Content
Winter garlic is a popular crop because it can be grown everywhere. The most popular varieties are those that are planted in winter. One of these is Komsomolets garlic. It is unpretentious in care, tolerates climate changes well and produces an excellent harvest. Reviews about Komsomolets winter garlic confirm that the variety is unique.
History of the appearance of the variety
The winter garlic variety Komsomolets was developed back in the 60s of the last century. The goal of the scientists was to create a species that would be suitable for cultivation in the lands of the Central Black Earth Region. Work was carried out on local varieties of garlic, and as a result of painstaking work, an unpretentious, cold-resistant plant was created.
Description of garlic
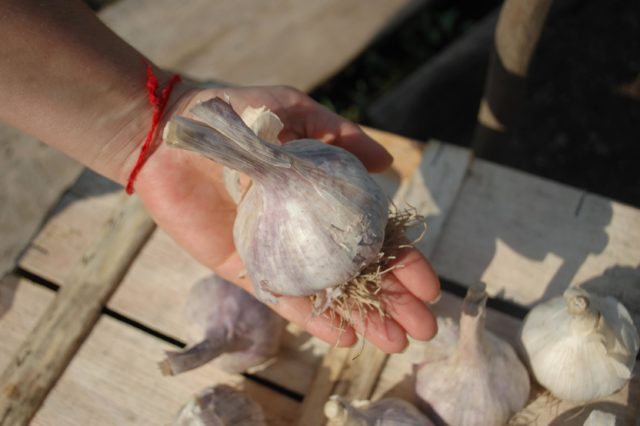
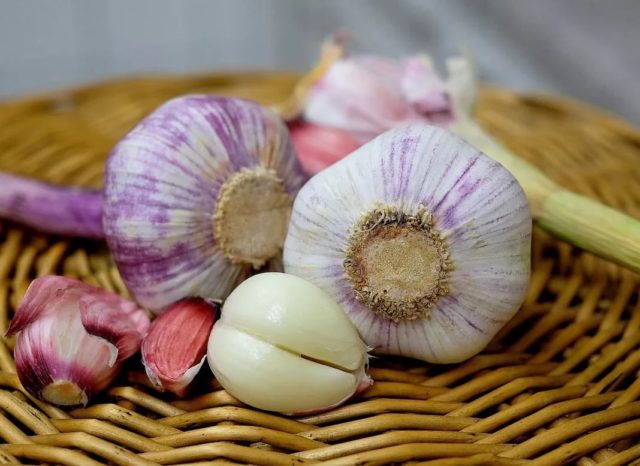
In the literature, this variety of winter garlic is described as the most productive. Its garlic heads have dense heads, each of them contains up to 10 teeth. They are all smooth and the same size. The weight of each bulb ranges from 35 to 110 g.The Komsomolets cloves taste sharp and hard. Each head is covered with uniform scales.
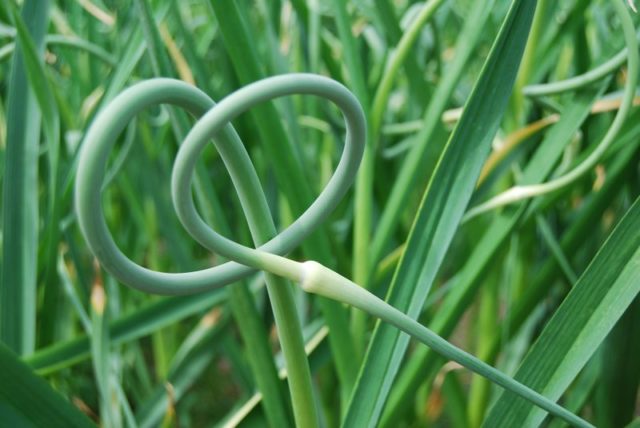
The stems of Komsomolets grow up to 45 cm in length and consist of several leaves coated with wax. Sometimes arrows may form on which small air bulbs ripen. Both garlic heads and feathers are used in cooking.
Characteristics of the variety
In order to get a high-quality and abundant harvest, you must follow some planting and care rules. Only then will Komsomolets delight with its high-quality and fragrant fruits.
Productivity
This variety is classified as mid-season, since the period of its active growth and reproduction is on average 115-120 days. In the south, Komsomolets ripens within 95-100 days.
There are approximately 1.3-1.4 kg of winter garlic per square meter. And this is an excellent indicator. In general, yield directly depends on the planting location and soil type.
