Content
Mushroom sites in the Tula region can be found in all forests with deciduous trees. Honey mushrooms are classified as saprophytes, so they can only exist on wood. Forests with dead wood, old stumps and weak trees are ideal places for growth. The area, part of the Tula region, is famous for its mixed forests, where oak, aspen, birch, and ash are found - the wood on which honey mushrooms appear.
Types of edible honey mushrooms in Tula and the Tula region
The presence of forests and the characteristics of the regional climate fully meet the biological needs of the species. The spread of mixed forests with a variety of tree species in the area promotes the growth of fungi. Honey mushrooms in the Tula region do not differ in appearance from specimens distributed throughout the temperate climate.The main difference is in the method of growth and the time of formation of fruiting bodies.
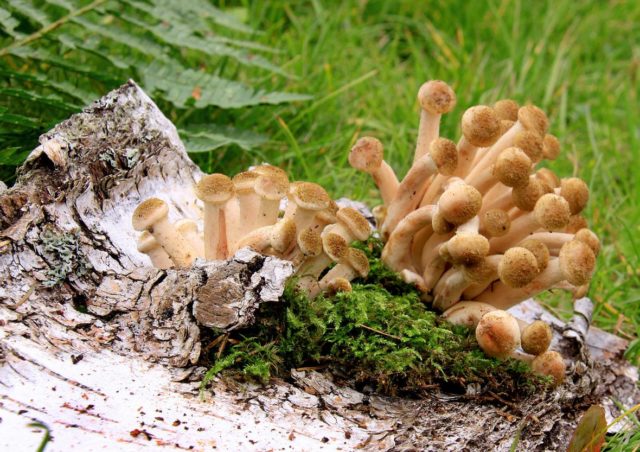
Collection begins with the appearance of spring specimens, which include wood-loving collibia. Its first colonies appear in April-May, after the spring rains, when a stable above-zero temperature sets in. Near oak or aspen trees, the harvest begins in mid-May.
The fruit body has a dark brown, hygrophanic cap and a long fibrous stalk. The mushroom is small in size and forms numerous families.
Then the season of summer mushrooms begins in the Tula region; Cyneromyces variablea is popular among mushroom pickers.
Grows on the remains of trees, prefers linden or birch. Fruiting is abundant, but short; the mushroom season in the region for summer representatives lasts no more than 3 weeks.
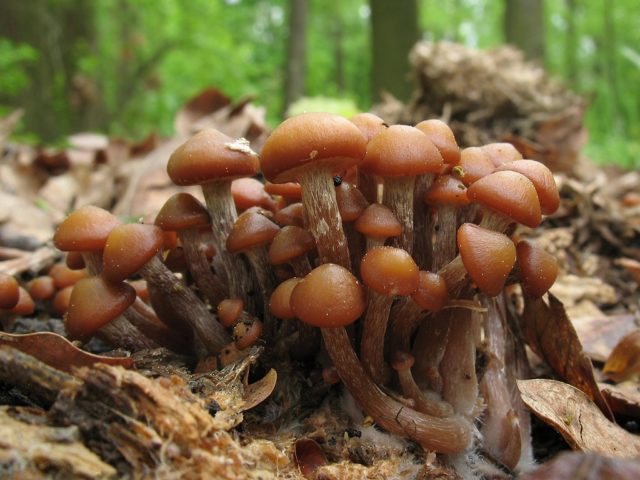
The duration of fruiting in real autumn honey mushrooms varies. The first families appear at the end of summer.
In Tula, honey mushrooms grow in waves, the initial period lasts within two weeks, followed by the next one, with the same duration, the last harvest is harvested with the onset of cold weather. They grow on the remains of any type of wood, except coniferous. They settle on trunks near the root system of old and weak trees.
