climbing roses can decorate any park, summer cottage, garden. Most often, such flowers are grown in regions where the climate is mild and warm. But in recent years, rose bushes are being grown more and more often in the Moscow region, and even flower growers in Siberia are not lagging behind.
The value of roses with flexible shoots that grow up to three meters is widely used in vertical gardening. Landscape designers decorate arches, gazebos, and walls of houses with them. There are many varieties of roses; flower growers are faced with the question of how to propagate climbing rose. We will try to talk about possible ways.
A few words about climbing roses
Kinds
Among the large number of varietal diversity of rose climbing bushes, two types are distinguished:
- Multi-flowered roses stand out by blooming up to 20 buds at a time. They are small in size, approximately 2.5 cm, and there is practically no smell.
- Large-flowered roses are similar to hybrid tea varieties. They bloom for a long time, opening new buds one after another. Inflorescence with ten buds. These flowers have an intoxicatingly fragrant aroma.
The most popular varieties
- Climbing variety "Dortmund" can be planted everywhere. Flowering throughout the warm season;
- "Climber" attracts with its high resistance to diseases and its vitality. The shoots can reach four meters, which is convenient for creating any flower arrangement.
- "Rambler" has a long flowering period and has large double flowers. The shoots are tall and powerful. This climbing variety is suitable for creating bright hedges.
- Height "New Down" up to two meters. The shoots are slightly curved, so it is convenient to hang them on supports. Flowering is abundant.
- Variety "Cordesa" - a newcomer among its climbing relatives. Flowering is vigorous and long lasting.
Reproduction methods
Many novice gardeners are interested in propagating climbing roses with their own hands. Professionals know how to propagate rose bushes, which include climbing varieties, in different ways:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- budding;
- seeds.
Each method of propagation has its own characteristics and difficulties, which are not always amenable to those who are just starting to breed these amazing plants. The simplest, giving a higher percentage of survival, is the propagation of climbing roses by cuttings, root suckers and layering.
Cuttings
Cuttings of climbing varieties are a fairly common method; they can be propagated in the following ways:
- Rooting in soil, water;
- Rooting in a bag, potatoes.
Preparing the cuttings
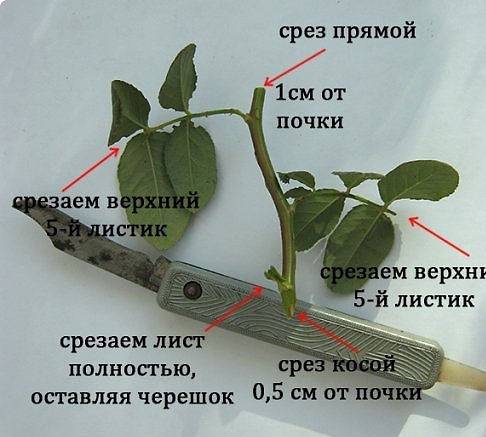
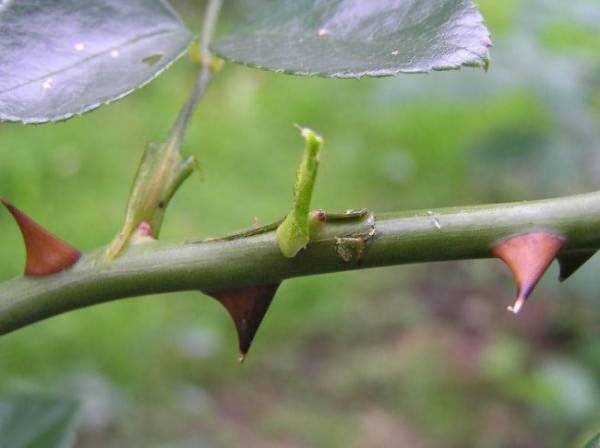
To propagate a climbing rose by cuttings, the planting material is cut before the shoot blooms. This is usually done in the spring. At this time, the cutting will take root faster. The middle part is separated from the shoot, on which there should be three living buds.The bottom is cut at an angle of 45 degrees, and the top is cut at 90 degrees. The leaf on top is shortened by more than half. Everything is clearly shown in the photo.
