Content
The functionality and design of greenhouses is no different from greenhouses. All of them are designed for growing vegetables and seedlings. The only difference between the shelters is the size. Greenhouses are large structures that are permanently installed on a foundation. If heating is available, vegetable growing can take place in winter. A greenhouse is a smaller copy of a greenhouse and is most often used for early planting of seedlings or growing vegetables in the summer in cold regions. Making greenhouses for a summer residence is much easier than building a large greenhouse. We will now talk about choosing a place to install the shelter, developing a drawing, and making a frame.
The optimal location for a shelter for a garden bed
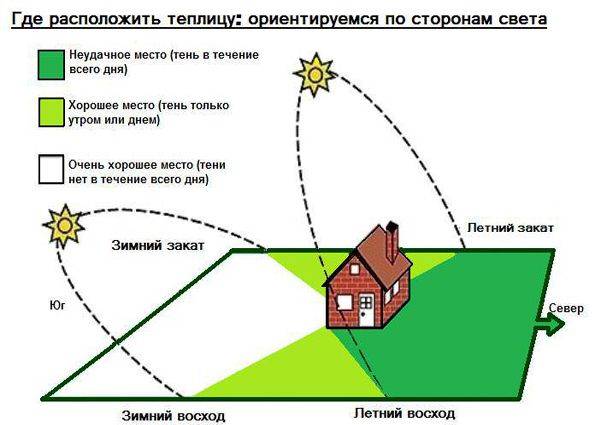
Among inexperienced summer residents there is an opinion that such a simple structure as a greenhouse can be installed anywhere on your site. The simplest shelter option is to stick arcs into the ground and stretch the film on top.But what is the essence of a greenhouse? Inside, the optimal room temperature for seedlings should be maintained around the clock. The microclimate is influenced by the location of the shelter:
- Some summer cottages may not even be suitable for installing greenhouses. Shelters are placed on a flat and dry place. Difficult terrain and flooded areas are an obstacle to the construction of a greenhouse.
- To install the shelter, choose a place with good lighting. Shady areas under trees or other barriers are not suitable. The greenhouse must be exposed to the sun during the day so that inside the shelter was warm.
- It is good when the constructed greenhouse will not be blown by cold winds much. If the site allows you to place a shelter lengthwise and crosswise, then it is better to turn its length to the south. This arrangement guarantees good lighting throughout the shelter.
- The high location of groundwater can lead to increased dampness inside the greenhouse. The water will stagnate and bloom, which will lead to the death of the seedlings. The problem can only be solved by installing drainage.
Following these simple rules will help you get a good harvest from seedlings grown in a greenhouse.
Heating methods
Before you build a greenhouse with your own hands, you need to think about a way to maintain the optimal temperature inside. Plants love consistency. If there are frequent temperature fluctuations under cover, the seedlings will slow down their growth. Heat-loving and capricious plants may even die.
There are several ways to heat greenhouses:
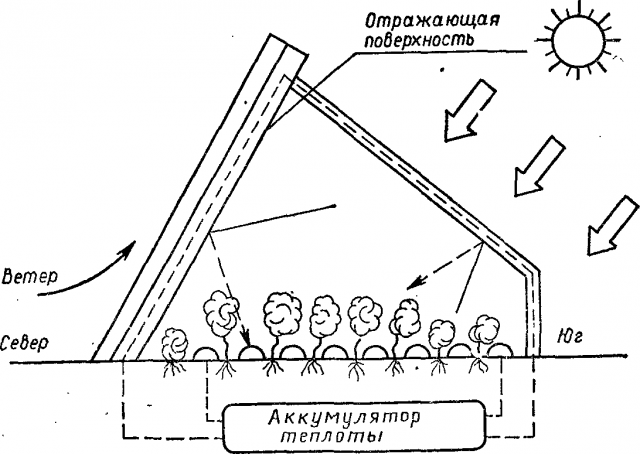
- A free and easy way to heat is using solar energy. The rays penetrate through the film cover of the greenhouse, warming the plants and soil during the day. At night, the source of heat is the heated soil. Solar heating is used by most vegetable growers. However, this method of generating heat is unstable. The heat accumulated in the soil is not enough to last all night. In the morning, there is a strong drop in temperature inside the greenhouse.
