Content
Garlic is an undemanding crop that can grow in any soil. But to get a truly luxurious harvest, you need to know the rules for growing garlic, using fertilizers and applying them in your beds.
Preparing the beds
Preparation rules garlic beds and applying fertilizers to them is the same for both winter and spring planting of garlic.
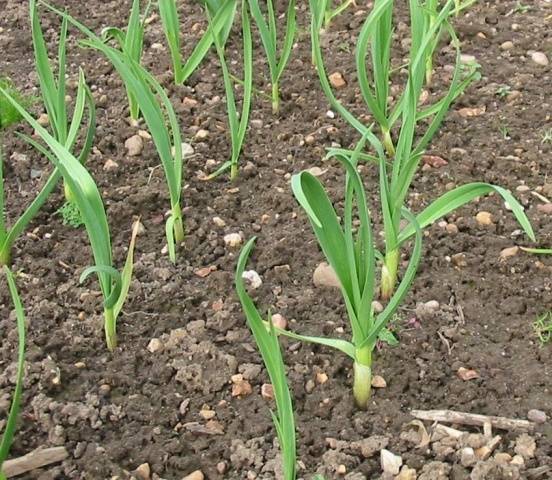
To plant garlic, you need to choose a bright area with fertile soil; in partial shade it develops slowly and often gets sick. The plant does not tolerate stagnant water, so it is necessary to build a good drainage system.
Garlic grows best in light, nutritious sandy soils with neutral acidity. If the soil characteristics in your garden are far from ideal, you can try to improve the soil characteristics to get a good harvest.
Heavy clay soils slow down the development of garlic, it grows later than expected, and the cloves are small. Winter garlic suffers the most from such soil; clay soils often poorly conduct water and air; cloves quickly rot in conditions of high humidity and low temperatures.
You can improve the soil structure in garlic beds using the following additives; they can be combined or applied separately:
- Sand;
- Sawdust;
- Humus;
- Peat;
- Rotted manure.
Sand is added when digging the soil, most often in the fall. Add 1-2 buckets of sand per square meter of soil; you can use river sand or one obtained from quarries. The sand is evenly scattered over the garlic bed, after which the soil is dug up.
To improve the soil structure, you can add sawdust; any sawdust will do, except oak, as they contain substances that can inhibit the root system of plants. It is advisable to use well-rotted sawdust; as a rule, they are dark brown or black in color. Fresh sawdust uses a lot of nitrogen during rotting in the soil; the plant will experience a deficiency of this substance.
Humus and peat will perfectly improve the soil in garlic beds; in addition, they will enrich it with nutrients and can be used as nitrogen fertilizers. 2 buckets of humus or peat are evenly scattered on a square meter of garlic beds, after which the soil is dug up to 20–25 cm.
Manure must be applied to garlic beds carefully; excess content can damage the garlic crop. In small doses it will be a good fertilizer. Poorly rotted manure can be a source of fungal spores that can cause fungal diseases in the plant and infect the soil in the garden. It is advisable to treat manure with fungicides before applying it to the soil. Apply no more than half a bucket of manure per square meter of bed.
In this case, the recommended dosage of ready-made fertilizers is halved.
High acidity of the soil does not allow the root system to fully absorb nutrients from fertilizers, the plant develops very poorly, and the harvest will be meager. To avoid this, during the preparation of garlic beds, substances are added along with fertilizers that can reduce the acidity of the soil. You can use dolomite flour and lime.
Before digging up garlic beds, it is advisable to apply complex fertilizer to avoid a deficiency of microelements in the soil. The fertilizer must necessarily contain potassium, phosphorus, boron, calcium and nitrogen. Recommended doses of fertilizers are indicated in the instructions for the drug.
When planting, complex fertilizer for garlic is chosen based on the manufacturer’s reputation and one’s own preferences. Can't buy fertilizers for garlic in random places, storage errors can significantly degrade the product’s performance.
Processing of planting material
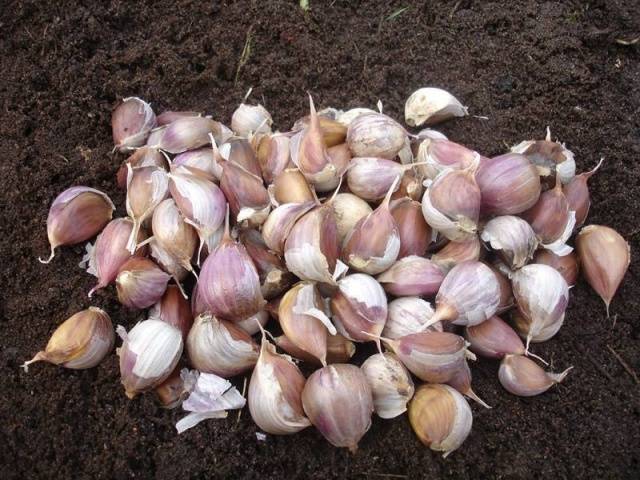
Before planting, the head of garlic is disassembled, large, dense cloves without stains or mechanical damage are selected. Softness of the cloves may be a sign of a bacterial or fungal disease; they will not produce a good harvest.
