Content
- 1 History of selection
- 2 Description of the Canadian park rose Alexander Mackenzie and characteristics
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages
- 4 Reproduction methods
- 5 Planting and caring for roses Alexander Mackenzie
- 6 Pests and diseases
- 7 Application in landscape design
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Reviews with photos about the Canadian park rose Alexander Mackenzie
Rose Alexander Mackenzie is an ornamental, varietal plant. It has gained love and popularity in many countries. The culture is classified as a typical remontant park species. Thanks to the efforts of Canadian breeders, it has acquired excellent decorative qualities, while being unpretentious. The main varietal characteristic is vigorous growth in width.
History of selection
Rose Alexander Mackenzie was bred in Canada in 1985 on behalf of the Ministry of Agriculture. The province of Ontario is considered the birthplace of the variety. The culture was named after the traveler, naturalist Alexander Mackenzie, who explored the entire Pacific coast at the end of the 18th century. To create it, the following varieties were used: Queen Elizabeth, Suzanne, Red Dawn.
Description of the Canadian park rose Alexander Mackenzie and characteristics
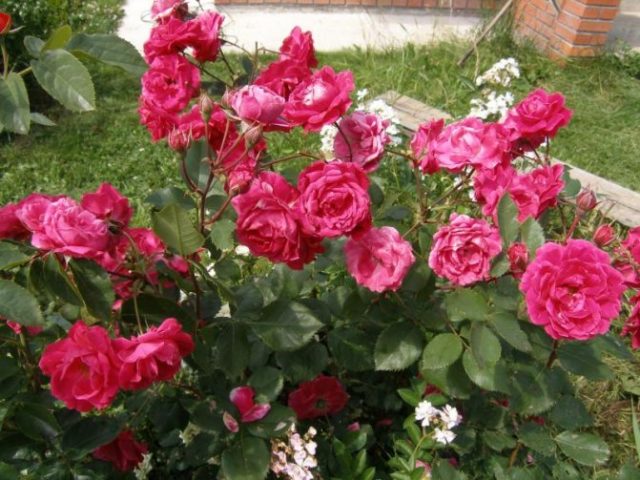
This is a tall, powerful bush, the length of which reaches 2 m; rare specimens stretch up to 300 cm. Because of these qualities, the rose is considered semi-climbing.The shrub can grow up to 1.5 m in width. Its crown is dense, lush, and spreading. During the flowering period, the rose bush looks especially impressive.
The shoots are erect, thick, and become drooping towards the ends. They do not need support and can easily decorate any vertical structure.
The leaves are large, smooth, shiny, with a shape characteristic of roses. Their surface is as if waxy.
The buds of the Alexander Mackenzie rose are bright crimson, small, up to 10 cm in diameter. They are collected in large brushes of 10-15 pieces each.
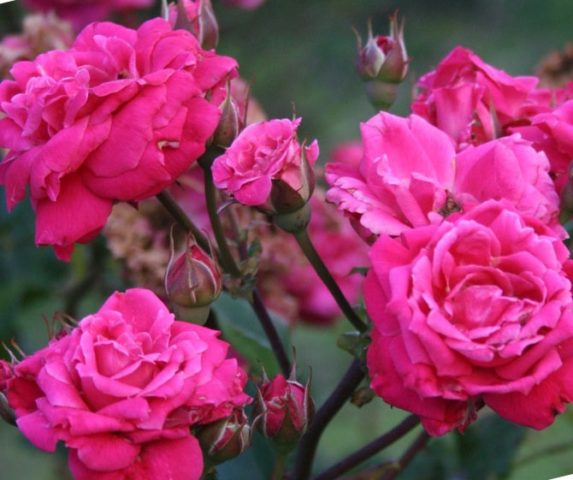

