Content
Subinvolution of the uterus in cows is a common phenomenon that is diagnosed in cattle soon after calving. Violation of the development of the uterus, with proper treatment, does not cause serious consequences and does not lead to death, but the economic damage due to the loss of offspring can be quite significant. The causes of uterine subinvolution are most often its overextension during multiple pregnancies or large fetuses, however, the conditions of keeping animals are also of no small importance in the development of the pathology.
What is uterine subinvolution in cows?
Involution of the uterus in cows is a slowdown in the processes of restoration of the organ to the state in which it was before the onset of pregnancy. Subinvolution of the uterus manifests itself in the following:
- its contractile functions are significantly weakened;
- the contraction of muscle fibers slows down;
- atrophic (degenerative) processes begin;
- there is a suspension in the regeneration of the mucous membrane and blood vessels in the uterine area;
- recovery of the ligamentous apparatus slows down.
All this leads to the fact that during subinvolution, a large amount of lochia begins to accumulate in the uterine cavity - physiological postpartum discharge, which mainly consists of blood and mucus. As a result, the walls of the uterus are stretched, which interferes with its contractile processes. If at the same time harmful microorganisms penetrate the lochia, the process of their active decomposition and rotting begins - the decay products of the lochia and toxins are absorbed into the blood and provoke severe intoxication of the animal’s body.
The danger to the health of cows is not so much the subinvolution of the uterus itself, but its consequences. Very often, if treatment is started, the disease leads to the development of acute and chronic endometritis in sick individuals, which can cause infertility. In addition, subinvolution of the uterus in cows in severe cases provokes functional disorders of the ovaries.
Etiology of uterine subinvolution in cows
The medical history of subinvolution of the uterus in a cow includes the following possible factors contributing to the development of the pathology:
- lack of regular walking, lack of movement (especially closer to calving);
- poor feeding;
- excessive consumption of succulent feed (silage, stillage, pulp);
- lack of vitamins;
- sufficient, but extremely monotonous diet;
- mechanical overstretching of the uterine cavity due to a large fetus or multiple fetuses;
- hydrocele of the embryo and membranes;
- delayed release of placenta;
- difficult birth and lack of timely assistance at calving;
- general weakness of the animal after a long illness.
It is also believed that the development of subinvolution of the uterus in cows occurs during mastitis, which disrupts the connection between the contractile functions of the uterine cavity and the mammary glands. In addition, pathology can manifest itself if, after giving birth, the cow is not allowed to lick the calf - this process usually triggers the awakening of the maternal instinct in animals.
Signs and diagnosis of uterine subinvolution
The first symptoms of uterine subinvolution include the following changes in the physiology and behavior of animals:
- the cow behaves sluggishly, apathetically;
- appetite noticeably decreases;
- weight loss occurs;
- milk production drops significantly;
- absence of discharge from the birth canal within a week of birth, after which watery brown lochia is released in large quantities;
- the cervical canal remains slightly open (1-2 fingers can freely pass into it).
Subinvolution of the uterus in cows is diagnosed through vaginal and rectal examination. Signs of pathology are severe swelling of the mucous membranes of the vagina and hyperemia of the birth canal. Even two weeks after birth, the uterine cavity is noticeably increased in size compared to its state before pregnancy and is located at the bottom of the abdominal cavity. With physical contact through the rectum, uterine laxity is clearly felt, and there is no contraction reaction to massage. Sometimes you can feel the caruncles through the wall of the uterine cavity.
Treatment of uterine atony in cows
There is no point in delaying the treatment of uterine subinvolution in cows - delay can lead to the pathology becoming chronic.Animals are treated comprehensively, using both stimulating and symptomatic agents:
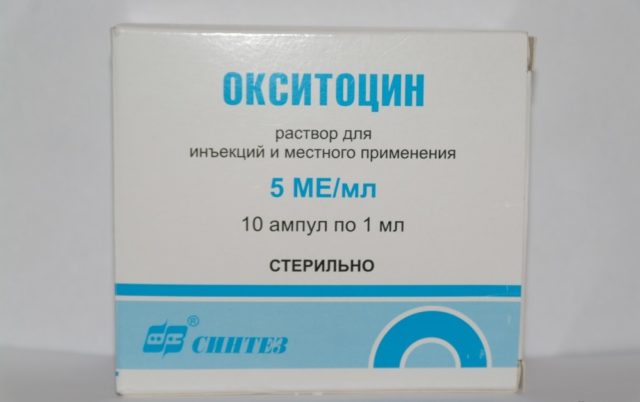
- Sick cows are administered intravenously or intraaortically with Oxytocin or Nitutrin (10 units for every 100 kg of weight at intervals of 3-4 days).
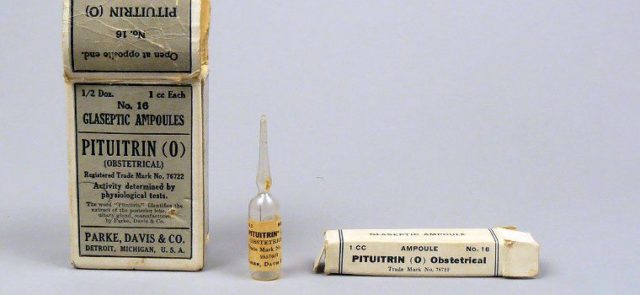
- Pituitrin is administered subcutaneously (4-6 units per 100 kg of weight).