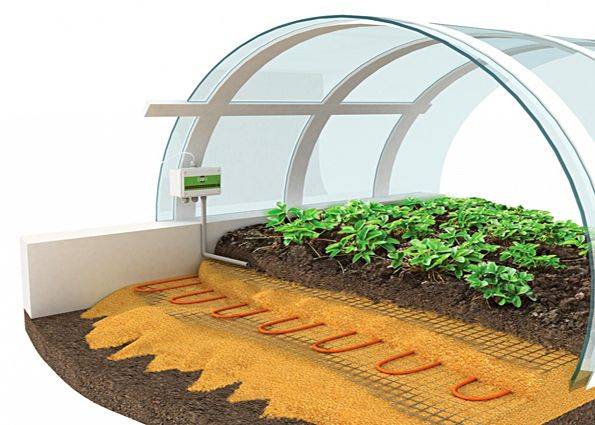
- The electric heating method is based on laying a heating cable in the ground. Such shelters are installed permanently due to the complexity of manufacturing. The establishment of a greenhouse begins with backfilling a gravel bed 20 mm thick. A layer of sand 30 mm thick is poured on top and the heating cable is laid out like a snake. All this is covered with a 50 mm layer of sand, after which the finished cake is covered with a metal mesh or sheet iron. Such protection will prevent damage to the cable when digging the beds. The advantage of electric heating is to constantly maintain room temperature inside the shelter, regardless of weather conditions. The disadvantage is the high cost of materials and unnecessary costs for electricity.
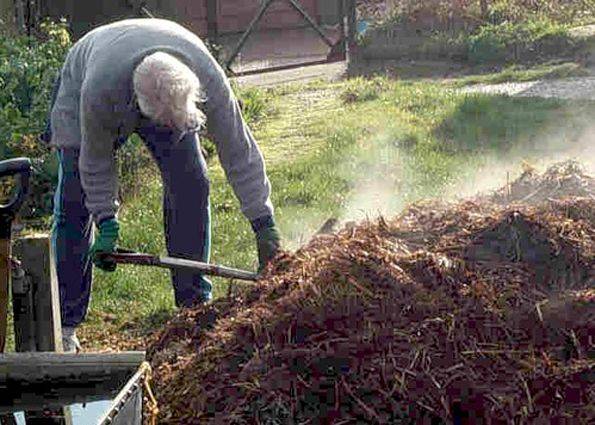
- The golden mean between the two methods of heating a shelter is the use of biofuel. To build such a greenhouse with your own hands at home, the bottom of the bed is made with a depression. Manure, vegetation, straw, in general, all organic matter are poured there. During the process of biological decomposition, heat is released from waste. The method is quite simple and free, but does not allow you to regulate the amount of heat released. When the air temperature in the greenhouse increases significantly, periodic ventilation is performed.
What materials and what shape can a greenhouse be built from?
To understand how to build a greenhouse, you need to understand what it consists of. The basis of the shelter is the frame. The complexity of the design determines whether the finished shelter will be stationary or portable.
So, the simplest frames are installed from arcs. More complex structures are constructed from wooden or metal blanks and window frames. Several materials are used as cladding:
- Polyethylene film is the most popular covering material, but it usually lasts for 1-2 seasons. Reinforced polyethylene will last longer.
- The ideal option for covering is non-woven fabric. The material is sold in different densities. The canvas is not afraid of sunlight and, if treated with care, will last for several seasons.
- Stationary frames made of wood or metal can be covered with polycarbonate, plexiglass or plain glass. Such cladding will cost more, and the option with glass can be dangerous due to the fragility of the material.