Resistance to diseases and pests
This variety tolerates frost and various weather changes well. The plant is also resistant to many diseases and is resistant to the spread of bacterial rot.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Winter garlic Komsomolets has a lot of advantages that make it popular and in demand among gardeners and gardeners with different experience and level of knowledge.
Positive qualities of garlic:
- resistant even to sub-zero temperatures;
- he is not afraid of most diseases;
- You can get a large-scale harvest if you properly care for the plant.
If Komsomolets is planted in poor soil, the harvest will be small and the garlic crops will be very small.In this case, the result will not justify the funds invested in the plant.
Planting and caring for garlic
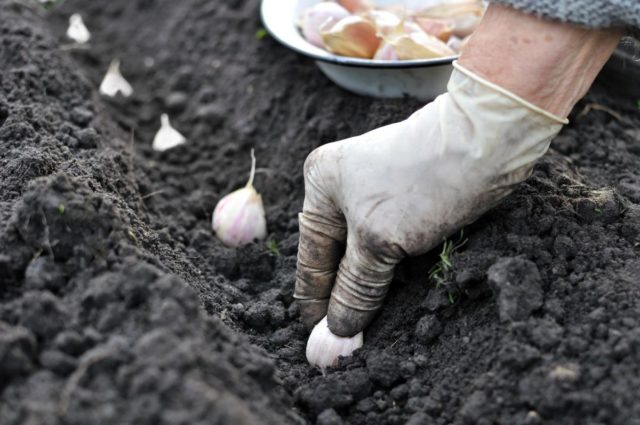
To get excellent fruits, you should listen to the advice of professionals regarding planting. Despite garlic’s good tolerance to cold, it should still be planted away from trees and bushes, in open areas. If you plant it in the shade, this will lead to a decrease in yield.
Time to plant garlic Komsomolets
The best time to plant winter garlic is mid-October. If the region has a cool climate, then you can plant the plant a little earlier.
Preparing the beds
Experts advise planting Komsomolets on those plots of land where cucumbers, beans, cabbage or zucchini grew last year. But it is better not to place winter garlic in a garden bed where potatoes, onions or tomatoes were previously planted.
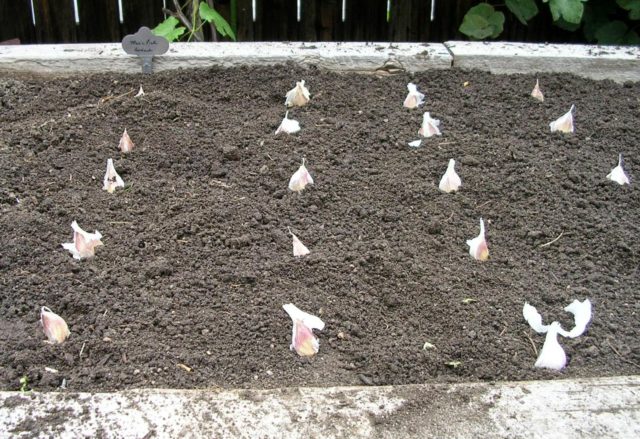
Only large teeth should be planted, without flaws. Before starting the procedure, each specimen must be kept in a solution of copper sulfate or potassium permanganate.
Winter garlic Komsomolets thrives in heavy and loamy soils. To get a large harvest, it is recommended to fertilize the soil before planting. Compost or humus is perfect as a top dressing. 1 kilogram of fertilizer is used per square meter of soil. In addition to organic preparations, mineral complex formulations should be used - they are useful for Komsomolets.
Planting garlic
Compliance with these rules guarantees abundant fruiting:
- Between the rows you need to leave gaps of 35-40 cm.
- Between plants in a row, the distance should be within 6-10 cm.
- The tines should be planted to a depth of 2-7 cm, depending on the size.
Growing Garlic
After planting, insulation measures and mulching with sawdust should be carried out. With the onset of spring, all material is removed, and the soil is abundantly watered with water at room temperature.
Watering should be stopped a month before harvest. If you ignore this condition, the fruits will not acquire their specific taste.
Those who have not mulched should regularly loosen the soil and also remove weeds. It is recommended to cut off the arrows if there is no need to collect seeds. They need to be broken off at the level of the upper leaves.
Fertilize the soil with winter garlic a couple of times throughout the season. Preparations are added to the soil along with watering. The best mineral composition for feeding garlic is Amofoska. Liquid Mullein will also work.
Harvest and storage
A little more than 100 days should pass from the moment the shoots emerge, and then winter garlic will fully ripen. Experts say that it is recommended to dig up fruits after 80-90 days. External signs of the plant can help determine the readiness of garlic.