After rain, the outer petals of the Alexander Mackenzie rose may darken and dry out.
The flowers are elongated, densely double, lush. They consist of 20 or 40 petals. The newly opened buds are bright crimson, darken as they ripen, and during the period of wilting they can turn dark pink. If an ornamental bush grows in open areas under direct sunlight, the buds may fade and become pale ruddy, which does not spoil their appearance.
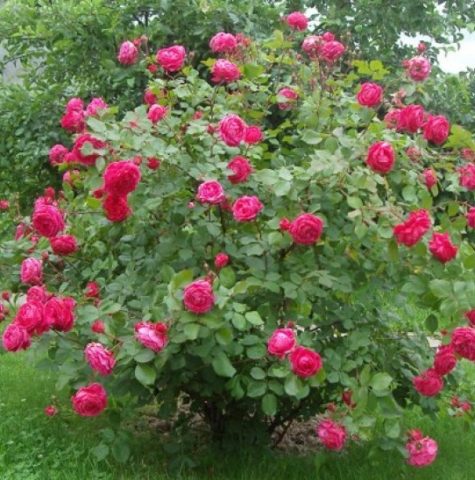

During the budding period, the rose Alexander Mackenzie exudes a subtle berry aroma, reminiscent of the smell of strawberries or raspberries
The flowering of the Alexander Mackenzie variety is remontant, continuous or wavy, repeated twice per season. The first time the rose bush produces buds is in early July, then in August. Between these periods, several bright inflorescences remain on long shoots.
The variety is resistant to low temperatures; in winter it tolerates drops to -35 ᵒC. The culture does not suffer from harmful insects and is not susceptible to fungal diseases. In late summer, some plants may suffer from black spot.
Rose Alexander Mackenzie is demanding on soil composition and exhibits good decorative qualities on soils rich in humus with an admixture of clay.Also, the soil should be light, breathable, slightly acidic. In spring, the crop needs pruning.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main disadvantage of this variety is that it is demanding on soil composition. But this negative quality can be attributed to its characteristics.
Advantages:
- high decorative qualities;
- repairability;
- frost resistance, no need for winter shelter;
- plant versatility;
- resistance to pests and diseases.
Also, the culture tolerates rooting easily and painlessly and quickly takes root in a new place.
Reproduction methods
The park rose Alexander Mackenzie can be propagated by three methods: cuttings, layering, and dividing the bush.
For the first method, lignified shoots up to 4 mm thick are used.
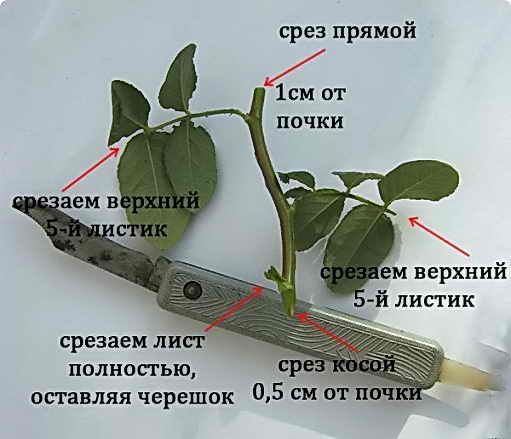