Now we will look at the photo of do-it-yourself greenhouses made from different materials. Maybe one of the shelter designs will appeal to you too.
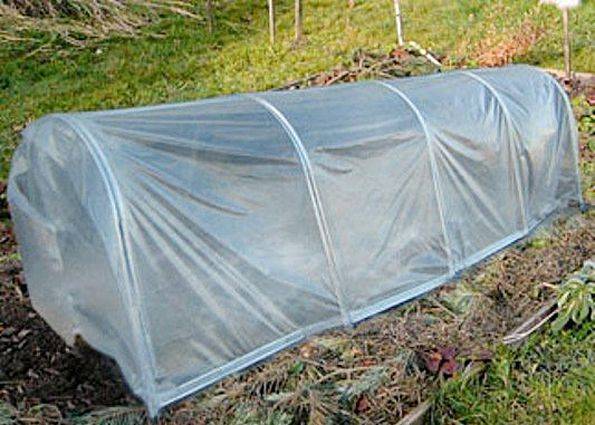
Arc shelter
The appearance of the greenhouse resembles a tunnel. Its diagram does not contain complex connecting nodes. The shelter frame is made of arcs bent in a semicircle. The more you install them in one row, the longer the shelter will be. Arcs are made from any plastic pipe with a diameter of 20–32 mm. The stronger the pipe, the larger the arc radius can be made. They are secured into the ground using wooden pegs or placed on driven pieces of reinforcement. To ensure the strength of the tunnel shelter, the arcs can be connected to each other with a transversely laid pipe.
Stronger arcs will be made from a steel rod 6–12 mm thick. If you insert the rod into a flexible hose, it will be protected from corrosion.
If desired, ready-made arcs for shelter can be purchased at the store.At the summer cottage, all that remains is to install them in place of the beds.
Cover the arc frame with film. From below it is pressed to the ground with boards or bricks. It is allowed to use non-woven fabric instead of film.
In the video you can see the structure of an arc greenhouse:
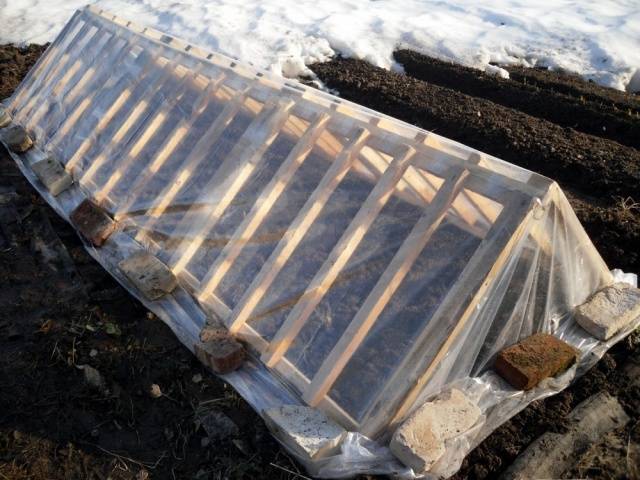
Collapsible shelter made of wooden lattice
Looking at the photo of a greenhouse made of wooden gratings, we can conclude that this is the same tunnel, only more reliable. The gratings are made from wooden slats. Moreover, they can be made in small sections connected by bolts. A wooden frame of this design is easy to assemble and also quickly disassembled for storage.
A greenhouse made of wooden gratings is durable and not afraid of strong gusts of wind. Here, plexiglass or polycarbonate may be suitable as a covering, but access to the plants will be difficult. You will have to make opening sections on hinges. The easiest way is to use a traditional cover made of film or non-woven fabric.
