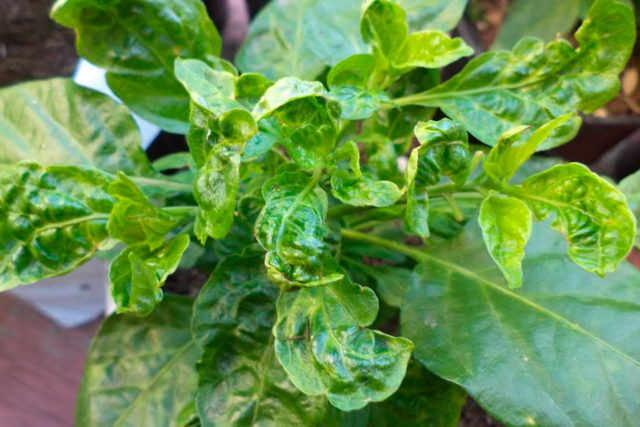

With an excess of boron, the leaves of crops become distorted and have an unnatural shine.
To correct the situation, the plants need to be urgently fed with potassium, and a week later fertilized with nitrogen.
Conclusion
The use of boric acid in the garden can strengthen the endurance of crops and increase yields. The substance can also be used against pests; for them it is poisonous.