Preparation of layering is carried out in the fall, and cuttings in early spring.
At the end of winter, the shoot is divided into parts 15 cm long. Afterwards, they are immediately lowered into water. A few days later, the cuttings are planted in open ground under a jar and watered regularly until rooting.
The bush is divided at the end of April before the buds open.
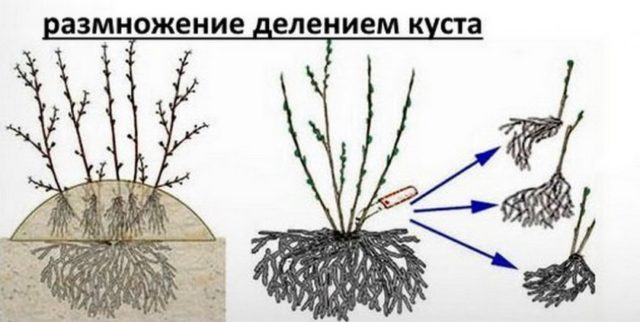
For propagation, mature, overgrown specimens with a strong root system are selected.
The rose is dug up, trying to preserve all underground shoots. Using a sharp pruner, the bush is divided into several parts, each of them should have a root and several shoots. Long or damaged shoots are cut off from the underground part. The shoots are shortened, leaving 3 living buds. The cut areas are treated with garden varnish, and the root is dipped into a clay mash. The young plant is planted in open ground.
The rose variety Alexander Mackenzie is convenient to propagate by layering, as it has long flexible shoots.
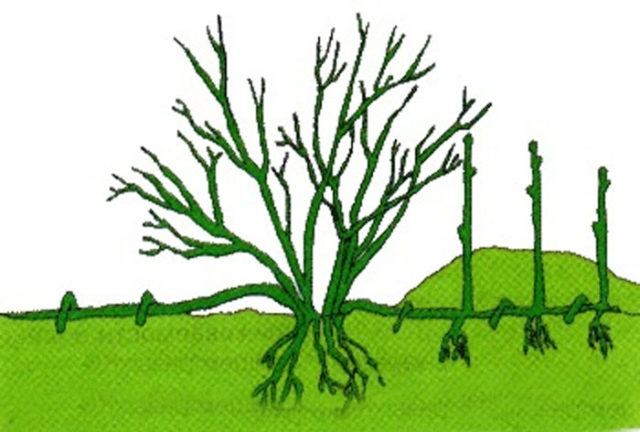
The rooting procedure is carried out in the spring until the buds open.
The area around the rose bush is fertilized and dug up. Select a flexible, mature shoot and make a notch on it around the circumference in the place where it will come into contact with the soil. The shoot is bent to the ground and secured with staples. The cut site is lightly sprinkled with soil mixed with humus.
Planting and caring for roses Alexander Mackenzie
A place for rooting is chosen that is well-lit, without groundwater, and protected from drafts. This culture prefers nutritious, fertile, slightly acidic soils. Before planting, the area is carefully dug up, peat and humus are added.
Rose seedlings Alexander Mackenzie are first kept in a root formation stimulator for 4 hours.
Landing algorithm:
- Dig a hole 0.5 m deep.
- Place a thin layer of expanded clay or sand on the bottom.
- Pour peat into the second layer.
- Lower the seedling into the hole; the root collar should be 3 cm below the soil level.
- Cover the rhizome with soil and compact it.
After planting, the plant is watered and mulched.

When marking a flower bed, the dimensions of the decorative bush are taken into account; the spaces between the holes are made at least 2 m
Water the rose Alexander Mackenzie with warm, settled water at least 2 times a week. After irrigation, the weeds are removed and the bushes are inspected.
Roses Alexander Mackenzie are pruned 3 times a year: in spring, summer, and autumn. After winter, frozen shoots are removed, the rest are shortened, leaving 5 to 7 buds on them. In summer, cut off long branches and remove faded buds. In the fall, a sanitary procedure is carried out, removing dry, broken, thin and long shoots.
As soon as Rose Alexander Mackenzie turns 3 years old, they begin to feed her. Nitrogen fertilizers are used in spring, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers are used in summer. After August, no fertilizing is applied.
Pests and diseases
Rose Alexander Mackenzie rarely gets sick. In cold, rainy summers it may suffer from black spot. In this case, garden antifungal drugs are used.

As a result of black spot damage, the rose bush intensively loses foliage and flowering stops
In hot, dry weather, the green part of the park rose Alexander Mackenzie is attacked by spider mites. Affected and fallen leaves are collected and destroyed. The plant is treated with systemic insecticides 3 times with an interval of 7 days.

Improper and insufficient care, abnormal heat are the main reasons for the appearance of spider mites on roses
Application in landscape design
Rose Alexander Mackenzie is grown as a tapeworm (single plant) or in group landscape plantings. The flowering plant can be used as a climbing plant, decorating a small arch, gazebo, fence or wall of a building. The budding process will continue throughout the summer, the bush will revive and decorate a country estate, city alley or flowerbed.

It is the Alexander Mackenzie rose that is often used in park landscape designs
Conclusion
Rose Alexander Mackenzie is a good varietal plant that is resistant to frost, pests, and diseases. It can be cultivated in central Russia and in the northern regions. Despite its high decorative qualities, the rose is quite unpretentious; even a novice gardener can handle its explantation. The plant is universal, it can be arranged as a bush or in the form of a loach, and can be combined with any garden crops.
Reviews with photos about the Canadian park rose Alexander Mackenzie