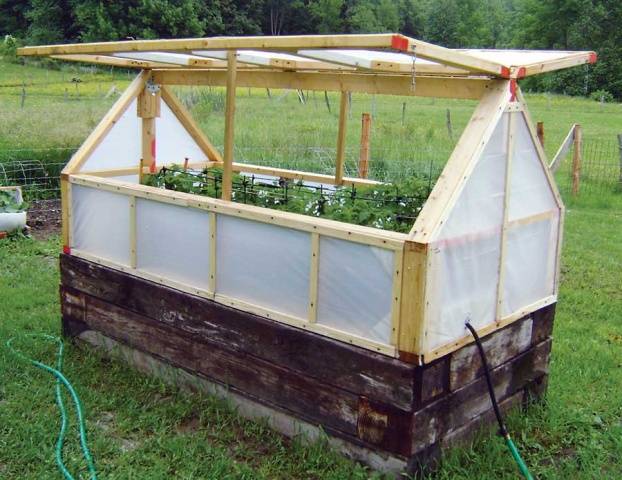
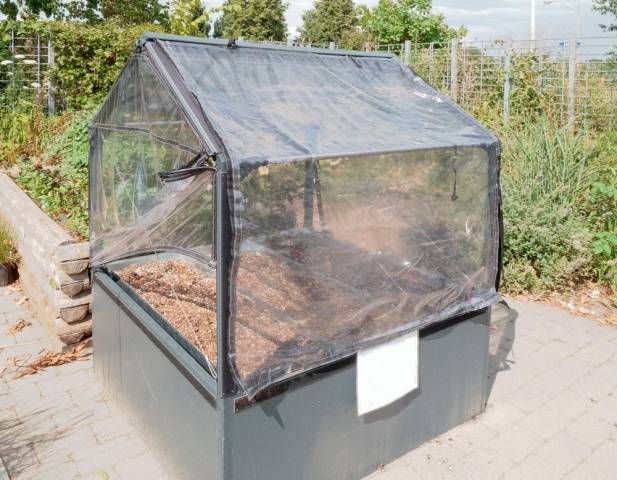
Stationary greenhouse made of wooden beams
Stationary greenhouses for summer cottages are convenient because they do not need to be assembled and disassembled every year. The wooden frame always stands in its place; you just need to prepare the soil in the garden bed, and you can plant the seedlings. The design of such a shelter already resembles a small greenhouse. A base is built under the wooden frame. The foundation is poured from concrete, laid out from blocks, asbestos pipes are buried vertically or a wooden box made of thick timber is knocked down.Each summer resident chooses the best option for himself.
The frame of the shelter is made of wooden beams with a section of 50x50 mm. The roof of stationary greenhouses is made to open to allow access to the plants. Film for covering a wooden frame is not the best choice. It will have to be changed every season. It is better to glaze the frame, cover it with plexiglass or polycarbonate. In extreme cases, non-woven fabric will do.
Greenhouse with metal frame
Stationary greenhouses are made with a metal frame. A collapsible bolted structure is rarely made due to the complexity of manufacturing the connecting units. Usually the frame is simply welded from a pipe, angle or profile. The frame turns out to be quite heavy and requires a concrete base.
Plexiglas or polycarbonate is suitable as a cover. You can sew covers from reinforced polyethylene or non-woven fabric. The covers have fasteners for access to the plants.
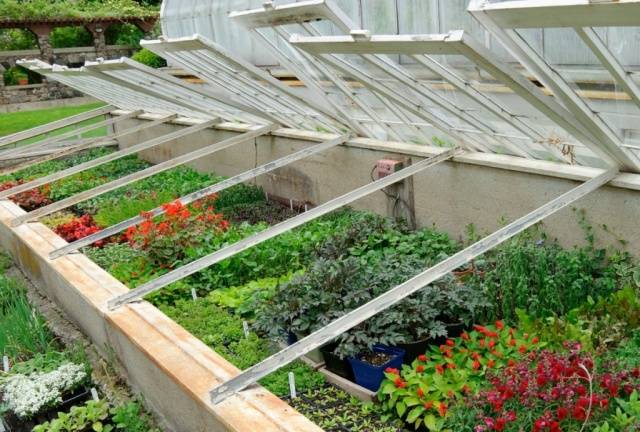
Using old window frames to make a greenhouse
After installing plastic windows on your country house, you should not throw away the old wooden frames. They will make an excellent greenhouse. It should be noted right away that the structure will be heavy and a solid foundation will be installed under it. The easiest way to make a foundation is from cinder blocks or bricks laid without mortar. I build a greenhouse from wooden frames as a separate structure or attached to the house. In the second option, there is no need to build a fourth wall.
