Content
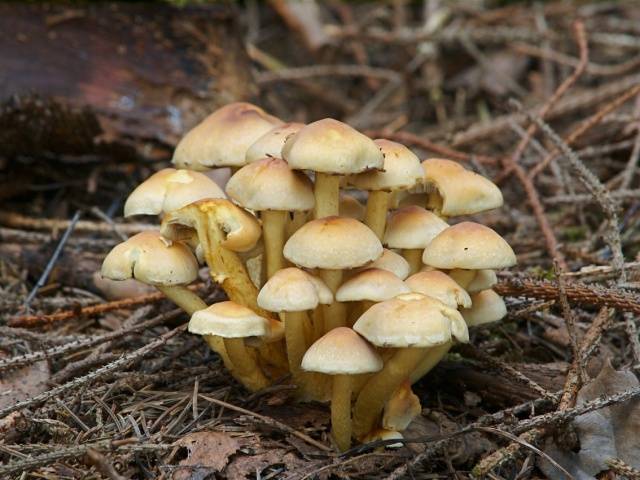
Edible meadow mushrooms are easily recognized by their small cap with a diameter of up to 6 cm. In young mushrooms it is slightly convex, but over time it becomes smooth with a small tubercle in the center. The cap of the edible meadow grass is also recognized by its light brown color and sticky surface when it gets wet. A characteristic feature is a short cylindrical stem with a small ring near the cap. All other similar mushrooms that do not fit the description are false mushrooms.
Where do honey mushrooms grow?
Photo: what edible meadow mushrooms growing in a clearing look like
The peculiarity of this type of mushroom is that they do not grow on a stump, but have chosen the soil for their place of residence. The habitat and reproduction of meadow mushrooms occurs in clearings. They can be found among thick grass in the forest, between groups of trees, in pastures, meadows, and along garden paths. Meadows do not grow alone. They usually form families by crawling out in rows among the thick grass. Sometimes in a clearing there is a ring with a diameter of about 80 cm. People call this phenomenon witches’ circles.
When to collect meadow mushrooms
Photo: meadow honey mushrooms in a clearing
Meadow mushrooms grow in damp, warm weather. Experienced lovers of quiet hunting intuitively determine the collection time. If spring was accompanied by warm rains, in early June you can wander through the meadows. Under suitable weather conditions, meadows can emerge from the ground all summer and autumn before frost begins. In order not to miss out on the harvest, a novice mushroom picker should know that these mushrooms sprout en masse and quickly die off.
The video talks about meadows:
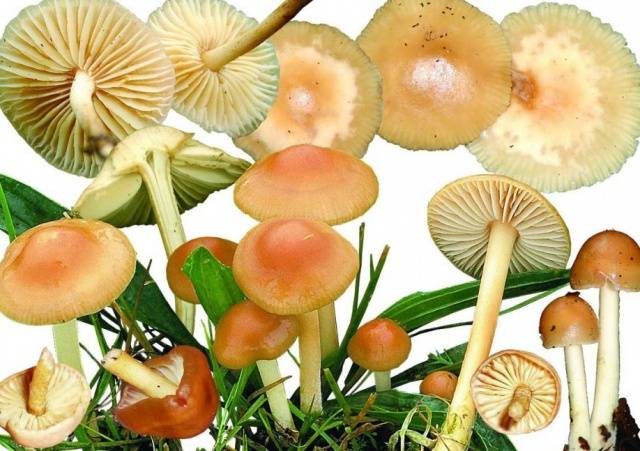
How to distinguish edible meadow mushroom from inedible one
Explanatory photo: how to distinguish meadow mushrooms from false ones
Edible meadow mushroom is recognized by the following characteristics:
- Leg. The edible meadow grass has a ring in the upper part under the cap. The height of the stem is about 6 cm. An exception may be an old large mushroom. The false mushroom has a leg without a ring or has a thin growth. They always grow elongated. The length of the leg varies from 10 cm or more.
- Records. If you look under the cap, the edible mushroom's lamellar tissues are dull yellow, sometimes cream-colored. In false young meadow grass they are bright yellow.As the cap begins to age, the color of the lamellar tissues changes from green to black.
- Hat. Regardless of where it grows, the weather or the environment, the top of the edible meadow grass cap is dull brown with dark scales. The cap of the false honey fungus is always full of bright flowers with a predominant red tint, and there are no scales.Important! Without scales there can be an edible meadow grass. They disappear when the mushroom ages. This specimen can be recognized by its dark brown cap.
- Taste qualities. It is believed that all inedible mushrooms are bitter. It's a delusion. There are many poisonous mushrooms with normal taste. It is impossible to identify edible specimens based on such signs.
- Smell. If you pick an edible meadow grass, it immediately emits a pleasant mushroom aroma. False honey mushrooms smell like rotten soil or mold.
- Contact with water. Edible meadow grass does not change color when soaked in water. False honey mushrooms turn black or acquire a dark blue color.
Despite the large number of signs, it is difficult for a beginner to recognize which category the honey mushroom belongs to. Before use, it is better to ask an experienced mushroom picker for advice.
False meadow mushrooms
Now it’s time to take a closer look at the photo and description of false meadow mushrooms. This is necessary to learn how to better recognize them on the lawn and avoid them.
