Content
Tall trees have become popular as decoration and beautification of the yard. garden beds, as well as bulk flower beds. The simple device consists of a fence along the sides of a plot of land filled with bulk soil. High beds allow you to grow ornamental plants and garden crops. Fences are made from leftover building material. Now we will try to describe in more detail the process of making high beds and consider the variety of designs in photographs.
What is the demand and why high beds are not always convenient
First, it is advisable to find out what the pros and cons of high beds are in order to determine the usefulness of their construction in your yard:
- if the dacha plot is not destined for fertile soil, the fence allows you to use purchased soil;
- For each type of garden crops and ornamental plants, it is possible to arrange individual drainage;
- the sides do not allow creeping roots weed enter the territory of a fenced area with cultivated plants;
- it is more convenient to weed a high bed and it is easier to harvest;
- insulation and stretching of greenhouse film on top allows you to get an early harvest in cold regions;
- a fence body made of boards, plastic or metal allows you to get a mobile bed, which, if necessary, can be moved to any end of the yard;
- from purchased fencing you can organize a decorative flower garden near the house;
- the high efficiency of an insulated bed allows you to get a larger harvest than from the same plot of land in the garden;
- the soil inside the fence remains loose for a long time, which allows the root system to receive oxygen.
High beds may not always be beneficial, and sometimes they are simply inconvenient for the summer resident. Let's touch on their main disadvantages:
- the higher the embankment is from the ground, the faster its surface dries out, which increases the frequency of watering;
- the soil in limited conditions is quickly depleted and requires additional mineral fertilizing;
- due to the biological activity of unripe compost, crop seeds often do not sprout, so to be sure, it is advisable to plant seedlings on a high bed;
- For the mole cricket, a fenced area with humus is a favorite habitat, and in order to save the plants it is constantly necessary to fight the pest.
If the listed pros outweigh the cons, you need to take the tool and make high DIY beds, and our advice will help you in your work.
We determine the optimal dimensions of the beds and their fences
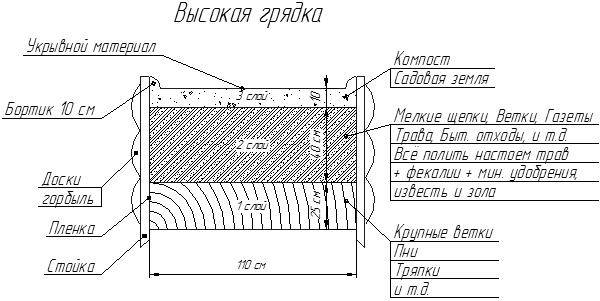
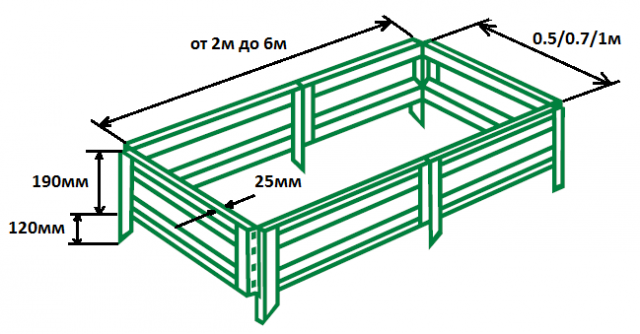
To figure out how to make a high garden bed at your dacha, you must first decide on its size.The height of the sides often depends on the quality of the soil at the dacha. If the yard is on fertile soil, 150 mm of elevation of the fence will be enough. When making a bulk bed with purchased soil, it is advisable to avoid its contact with poor soil land plot, and raise the height to 300 mm. For potatoes, the height of the fence will have to be made even higher.
The “warm bed” technology involves multi-layer backfilling of different components. In this case, it is necessary to build the sides of the fences at least 500 mm.
Length is the only value that does not require observance. The length of the embankment can be made as long as the yard, greenhouse or vegetable garden allows. The only problem can be the unstable long sides of the fences, which require additional reinforcement with stakes.
The width of the box is an important parameter. Ease of maintenance depends on it. The optimal width of a fenced embankment ranges from 0.9–1.2 m. Factory-made collapsible sides are most often from 0.5 to 1 m in width.