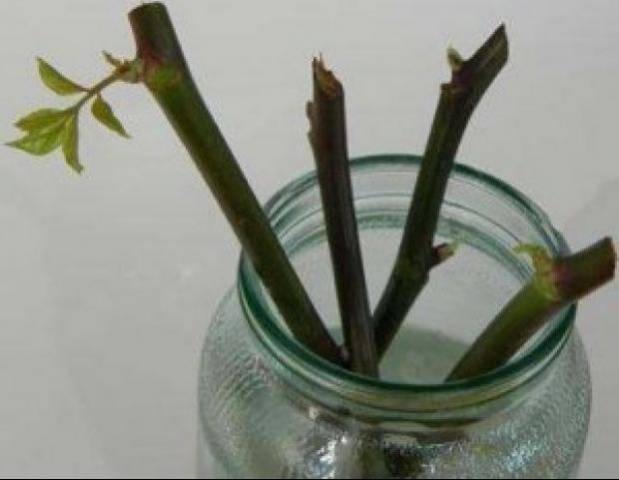
Rooting in water
To obtain a healthy climbing rose, the cuttings must be placed in boiled water. The cutting requires a shaded place, so the sun can burn the planting material. The water is changed every other day.
As a rule, the root system will form in about a month. The cuttings can be planted in a permanent place.
Rooting in the ground
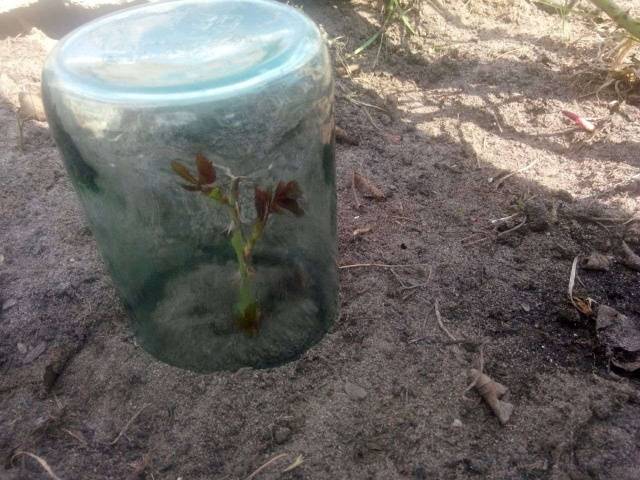
Climbing roses can be propagated by rooting cuttings directly into the soil. To prevent rotting, coarse sand is added under the planting material. It must be scalded with boiling water to kill harmful microorganisms. After abundant watering from above, the planting is covered with a glass jar. The jar can be painted with white water-based emulsion or covered with white cloth.
The container is placed on a well-lit window, but not in the sun. Cuttings root well at temperatures from + 23 to + 25 degrees. The “greenhouse” is raised from time to time for ventilation.
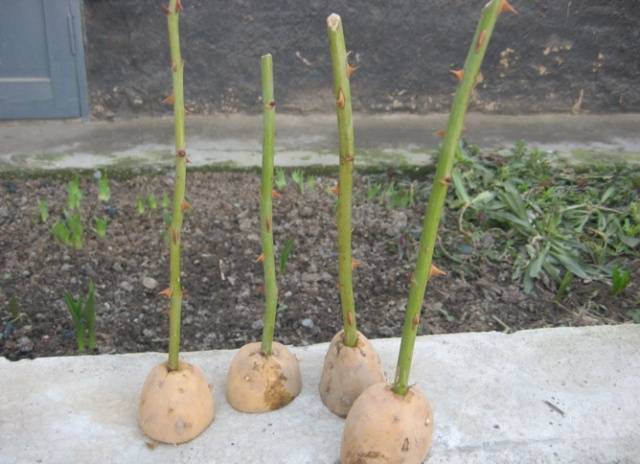
Roses in potatoes?
