Content
No matter how fertile the soil is, over time, with constant use and without applying fertilizer, it is still depleted. This negatively affects the harvest. Therefore, sooner or later you will have to start feeding. Urea is a fertilizer with a high content of nitrogen, which plants need for growth and development. The rules of use for different garden and vegetable crops will be discussed in the article.
Description and characteristics
This fertilizer is known to gardeners by two names - urea or urea.
Appearance
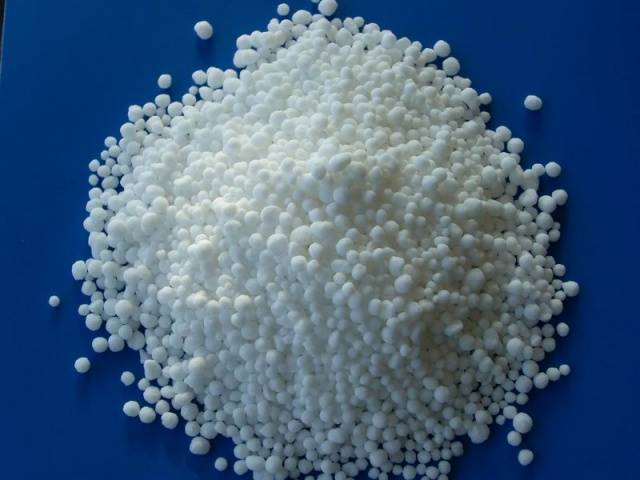
Produced by any manufacturer in the form of round granules, the size of which ranges from 1-4 mm. They are light, white or transparent, and odorless.
Physical properties
- Affects plants in dry and dissolved form.
- Dissolves well in water or soil after watering. The percentage of solubility depends on the temperature of the water and the environment.
- In addition to water, urea can be dissolved in methanol, ethanol, isopropanol and other media.
- Forms compounds with organic and inorganic substances.
- The granules do not cake or stick together during storage and do not lose their properties.
Compound
Urea fertilizer is a complex chemical compound. This is a product of protein metabolism with a high concentration of nitrogen, the only mineral fertilizer in the world with such indicators.
Experts often call urea carbonic acid diamide. This chemical compound is synthesized from organic substances and has its own formula: (NH2)2CO. In urea, about half of the composition is directly nitrogen.
Urea is an excellent option for root and foliar feeding of garden and vegetable plants.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any chemical compound, urea has its pros and cons. The advantages include the following:
- ease of absorption by plants in the shortest possible time;
- suitable for foliar feeding, since with the correct dosage it does not burn the green mass;
- can be used on any soil.
- in irrigated areas the result of assimilation is increased.
If we talk about the disadvantages, then these are:
- if the soil is highly acidic, you need to add dolomite flour or other organic fertilizers to increase the effect;
- deviation of the dosage upward leads to a decrease in seed germination;
- Urea is hygroscopic, so you need to use a dry room for storage.
Instructions
Urea is a special type of fertilizer to which plants respond instantly. Transformations occur very quickly due to the fact that bacteria in the soil process nitrogen and release ammonium carbonate. Since it is a gas, its decomposition in air occurs in a matter of minutes.In order for the process to occur more slowly, and for urea to give the desired effect, it must be added to a certain depth.
If we talk about urea as a fertilizer, then its use in the garden and garden is possible both in open and protected ground.
When using nitrogen fertilizer, you should carefully read the instructions for use on the package. It sets out in detail the standards that apply to vegetable and horticultural crops at different stages of plant cultivation.
Urea is added:
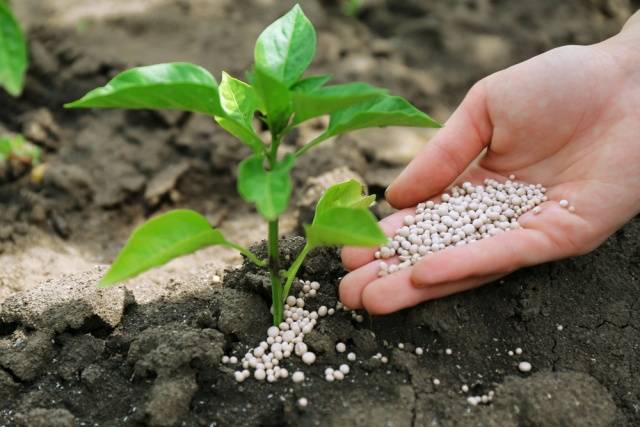
- As the main fertilizer before sowing with a depth of 4 centimeters to retain ammonia in the soil.
- As a top dressing when planting plants. In this case, a layer of soil must be laid between the root system and the fertilizer to prevent burns. Potassium fertilizers are added as an accompanying fertilizing.
- To increase soil nutrition during the growing season.