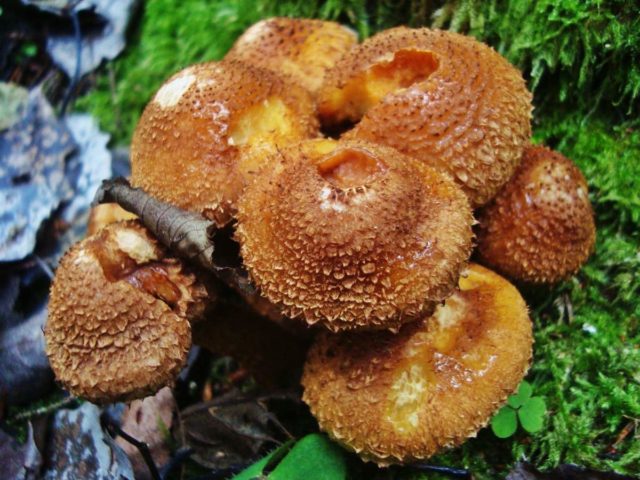
The thick-legged honey mushroom is also classified as an autumn variety; you can collect these honey mushrooms in Tula from the end of summer. Their accumulation is observed near pines or spruces. They grow on woody debris covered with pine needles.
This is a dark brown mushroom with a thick short stem and a scaly cap.
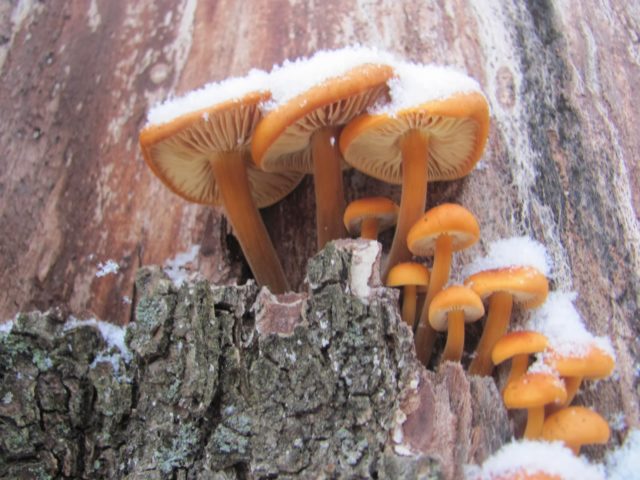
No less popular is the winter species - Flammulina velvetypodia.
It parasitizes damaged trees (willow or poplar) that grow near water bodies. Found on rotting wood in park areas. A variety with a pronounced taste and smell.The surface of the cap is covered with a mucous film, the color of the fruiting body is dark orange. In the Tula region, this is the only mushroom that is collected in winter.
The meadow species or talker is no less in demand than forest representatives.
It grows in rows or semicircles in forest clearings, among low-growing bushes, and in pastures. Fruiting begins in spring and continues until autumn; mushrooms appear after heavy rains.
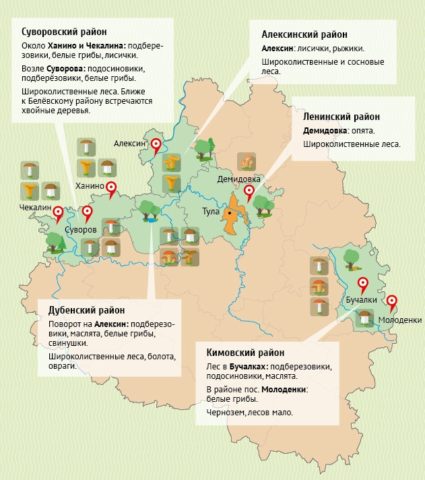
Where honey mushrooms grow in the Tula region
The main accumulation of honey mushrooms is noted in the northern and northwestern direction of the region. There are forests with linden, birch, aspen, and oak here. To the south, on the border with the steppe regions, there are mixed forests with a predominance of ash and oak. These places are ideal for mushrooms.
Where in Tula you can collect honey mushrooms
Honey mushrooms in the Tula region can be collected in any area where mixed forests are located. The territory (except for the suburbs) is ecologically clean, with fertile soil, so mushroom picking is unlimited. Places popular with mushroom pickers where all types grow:
- Teplo-Ogarevsky district near the village of Volchya Dubrava. From Tula there are shuttle buses “Tula-Efremov”.
- Venevsky district, Zasechny village. From there it is 4 km to Karnitskie Zasek, famous places throughout the region where all types of mushrooms grow. You can get there from Tula by private transport in 2 hours.
- The famous pine forest near the city of Aleksino, can be reached by rail.