A box is installed on a prepared timber foundation, with one of the side walls being made higher. The slope will allow rainwater to drain from the windows. Jumpers are installed inside the wooden box, and window frames are attached directly to them.It is better to open the windows from yourself, then the front of the greenhouse provides free access to the plants.
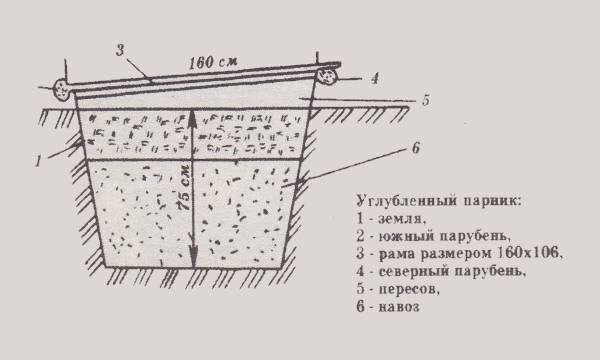
Scheme of a greenhouse with a recess
The above-ground part of the greenhouse with a recess can be anything. Although more often it is made in the form of an inclined protrusion from the ground. A special feature of this design is the arrangement of the bed itself, which allows you to preserve the internal heat of the earth.
At the site of the future greenhouse, a layer of soil up to 400 mm deep is removed. The bottom of the pit is covered with slag or expanded clay. A box is made from a wooden beam around the perimeter of the pit, fertile soil is poured in and an upper cover of any type is organized.
According to the diagram presented in the photo, you can see a similar design of a greenhouse with a recess for biofuel. The principle of arrangement is the same, only the hole for organic matter will have to be dug deeper.
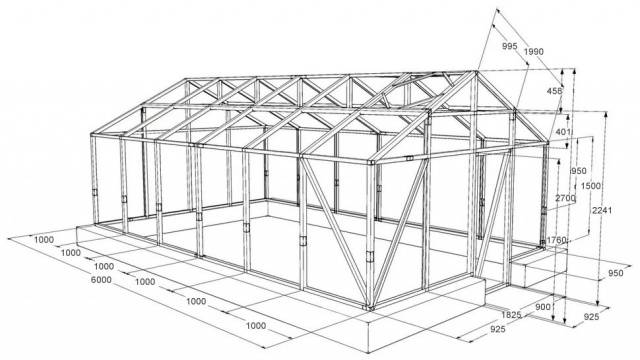
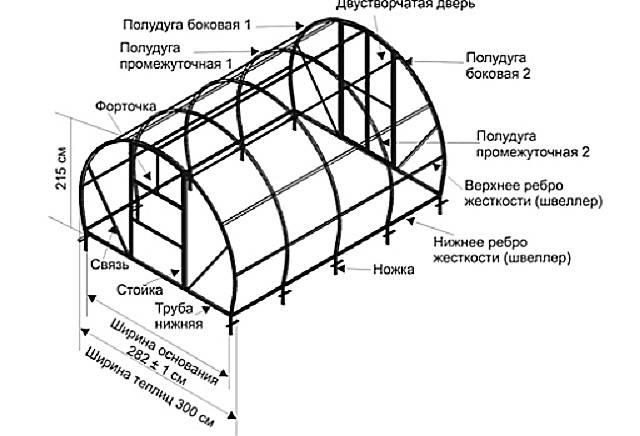
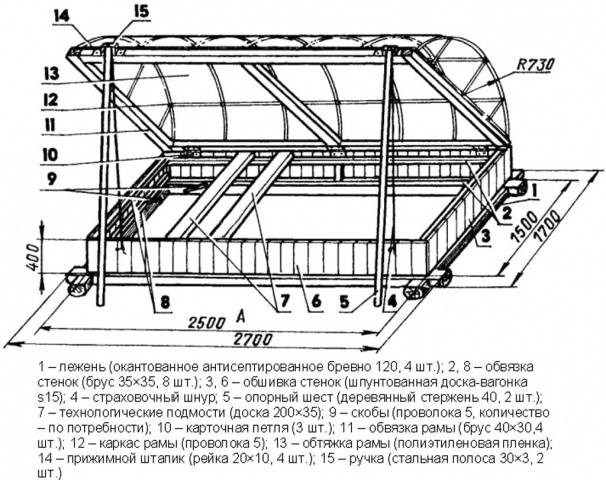
Drawings of stationary greenhouses
It is quite difficult to draw drawings of stationary greenhouses with your own hands without having experience in this matter. For your reference, we present several simple diagrams. Dimensions are shown as an example. They can be changed at your discretion to obtain a frame of the required dimensions.