Varieties recommended for planting in spring can freeze even under cover. Preference is given to zoned varieties of garlic.
Selected garlic can be soaked for several hours in a solution of fertilizers and stimulants, this will help increase the supply of nutrients in the cloves, therefore, the shoots will be stronger, with good immunity. Fertilizers should include increased doses of potassium and magnesium, which help accelerate photosynthesis, and accordingly, seedlings will appear earlier.
To soak 1 kg of garlic cloves you will need a tablespoon of honey.
In addition to treating with fertilizers, it is advisable to use disinfectants before planting garlic. When planting, the cloves may be injured; treatment can help avoid infection with fungal and other diseases.
Fertilizers during growth
The first feeding with fertilizers is carried out when it has 3-4 feathers. This is a time of intensive growth, the most important microelements are nitrogen and phosphorus, which contribute to the development of the root system and green mass. For winter garlic, it is necessary to apply magnesium fertilizers; they will help it survive the winter better.
The second feeding is carried out two weeks after the first. Nitrogen fertilizers are not applied this time; it is necessary to choose fertilizers that contain phosphorus, potassium and boron. You can use fertilizer watering at the root, or spraying the green parts of the plant. Spraying with a fertilizer solution is carried out in dry, windless weather, early in the morning.
The third application of fertilizers is carried out three weeks after the second. This time it is necessary to add: nitrogen, potassium, boron, magnesium, phosphorus and other trace elements. You can use ready-made complex fertilizers for garlic, all components in them are in the correct proportion.
Further application of fertilizers is carried out if necessary, focusing on the appearance of the garlic. If there are no signs of nutrient deficiency, you can stop fertilizing.
Wood ash can be used for these purposes. To speed up the absorption of the chemical element, use a solution containing 5 tablespoons of wood ash per 2 liters of water.
Signs of micronutrient deficiency
A lack of microelements can be determined by the appearance of the plant.
Nitrogen
This chemical promotes the growth of garlic.
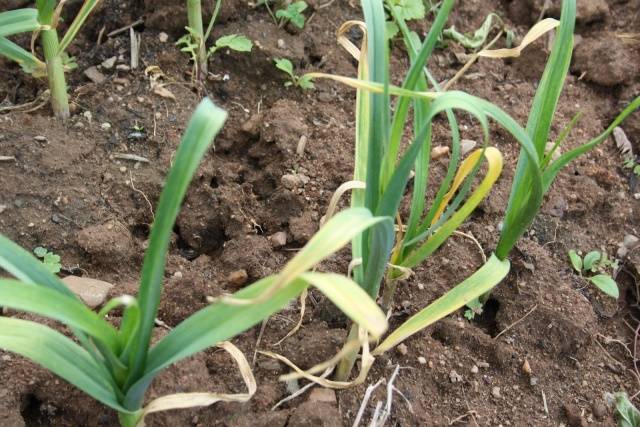
If there is not enough nitrogen in the soil, plant growth stops and bulb formation stops. Garlic ends its growing season ahead of time; the garlic heads turn out to be very small.
Externally, a lack of nitrogen can be noticed by a change in the color of the leaves - they lose color intensity and noticeably lag behind in growth.
Potassium
Affects the keeping quality of garlic.
A lack of potassium retards the growth of garlic, reducing resistance to drought and other unfavorable factors. Leaves with potassium deficiency lighten, starting from the veins, and gradually the spots spread to the entire leaf. The ends of the garlic dry out, and the entire leaf gradually begins to dry out.
Phosphorus
Promotes the formation of the bulb, the development of the root system, and improves the ability to resist adverse factors.
Lack of phosphorus causes the development of the root system to stop, and garlic stops growing. The deficiency can be noticed by dark green leaves, sometimes with a bronze tint, garlic roots are small and underdeveloped.
Magnesium
Promotes metabolic processes in garlic, growth and immunity. The lack of this microelement reduces the plant’s ability to winter and slows down the development and formation of teeth.
The deficiency is characterized by reddish leaves; the veins may remain green. Starts from the lower leaves.
Bor
Participates in all growth processes, promotes the formation of seeds.
Deficiency is expressed in chlorosis of young leaves, which are located closer to the middle of the plant. Later, the edges and tops of the leaves dry out.
Conclusion
The rules for growing garlic are simple; careful use of fertilizers and following the recommendations will help you grow a rich harvest of garlic, regardless of the vagaries of the weather.