There is nothing surprising about the propagation of climbing roses in young potatoes. This is a long-tested and reliable method that any beginner can handle.
What does a potato give to a cutting during propagation:
- maintaining a constant moist environment;
- The future rose feeds on the carbohydrates and starch contained in the root crop.
Before propagating roses by cuttings planted in potatoes, dig a trench at least 15 cm deep.The bottom is covered with sand with a layer of 5 centimeters. The cutting should be up to 20 cm. Thorns and leaves are removed from it. The eyes are cut out of the potato to deprive it of vegetation, and the cuttings are inserted with the sharp end. The living “container” is laid out at a distance of 15 cm.
The planting needs to be protected from wind and sun at first, so when propagating climbing roses, shelter is required. They can serve as an ordinary glass jar or a piece of tin.
You can open the rose bed slightly after 14 days to acclimate the plants to the climate. After another 14 days the rose opens completely.
In a plastic bag
To obtain a new rose bush, cuttings are first moistened with aloe juice, planted in a pot, and spilled with warm water. After this, they put it in a large bag, tie it and hang it in front of the window. The bag creates high humidity and fog. As a rule, rooting occurs after 30 days. All that remains is to plant the planting material in the ground. Cuttings take root best in the spring.
About propagation of climbing roses by cuttings:
Other methods of reproduction
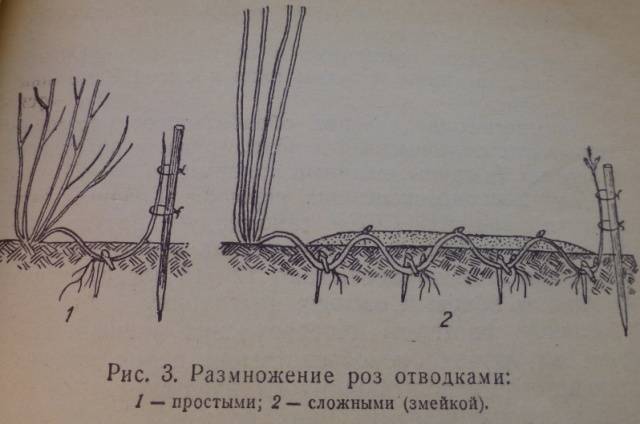
By layering
In the spring, when the lashes have already come to life, you can take one of them to the side, place it in a prepared furrow and dig in with fertile soil. To keep the whip firmly and not “jump” up, the shoot is pinned. The top of the shoot is removed and tied to a peg.
From one rose bush you can get many new plants if, during propagation, the shoot of a climbing rose is pinned several times, leaving one bud on the surface.How to do the job correctly is shown in the photo.
Care is carried out in the usual way, the main thing is not to overdry the soil under the plant. A viable root system will develop during the warm season. The cuttings are separated from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.
Already in the first year, by the end of summer, buds may appear on the rose bush. They need to be torn off so that the climbing rose obtained from layering does not waste energy on flowering.
Root suckers
Root suckers produce healthy rose bushes. The main thing is not to make a mistake. As a rule, roses are grafted onto wild rose hips. The offspring must move away from the maternal root system.
Budding
This method of propagating climbing roses is possible for specialists or gardeners with extensive experience. A cut similar to the letter T is made on the trunk, in a place closer to the ground. A bud of the desired variety is inserted into it. With such propagation, the new climbing rose uses the root system of the mother bush.
If a person does not have specific skills, a mistake can be made, which will lead not only to the death of the scion, but also of the rose bush on which the eye (bud) was transplanted.
Let's sum it up
Growing rose bushes in different ways is a fun activity. Having received a new plant with their own hands once, flower growers can no longer stop. Thanks to this world, new varieties of amazing roses with different colors and unique aroma appear.