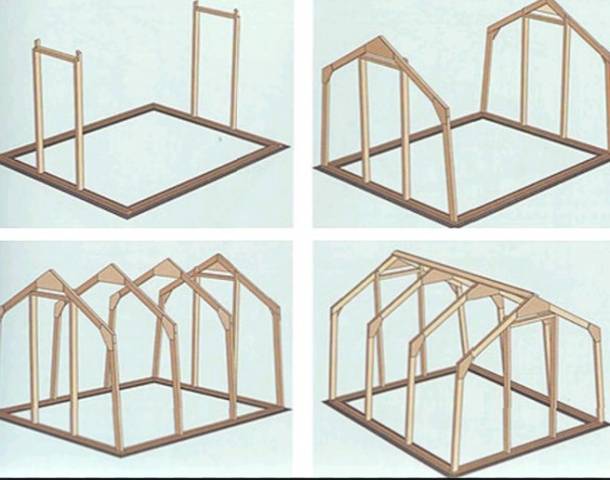
Making a stationary greenhouse from a board
Now we will look at a simple example of how to make a greenhouse with your own hands from a board 150 mm wide and 25 mm thick. Let's take the running size of a wooden house 3x1.05x0.6 m.
Let's get acquainted with the work procedure:
- To make a wooden frame for a greenhouse, two long panels measuring 3x0.6 m are knocked down from boards. These will be the side walls. For the upper and lower horizontal lintels, only solid boards 3 m long are used. Vertical wooden posts are cut 0.6 m long.A rectangular side wall of the greenhouse is laid out from the blanks on a flat piece of ground and knocked down with nails. To ensure accurate connection of wooden blanks, nails can be replaced with self-tapping screws.
- Using the same principle, two smaller panels for the end walls are made. In our example, the size of the boards is 1.05x0.6 m. A rectangular box is assembled from the finished four wooden boards. To fasten them, you can use bolts or overhead metal corners and self-tapping screws.
- Next, we begin to manufacture the rafters. For this example, take six boards 0.55 m long. One end is sawn at an angle of 60O, and the other – 30O. The pieces are laid out on the ground in pairs. You should get three rafters of a gable roof in the shape of a house. The resulting wooden angles are reinforced with a jumper.
- The finished rafters are fixed to the assembled rectangular box, and the roof begins to form. One solid board 3 m long connects the rafters to each other at the very top. A ridge forms at this point. Below the ridge, the rafters can be knocked down with short boards. They are needed only to secure the cladding material.
The finished wooden frame is treated with protective impregnation, after which they begin covering it with any material they like, be it film or non-woven fabric.
The video shows different options for country greenhouses:
A greenhouse in a country house is an important structure. Its production will take a minimum of money and time, and the shelter will bring maximum benefits.