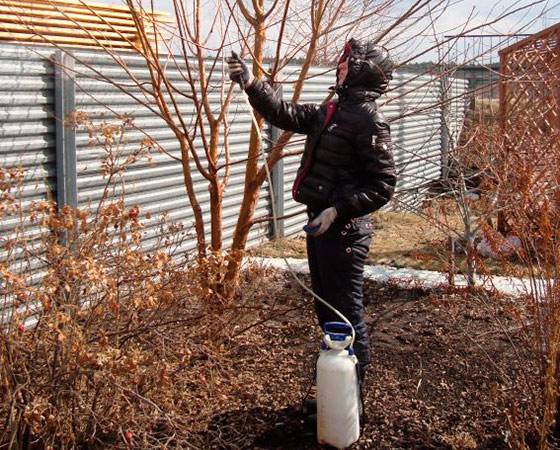
- As foliar fertilizer for spraying plants. Work is carried out early in the morning or late in the evening.
It is advisable to apply urea in dry form, as indicated in the instructions, two weeks before planting. The fact is that the granules contain boiret. With a high content of this substance, if it does not have time to decompose, the plants feel depressed.
Rules for using urea:
Determination of nitrogen deficiency
The application of any fertilizer, including urea, should not be spontaneous. Fertilizers are given to plants when they really need it.After all, an excess of minerals in the soil is much more dangerous than their deficiency. Therefore, plants are fed in strictly limited quantities. It is impossible to fertilize the soil, as they say, in reserve, under any circumstances.
Extraordinary fertilizing with urea can be carried out if the plants give specific signals.
Nitrogen deficiency can be determined by the following signs:
- Garden or vegetable crops grow very slowly and begin to suffer due to weakened immunity from diseases and pests.
- Shrubs and trees have short and weak shoots.
- The leaf blades become smaller, change color, become pale green, and yellowness appears on them, which can provoke early leaf fall. This is a sign of impaired photosynthesis.
- Problems also arise with flower buds. They are either weak and lag behind in development, or are formed in small quantities and even fall off. This leads to a decrease in fruiting and a sharp decrease in yield.
If there are obvious signs of nitrogen deficiency, plants are fed with urea solution as needed at any time during the growing season. To prevent the soil from acidifying (and urea has this feature), an equal amount of lime or dolomite flour is added to 400 grams of nitrogen fertilizer.
Benefits of urea
Unfortunately, not every gardener knows what kind of fertilizer urea is, so it is not in the arsenal. But it is precisely this nitrogen fertilizing that is very important for ensuring the normal functioning of garden and vegetable crops. It is ammonia, or otherwise ammonium carbonate, that has a beneficial effect on the development of plants at all stages of the growing season:
- cells begin to divide faster, therefore growth increases;
- if the required amount of nitrogen is available, the oppression of plants stops, they become stronger;
- According to reviews from gardeners and gardeners, strengthening the immune system helps fight diseases and pests.
Features of application
The use of urea in the garden is possible at different periods of plant development in precisely calculated dosages. It should be understood that violating the instructions will only harm the plantings.
Vegetative period
Let's consider recommendations for individual crops:
- For cabbage, beets, onions, peppers, tomatoes, garlic and potatoes, 19-23 grams per square meter is enough.
- The requirement of cucumbers and peas is from 6 to 9 grams.
- For squash, eggplants, and zucchini, 10-12 grams are enough. Feeding should be done no more than twice. The first time is when planting seeds or seedlings, the second time is in the fruiting phase.
- Urea is added to strawberries and strawberries when preparing the beds. Then, at the stage of budding and setting berries, the plants need to be sprayed with a solution: add 10 grams of nitrogen fertilizer to two liters of water. In order for the plants to bear fruit well in the next season, before covering for the winter, strawberries and strawberries need to be fed with a concentrated urea solution: 30 grams of a nitrogen-containing substance are dissolved in 10 liters of water.
- For grain crops, the consumption rate per hundred square meters is 300 grams. Urea is spread dry.
- Mineral fertilizer is used strictly according to the instructions for foliar feeding and plant protection. The solution requires 9-15 grams of urea per ten-liter bucket.
Pre-planting fertilizing
Before planting, fertilize the soil with dry granules: for each square meter from 5 to 11 grams of urea. Then they dig up the ground to mix the fertilizer. As a rule, such work is carried out in the fall, adding 60% of granules, based on the total need. The rest of the urea is added in the spring a few days before sowing.
Rules for obtaining the solution
The use of urea in the garden requires a special approach. As a rule, trees and shrubs are watered with concentrated solutions and less often with dry matter:
- For mature fruit-bearing apple trees, take 200 grams of urea per 10 liters of water;
- plum, chokeberry, irge and cherries require a less concentrated solution: 120 grams is enough for a ten-liter bucket.
You don’t always have a measuring spoon at hand to take out the right amount of mineral fertilizer. In this case, you can use improvised containers:
- a tablespoon contains 10 grams;
- a matchbox can measure 13 grams;
- 130 grams of urea are placed in a glass with a capacity of 200 g.
Storage Features
The packaging indicates that urea or carbamide can be stored for no more than six months. But if you create the appropriate conditions, then unlimited time. If the fertilizer has not been used completely, then the bag must be sealed tightly or transferred to a plastic container and tightly closed with a lid. No moisture should enter the room, since urea is hygroscopic.As a result, the quality decreases sharply and the mineral substance will not be beneficial.