Material for the manufacture of fencing
Numerous do-it-yourself photos of raised garden beds at the dacha prove that the sides can be made from any leftover building material or bought ready-made in a store. When making fences yourself, they most often use:
- Wooden sides are a simple and environmentally friendly option. The disadvantage is the rapid rotting of the material. Fences are made not only from boards. Cuttings of timber, picket fence, and round timber are used. The branches are used to weave a fence.Antiseptics and bitumen mastics help extend the life of wood, but the environmental purity of the material is lost.
- Stones, bricks, cinder blocks and other similar materials allow you to make reliable high beds with your own hands, but they will cost the owner dearly. To fasten the elements you will need cement mortar. If the fence is made without a foundation, seasonal heaving of the soil will tear the masonry.
- Wavy or flat slate is convenient for making fences, but the asbestos contained in it gradually poisons the soil.
- Black sheet metal sides are short-lived. Stainless steel is expensive. Ready-made galvanized boxes with a polymer colored coating are sold on the market. They will last longer, but their cost is high.
- If you do bed design in the yard for flowers, it is better to give preference to plastic sides or border strips.
There are a lot of options for choosing materials for making bed fencing, but it is more comfortable for plants to be near the edge made from natural raw materials.
Making a high bed from boards
Now we will look at how to properly make fences for a high bed from boards. Since wood has a beneficial effect on plants, let’s focus on it:
- To make the box you will need boards. If you have a choice, it is better to give preference to oak or larch. Boards made from this type of tree are the most resistant to rotting.
- Wooden blanks are cut with a hacksaw to the required sizes. To make a box, the boards must be fastened together. There are two ways to go here. The first option is to dig wooden posts in the corners of the future high bed.The boards are nailed to the resulting supports or screwed with self-tapping screws. The second option is appropriate if there are no wooden posts. The boards at the corners are fastened with metal corners. For fixation, you can use self-tapping screws, but bolts are better. Through fastening will be more reliable.
- When all four corners of the structure are fastened, the box is considered ready. The presented photo of a high bed shows the production of one of the box options step by step.
The resulting wooden box is installed in a permanent place. The bottom is covered with plastic film. Next, there is a layer-by-layer backfill of sand, small branches with grass, humus and fertile soil.
Converting a raised bed into a greenhouse
Now let's look at the construction of high beds equipped as a greenhouse. The principle of making the box remains the same. The frame is knocked down from boards and installed in a permanent place. Further actions are aimed at making the greenhouse itself:
- Fastenings for the arcs are screwed to the long side sides of the box. Each pair should be strictly opposite each other. The distance between adjacent fastenings is approximately 750 mm.
- The bottom of the greenhouse is covered with film. If there is a metal mesh, it can be placed under polyethylene to prevent rodents from getting inside the high bed. A metal mesh placed at the bottom of the greenhouse will save the crop from the mole.
- Layers of sand, wood waste, humus and fertile soil are poured on top of the polyethylene. Each layer is slightly moistened to speed up the rotting process.
- To make arcs, steel wire or a plastic water pipe with a diameter of 20 mm is suitable. Pieces of pipes of equal length are bent in a semicircle and inserted into fastenings on the sides.From above, the arcs are fastened together with a crossbar made from a similar pipe.
- The finished skeleton is covered with transparent PET film. The edges are fixed on the wooden sides of the fence.
After planting the seedlings under the film, the surface of the soil is densely covered with sawdust. They will prevent rapid evaporation of moisture. Instead of sawdust, some gardeners use black film in which holes are cut for the plants.
The video shows the making of the bed:
Features of Mittlider raised beds
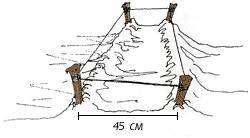
An American gardener developed his own design of high beds for strawberries. Their only difference is that the width does not exceed 45 cm. Any material can be used for the sides, including boards. The filler consists of a layer of sawdust and fertile soil. The vegetable grower allocated 90 cm of free space between the rows, and covered it with agrofibre to prevent weeds from growing.
Let's sum it up
Now you know how to make high beds and what material you will need for the work. As you can see, the work is not difficult, and is feasible for every vegetable grower.