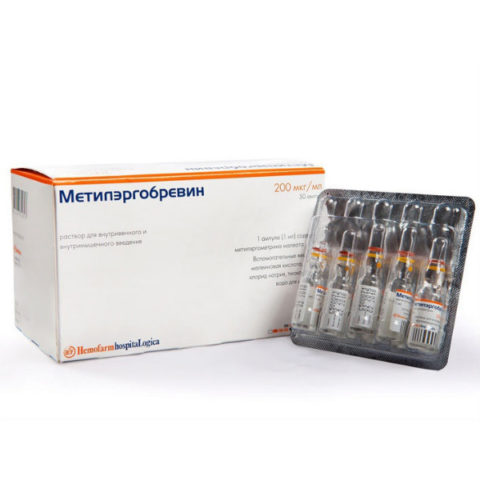
- The Methylergobrevin solution (0.1-0.2 mg) has proven itself well in the treatment of uterine atony.
- Positive results are observed after injections of "Mammophysin" (13-15 units for every 100 kg of weight).
- In case of severe intoxication, cows are injected intravenously with a 40% glucose solution (250-500 ml). The substance additionally helps restore the tone of the uterine cavity.
- Once a day for three days you can inject Kamagsol-G (200 ml). If necessary, this period is increased.
- A 1% solution of “Ichthyol” is injected three times into a vein. It must first be diluted according to the instructions.
- A tissue preparation (extract from the liver and spleen is suitable) is administered subcutaneously (30-40 ml). Usually a single application is sufficient, however, it is permissible to repeat the injection after a week if the first one did not give the desired result.
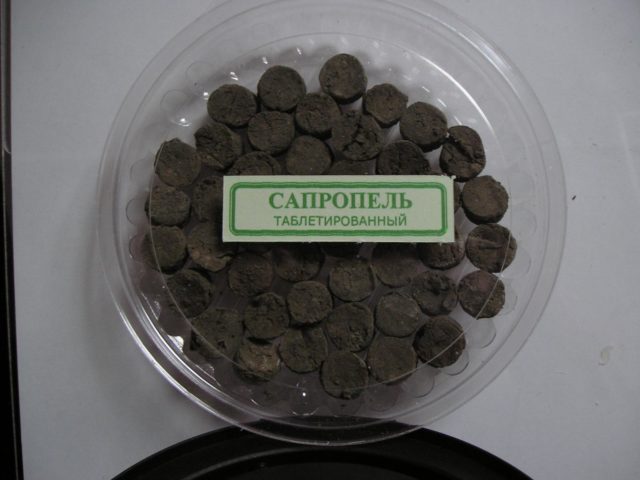
- In the second week after birth, heated “Sapropel” is used intravaginally, which should activate the contractile functions of the uterus in the cow and speed up the process of excretion of lochia.
It is worth noting that atony of the uterine cavity in cows greatly reduces the sensitivity of muscles to drugs such as Pituitrin, Mammophysin and Oxytocin. In order to enhance their effect on the body of a sick animal, it is necessary to carry out a single subcutaneous injection of a 2% Sinestrol solution in a dosage of 2-3 ml a day before administering the drug.
If a large amount of secretions accumulates in the uterine cavity, and the use of medications does not cause noticeable improvements, it is necessary to clean its contents mechanically. To do this, lochia is pumped out using a special vacuum pump.
It is especially important to pay attention to the nature of the bleeding. If they have a distinct smell of decomposition, this means that the process of intoxication has begun. In this case, it is necessary to additionally rinse the cow’s uterus with a disinfectant solution. A solution of 3-5% sodium chloride or 2-3% bicarbonate of soda is suitable as such means. After such treatment, the uterine cavity must be washed with clean water.
Disease prognosis
Subinvolution of the uterus is a fairly common phenomenon and, in general, does not cause the development of serious pathologies in a sick animal. Septic intoxication occurs in exceptional cases. With timely treatment, the prognosis is positive - cows recover quite quickly from the disease and will not experience problems with calving in the future.
On the other hand, if the disease is neglected, various complications can arise. Most often, cows develop endometritis after subinvolution of the uterus, which, in turn, leads to infertility.
Prevention of uterine subinvolution in cows
Prevention of the disease involves a set of the following measures:
- regular walking;
- a varied, nutritious diet using vitamin supplements;
- timely assistance during difficult childbirth;
- intra-aortic injection of 1% novocaine solution;
- injections of vitamins A, B, D, E in the cold season, when animals are in stalls;
- drinking colostrum after childbirth;
- dispensing warm salted water;
- postpartum massage of the uterine cavity through the rectum;
- subcutaneous administration of “Oxytocin” or “Pituitrin” (30-40 units);
- intravenous injections of 20% glucose solution (200 ml).
Separately, it is worth noting subcutaneous injections of colostrum to sick animals - this is a very effective method of preventing uterine subinvolution in cattle. Colostrum is taken from the cow shortly after calving and 30 ml of the substance is administered daily over the next few days. The effect of colostrum on the tone of the reproductive organs is based on the rich content of estrogenic compounds that activate the motor function of the uterus.
Conclusion
Subinvolution of the uterus in cows is caused by stretching of the organ after pregnancy, however, its insufficient tone is affected, first of all, by a monotonous diet, excessive feeding of succulent feed and lack of exercise. Thus, following simple preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing the disease in animals. Additionally, cows can be given a variety of stimulant medications for several weeks after calving to help them recover faster.
If you do not pay due attention to the treatment of sick animals, they will experience a decrease in their productive life. In other words, such cows have to be culled, which causes significant economic damage to the farm.
You can learn more about how to treat postpartum inflammation in the uterine cavity in cattle from the video below: