Content
- 1 Composition and release form of Glyphosate
- 2 Mechanism of action of Glyphosate
- 3 What weeds does it help with?
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages
- 5 Preparation of working solution
- 6 At what temperature does Glyphosate work?
- 7 Instructions for use of the drug Glyphosate and consumption rate
- 8 Compatibility with other tools
- 9 Effect of Glyphosate on the human body
- 10 Security measures
- 11 How to replace Glyphosate
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 Customer reviews about Glyphosate herbicide
Glyphosate herbicide is a broad-spectrum pesticide. The drug has become widespread among gardeners and gardeners due to its versatility and properties.
Composition and release form of Glyphosate
The main components of the drug are organophosphorus compounds: acids and synthesized compounds. And although there are many herbicides, they are most often based on glyphosate and a number of other components. In terms of its chemical formula, it can be described as C3H8NO5P.
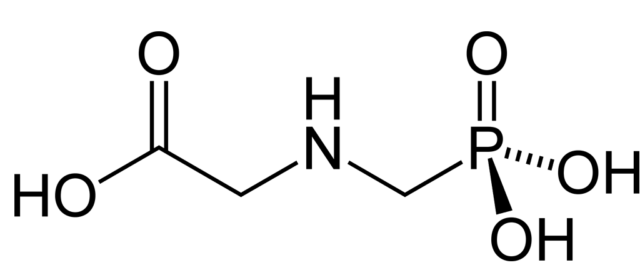
Glyphosate is a white crystal that has no odor and is highly soluble in water.
Manufacturers sell the herbicide in liquid form. It is poured into containers of 4 ml, 50 ml, 120 ml.Farm owners prefer to purchase glyphosate in large quantities: 5 liters, 10 liters or 20 liters.
Mechanism of action of Glyphosate
It is often called a pesticide, although the drug is a contact herbicide. The mechanism of action of Glyphosate is the biosynthesis of phenylalanine, inhibition of prephenate dehydratase and chlorismate mutase. This is manifested in the following: once it gets into the soil, it becomes biologically inert, that is, it does not interact with the environment. When irrigated, glyphosate penetrates with water into plants, where it interferes with the synthesis of amino acids. Because of this, the weeds die. Residues of the active substance Glyphosate go into the soil. Plant roots do not absorb the herbicide from the ground.
What weeds does it help with?
The drug Glyphosate has a wide spectrum of action. With its help you can fight not only weeds, but also shrubs:
- annual bluegrass;
- shepherd's purse;
- ordinary cross;
- woodlice;
- blunt sorrel;
- creeping wheatgrass;
- ordinary whining;
- dandelion;
- horsetail;
- Veronica of Persia;
- field thistle.

Glyphosate can be used not only in gardens, but also in industry and on farms.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any drug, a herbicide has both advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a product, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances so as not to harm cultivated plants.
Advantages of the herbicide:
- Glyphosate is an effective means of controlling vegetation and has a continuous effect.
- Effective against both annual and perennial crops.
- Low cost of the drug.
- Economical consumption.
- Possibility of use in crop rotation.
- Compatibility with other herbicides.
- Glyphosate has disinfection and deratization properties: it destroys beetles, mice and rats.
Disadvantages of the herbicide:
- Disturbance of microflora in the soil.
- High toxicity of the components of the product;
- Negative consequences for the flora on the site.
Preparation of working solution
To dilute the drug, clean water and Glyphosate are required. Dosages and proportions will depend on the area of the site and the crops placed on it.
Preparation of a herbicide solution is possible only in plastic or enamel containers. The use of metal buckets is prohibited.

If it is necessary to irrigate large areas, it is possible to mix the components directly in the sprayer tank
At what temperature does Glyphosate work?
The quality of processing will depend on the correct use of the drug. Please note that Glyphosate is a water-soluble compound. Many weeds have a protective waxy coating on their leaf blades that prevents the solution from penetrating into the crop. Based on this, the maximum effectiveness of the herbicide is observed if the surface of the leaves is moistened.
Excessively hot or cold weather also negatively affects the effectiveness of Glyphosate. This is due to the fact that at high temperatures the vital processes in weeds slow down.
If it is necessary to destroy perennial plants, then Glyphosate is best applied in the fall, two weeks before the onset of frost. At lower temperatures, the herbicide acts more slowly, although no less effectively.
Instructions for use of the drug Glyphosate and consumption rate
Treatment after sowing is possible both using ground sprayers and agricultural sprayers. Most often, a single irrigation with Glyphosate is sufficient for most crops.
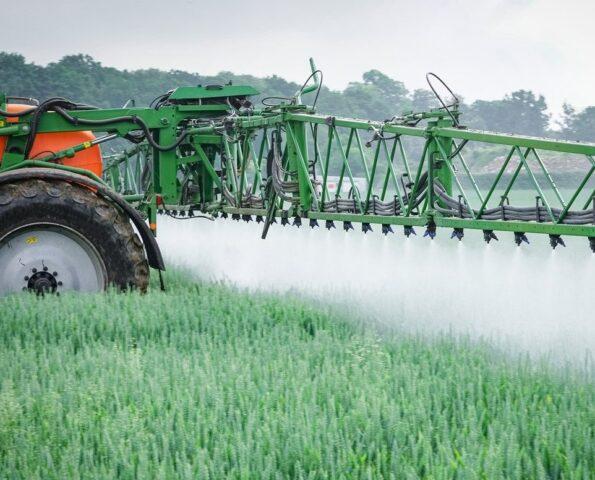

Work should be carried out if there is no danger of precipitation, there is no dew, and the air temperature has warmed up to +15 °C
Methods of using herbicide:
- In fields in fallows or stubble (sowing can be done 2-4 weeks after the procedure).
- On tree species, apply into cuts on the trunk, or irrigate the foliage.
- In gardens, targeted irrigation of weeds.
The dosage of the drug depends on the purpose of use. For 10 liters of water you need to take the following amount of Glyphosate herbicide:
- for the destruction of annual weeds in areas - 80 ml;
- against perennials - 120 ml;
- for processing a potato field until sprouts appear - 40-60 ml;
- before sowing, irrigate the area - 80-120 ml;
- spraying the soil under the lawn: 120 ml;
- cleaning areas near greenhouses, fences and places where crops are not planned to be grown - 120 ml.
If it is necessary to destroy trees, the dosage will depend on the type of object. For deciduous trees, 0.55 to 1.1 ml of product is required. For large trees, the dosage can be increased to 8 ml.
Compatibility with other tools
The herbicide Glyphosate can be used with other drugs:
- Dicamba;
- Atrazine;
- 2,4-D.
Gardeners have successfully combined post-sowing applications of Glyphosate with herbicides such as Simazine and Metribuzin.
Effect of Glyphosate on the human body
The drug is classified as a drug with the third hazard class. This requires people using the drug to wear full protective gear, including a gas mask. Protection measures do not depend on the concentration of the solution or the size of the treated area. One of the serious consequences of getting Glyphosate on the skin is cancer. This is one of the delayed diseases that will manifest itself if safety precautions are regularly neglected. Among the immediate manifestations is irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, manifested as redness and burning. A rash may appear on the skin after Glyphosate.
It has been established that the persistent carcinogenicity of the drug in the environment makes the consequences for the human body even more dangerous. Glyphosate residues enter the water and then into the human body, so not only farmers, but also other residents are at risk.
Consequences of long-term exposure to the herbicide on the human body:
- infertility in both sexes;
- the birth of children with genetic abnormalities (dwarfism, dementia);
- hormonal disorders in adolescents;
- the birth of children with autism;
- liver and kidney disease;
- various types of oncology.
Some countries from the European Union have introduced a ban on the use of Glyphosate on their territory. A number of retail chains have refused to sell products grown using the herbicide.
Security measures
A mandatory protective measure is the use of a waterproof suit, rubber gloves and a gas mask. It is recommended to apply the herbicide Glyphosate on the leeward side.

An important part of the protective suit is closed, thick rubberized shoes.
During the procedure, you should not take off your clothes, touch your face, or take food or water. The spray arm should not be raised high to minimize the risk of product getting on the body. All persons must leave the area during treatment with Glyphosate herbicide. At the end of the procedure, the irrigated area should be closed to visitors for 15 days.
If the drug gets on the skin or mucous membranes, it should be washed off immediately with clean running water. If a person swallows the solution, he must be urgently sent to the hospital, where he will receive medical care: gastric lavage and detoxification therapy.
How to replace Glyphosate
There are currently no effective herbicides that can replace Glyphosate. Many drugs contain the same active ingredient. The product will differ by manufacturer and release form.
Since 2018, scientists in Australia at Nontox have been developing a non-selective organic herbicide that will allow people to stop using glyphosate.
The new product must be completely non-toxic to both the environment and people. It is based on well-known minerals. The company received government support and excellent results were recorded as a result of 90-day testing. The bioherbicide does not have a trade name, but manufacturers promise to promote the distribution of the drug after receiving a patent.
Conclusion
The herbicide Glyphosate is a common plant killer. The drug has a wide spectrum of action, is economical in consumption, and is approved for use in crop rotation.Not only gardeners, but also industrial enterprises and farmers use the herbicide.
Customer reviews about Glyphosate herbicide