You can harvest if:
- most of the feathers turned yellow;
- the base of the stem thinned and lay on the ground;
- the lower leaves have acquired a yellow tint;
- the seed pods are cracked;
- the scales covering the head became transparent.
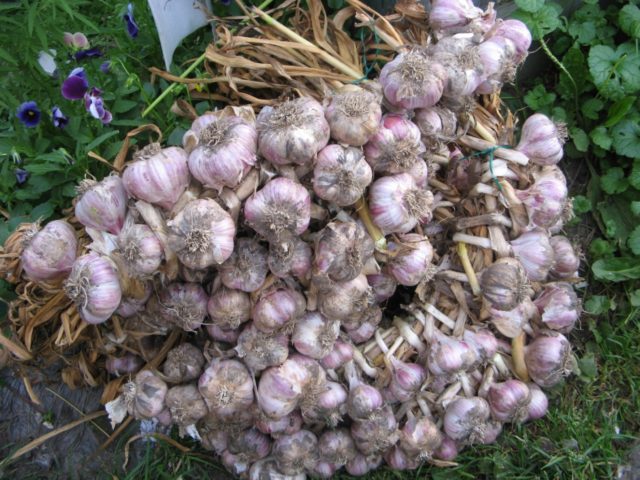
The best time to dig Komsolets is an early sunny morning. After harvesting, the heads should be spread on the ground to dry.Next, you need to bring it under a canopy or indoors and leave it there for several weeks. During this time, winter garlic will completely dry and be ready for use. Leaves and stems can be trimmed only when the shoots are completely dry.
After drying, the crop should be sorted. Heads that have blemishes or a wrinkled appearance should be set aside. If you do not notice them in time, you may lose some of the fruit. Good heads of winter garlic should be placed in a box or bag and stored in the cellar. Throughout the winter months, the crop must be ventilated so that it does not become damp and rot.
It is necessary to correctly determine the time of collection of Komsomolets, because this affects both the spiciness, taste and aroma of the cloves.
Methods for propagating garlic
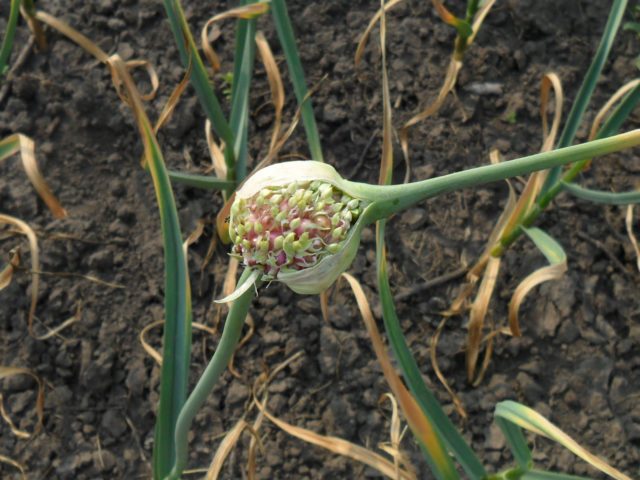
The Komsomolets variety is one of those plants that are thrown out by arrows. Therefore, it can be propagated in the following ways:
- cloves;
- seed bulbs.
Using the first method, there will be a guaranteed harvest next year. The second method is more difficult, and it will take several years before the plant produces good fruit.
Pests, methods of disease control and prevention
Damage to winter garlic can be caused by diseases that develop during the activity of fungi.
The following diseases of the Komsomolets variety are encountered:
- White rot. The causative agent is a fungus that affects the heads both after harvest and while they are in the soil. If you notice a sudden yellowing of the leaves, then this is the first sign of white rot.A light coating forms on the roots of the affected plants and on the head - this is how the fungus spreads. It can make the teeth watery and speed up the decay process.
- Green mold. The disease is typical for harvested winter garlic. Brown wet spots appear at the bottom of the head. Depressed yellow areas form on the teeth. To prevent the disease, you need to monitor the harvest, sort it regularly and throw away the affected fruits.
- Cervical rot. The disease affects winter garlic while it is still in the ground. Numerous factors can lead to this problem, for example, cold weather, excessive soil moisture, and a reaction to nitrogen fertilizer. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, the crop should be harvested in warm weather and dried well.
Conclusion
Winter garlic Komsomolets is an unpretentious plant; caring for it does not include any complex measures. For every gardener, grown Komsomolets is a guarantee of having a vitamin-rich vegetable in the house that improves immunity and can overcome various viral diseases.