All inedible meadows have the following characteristics:
- a long elongated leg without a ring at the cap;
- earthy smell;
- bright color of the cap with a predominant red tint;
- the plates are dark, sometimes black;
- Poisonous mushrooms grow for a short time in spring and autumn, and in summer they are not found.
Some false meadow mushrooms have a good taste, but it is not worth trying to recognize them.
Dangerous twins of meadow mushrooms
Looking at photos of meadow mushrooms, it is not always possible to determine in reality which category the mushroom belongs to. This is due to the presence of doubles.
Poisonous talker whitish
Externally, the mushroom is so beautiful that you want to put it in a basket. However, it is very poisonous. The talker is distinguished by its curved saucer-shaped cap and bright white color. The leg is short, the length does not exceed 4 cm. The whitish talker has two additional subspecies: waxy and grayish. The dangerous mushroom grows in the same places where the meadow grass lives.
Wood-loving collibia
This mushroom cannot be put in a basket if you know its habitat. They go to open meadows for edible meadows. Collibia loves to grow in mixed forests. The fungus takes nutrients from rotten wood and rotting leaves. Collibium is not found in open clearings. The doppelgänger can be recognized by its light-colored leg about 6 cm long, a brown hat with a white tint, and a sharp, unpleasant odor.
How to cook meadow mushrooms
It doesn’t matter what recipe you are going to use to prepare honey mushrooms, they are first cleaned. The harvested crop after the rain is very dirty. The sticky cap sticks to dirt, grass, and midges. If the meadows are collected in dry weather, there will be fewer problems with cleaning.
First, the crop is sorted. Throw away all wormy and suspicious mushrooms. Further cleaning depends on what you intend to do:
- If the meadows are going to dry, they cannot be soaked in water. Each mushroom is thoroughly wiped with a dry or slightly damp cloth, placed on a baking sheet, and placed in the oven. You can dry them naturally under the sun by stringing them on a thread.Important! If you soak mushrooms in water before drying, the heat treatment time will increase. In the oven, the watery pulp can cook, and when dried naturally, it can rot.
- When it is intended to cook or preserve meadow mushrooms immediately after assembly, they are thoroughly washed. Change the water at least 3 times. You can even soak the meadow grasses for several hours to better wash the sand out of the plates. During wet cleaning, the rings on the stem are removed. They give a sour taste and distort the aroma.
When all the mushrooms are thoroughly cleaned, you can start cooking.
There are different recipes for preparing meadow mushrooms, ranging from simple frying to masterpieces of culinary art. Foresters and experienced mushroom pickers claim that meadow mushrooms can be eaten even raw. Theoretically, yes, but the dirty ecology now does not allow this. To be safe, it is better to boil the mushrooms.
Short-term heat treatment completely cleanses mushroom tissue from harmful accumulations from the polluted natural environment.
The simplest preparation consists of the following steps:
- meadows are cleaned;
- large specimens are cut into several parts;
- mushrooms in a saucepan are filled with water and placed on high heat;
- after boiling, reduce the heat and continue cooking for another 15 minutes;
- The cooked mushrooms are drained, poured with clean water and boiled again for 15 minutes.
After the second cooking time has passed, the meadows are drained. Now honey mushrooms are considered practically ready for consumption, but in this form they are not tasty. Mushrooms are used for further cooking, depending on the recipe.
The benefits of meadow mushrooms
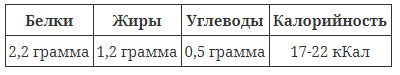
Mushrooms are a source of proteins, vegetable fats and carbohydrates, but they are low in calories. 100 g of pulp contains a maximum of 22 kcal. Additionally, there are fungal antibiotics, copper and other beneficial substances. Scientists have not yet fully explored all the benefits of mushrooms. However, traditional medicine uses them to strengthen the body, treat tumors, lower blood pressure, and as a laxative. Honey mushrooms are good for the heart, stomach and other organs, but you need to eat them in moderation.
Any mushroom is considered difficult for the digestive system. If there are serious problems with the gastrointestinal tract, then it is better to refuse to eat delicious gifts of nature. The intake should be limited to the elderly and children under 7 years of age. In all other cases, there are no contraindications for eating meadow grass.
A few secrets on how to avoid poisoning
Modern ecology is so polluted that you can even get poisoned by edible mushrooms. Often, trouble occurs as a result of mistakes made by the person himself when collecting or preparing honey mushrooms. To avoid poisoning, experienced mushroom pickers advise adhering to the following rules:
- If you didn’t pick the mushrooms yourself, but bought them at the market, sort them carefully. Between honey mushrooms there may be poisonous doubles or their pieces. All broken and suspicious meadow grasses should be thrown away.
- Many meadow grasses grow along roads and near factories. You cannot collect them. The porous tissue of the mushroom absorbs all harmful substances.
- It is unacceptable to violate the honey mushroom processing technology. Mushrooms should not be cooked in aluminum or zinc-coated pans. If you are not sure about the ecological cleanliness of the area where the crop was harvested, it is better to soak the meadows for three days. It is advisable to change the water every three hours.
In case of mushroom poisoning, first aid is aimed at inducing vomiting. Before this, the patient is given plenty of fluids. Call a doctor immediately, otherwise the consequences may be serious for the victim.
Conclusion
Meadow honey mushrooms are a tasty and healthy mushroom. However, it is more difficult to recognize than the traditional honey mushroom growing on a stump. If you are unsure of your knowledge, it is better not to collect unfamiliar mushrooms.