- The forests of the Suvorovsky, Belevsky and Chernsky districts are considered environmentally friendly.
- Kimovsky district in the forest near the village of Bugalki.
- The mixed forests of the Yasnogorsk region are famous for their winter views.
- In the Dubensky district, large harvests of meadow mushrooms are harvested in ravines and wetlands.
Forest areas where there are honey mushrooms in the Tula region and Tula
A good harvest of honey mushrooms is being collected in the Tula region in the protected forests “Tula Zaseki” and “Yasnaya Polyana”. The Tula forestry is also famous for places where species grow en masse. Forests for “silent hunting” are located in the Prioksky, Zasechny, Odoevsky districts. Forests - Central forest-steppe, South-Eastern, Northern.
Where do autumn honey mushrooms grow in the Tula region and Tula?
If autumn honey mushrooms appear en masse in Tula, they are sent to the following areas:
- Dubensky, where oaks and birches grow;
- Suvorovsky, to the settlements of Khanino, Suvorovo, Chekalino;
- Leninsky, to Demidovka in deciduous forests;
- Shchelkinsky is a massif near the village of Spitsino.
And also in the village of Ozerny, Tula Urban District.
When will honey mushrooms begin in the Tula region in 2024?
In 2024, in the Tula region, honey mushrooms can be collected throughout the year, because each species grows at a certain time. Because the winter was snowy and the soil received enough moisture, and spring was early and warm, so harvesting begins in May. Favorable weather with precipitation promotes the appearance and abundant growth of summer mushrooms. Judging by the forecasts, the year will bring a good harvest of autumn species.
Spring
Spring honey fungus is not as popular as autumn or summer species. Novice mushroom pickers mistake wood-loving collibia for false doubles, unsuitable for consumption. They are inferior in taste to ordinary honey mushrooms, but are suitable for any processing. The first specimens in the Tula region appear during the period when the temperature does not drop below -7 0C (at the end of April). They grow in groups on moss or leaf litter and prefer to be located near oak trees.
Summer
Summer mushrooms in the region begin to grow in the second half of June. In years with variable yields for Cyneromyces, more than three buckets can be collected from a small plot.They grow in large families on aspen and birch remains. The harvest lasts until September.
Autumn honey mushroom season in the Tula region
In 2024, the collection of autumn honey mushrooms in the Tula region is planned to begin in mid-August. At the first drop in temperature, harvesting will begin in all directions of the region where forests are located. The harvest promises to be bountiful. Last season there were few mushrooms. If we take into account that the level of fruiting is characterized by decline and rise, then 2024 will please mushroom pickers. You can find out that autumn honey mushrooms have begun in Tula by the warm rains that have begun.
Timing for collecting winter mushrooms
Velvety-footed flammulina grows when the autumn mushroom picking season is over. In the Tula region, the first specimens are found in November on tree trunks, bearing fruit abundantly until the temperature drops to -10 0C. Then they stop growing and resume the formation of fruiting bodies during a thaw, approximately in February.
Collection rules
Experienced mushroom pickers do not recommend going into the forest in unfamiliar areas alone.
Mushrooms are not collected near Tula, because there are many plants and factories in the city that affect the environment.
How to find out if honey mushrooms have started growing in the Tula region in 2024
Honey mushrooms begin to grow actively only with high soil moisture and temperature conditions:
- in spring not lower than +12 0C;
- in summer +23 0C;
- in autumn +15 0C.
In dry summers there is no need to expect a high harvest.Spring and summer honey mushrooms grow after rains at constant air temperatures. The fact that autumn honey mushrooms have spread en masse in the Tula region is determined from the precipitation map for 2024. After the rains, fruiting bodies are formed in 3 days. Mass collection occurs on warm days, when there is no sharp drop in temperature at night.
Conclusion
Mushroom sites in the Tula region are located in all directions where mixed and deciduous forests grow. In 2024, honey mushrooms can be collected in the Tula region from April until late autumn; even the first snow is not an obstacle to quiet hunting. The harvest is found on stumps, fallen trees, and in the area of clearings on the remains of cut down trees. Each species has a specific fruiting time; in total, the season lasts the entire year.