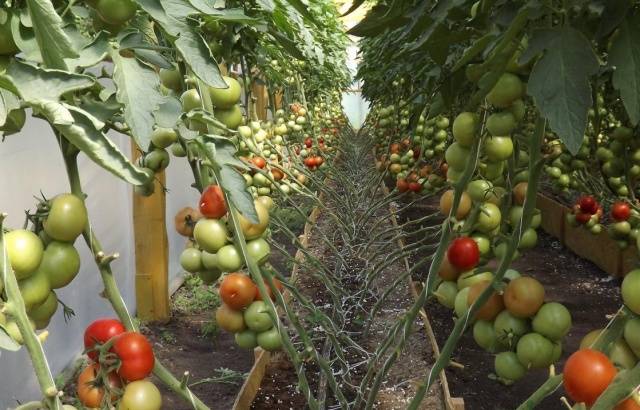
Greenhouse tomatoes appear much earlier than ground tomatoes, and the number of such fruits will be at least twice as large. Technology growing tomatoes in a greenhouse and in open ground it is somewhat different. In order to get a good harvest of greenhouse tomatoes, you need to know some secrets and features of this process.
What are the rules for growing tomatoes indoors, how to care for greenhouse tomatoes, what fertilizers to feed and how often to water - this article will be about this.
Growing tomatoes in a greenhouse step by step
Having decided to grow tomatoes in a greenhouse, a gardener must know some nuances. For example:
- greenhouse tomatoes are more likely to suffer from fungal infections, so disinfection should come first;
- Only parthenocarpic or self-pollinating varieties that do not need pollinating insects should be planted in greenhouses and greenhouses;
- if tomatoes in need of pollination have been selected for planting in a greenhouse, you need to attract bees to the greenhouse or do manual pollination using a brush, for example;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse, because tomatoes love the following conditions: 23-30 degrees and 60-70% humidity;
- Regular ventilation is mandatory, so when building a greenhouse you should take care of a sufficient number of vents or install a forced ventilation system;
- Growing tall tomatoes in a greenhouse will require supports or rods to which the plant stems can be tied;
- Planting tomatoes in a closed greenhouse should under no circumstances be thickened, as this significantly increases the risk of fungal infections and rot on the tomatoes.
After the greenhouse is built, you can proceed directly to growing tomatoes in the greenhouse. This process must consist of several mandatory steps:
- Buying planting material or growing tomato seedlings yourself.
- Preparing the soil and the greenhouse itself for planting tomatoes.
- Transferring tomato seedlings to a greenhouse.
- Pollination of tomatoes (if necessary).
- Tying tomatoes to supports and forming bushes.
- Watering and fertilizing tomatoes.
- Harvesting and storage.
Sowing tomato seeds for seedlings
Externally, greenhouse tomatoes are indistinguishable from ground tomatoes: absolutely any variety of tomatoes can be grown in a greenhouse. But anyway Special tomatoes have also been selected, intended specifically for indoor soil.. These varieties have a number of features:
- have immunity to fungal infections;
- do not require pollination;
- love warmth and humidity;
- most greenhouse tomatoes belong to the group of indeterminate varieties, that is, tall ones;
- are characterized by increased productivity.
Having decided on the variety of tomatoes for your greenhouse, you can go buy seeds. If tomato seeds enclosed in colored capsules are selected, additional treatment they will not need it before sowing - the capsule already contains all the substances necessary for normal and rapid development.
Untreated seeds will need to be prepared for sowing seedlings:
- Treat with an antiseptic (for example, soak in a weak solution of potassium permarganate).
- Sprout by covering with a damp cloth and placing in a warm place.
- Harden by putting sprouted tomato seeds in the refrigerator for a couple of days.
- Soak tomato seeds in a growth stimulator or complex mineral fertilizer for several hours.
Now the seeds can be planted in the prepared substrate. The soil for tomato seedlings should be slightly acidic, loose, retain moisture well and allow air to pass through. A mixture of equal parts of the following ingredients is suitable: peat, turf soil, humus.
You can add a liter jar of coarse river sand and the same amount of wood ash to the mixed soil.Now the soil needs to be disinfected; to do this, you can freeze it outside (if the temperature there is below zero) or keep it in the oven for about 30 minutes (you can do it in the microwave).
A solution of potassium permarganate is considered a good antiseptic - simply pour it over the soil placed in containers. By the way, containers for tomato seedlings should be shallow - about 5-7 cm high. This way, the root system can develop normally.
Drainage made of pebbles, bark or crushed stone is placed at the bottom of each pot or box for tomato seedlings. Pour the substrate on top and tamp it down a little. Now make holes and place the sprouted prepared tomato seeds in them. Cover the seeds with a thin layer of fine soil and spray with warm water from a spray bottle.
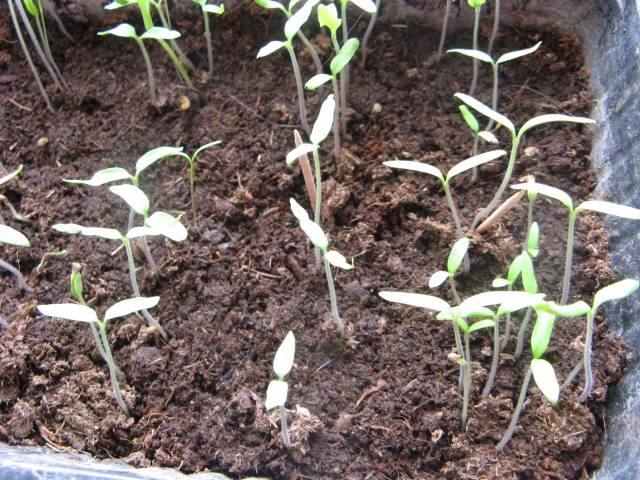
Containers with tomato seedlings are covered with glass or film and placed in a very warm place - there they will remain until green sprouts appear.
As soon as tomato loops begin to appear from under the ground, the shelter is removed and the containers with seedlings are placed on a windowsill or in another bright and warm place.
Caring for tomato seedlings
Like regular seedlings, greenhouse tomatoes need to be watered regularly. At first they do this only with a spray bottle, when the plants get stronger, you can use a small watering can or mug. Water can wash the roots of plants - you need to remember this.
At the stage of appearance of two or three true leaves, the tomato seedlings are picked and transplanted into larger containers. Diving also helps the tomatoes prepare for future transplantation into the ground; at this stage, you can also control the length of the stems and form the root system.
After the dive, you can lower the temperature a little - it can be 18-23 degrees. It is not worth feeding tomato seedlings; it is better to apply fertilizers after the tomatoes are transplanted into the greenhouse and go through the acclimatization process.
Tomatoes in a greenhouse will be healthier if you take them outside or onto the balcony a couple of weeks before transplanting (you can leave the seedlings for several hours in the same greenhouse every day).
Transplanting tomato seedlings into a greenhouse
Tomato seedlings are ready to be transplanted into a greenhouse when the stems have reached 18-25 cm in height, the plants have 7-8 true leaves, the first inflorescences begin to appear, but there are no ovaries yet.
Until this moment, the soil in the greenhouse should also warm up - the soil temperature at a depth of 10 cm should be at least 12 degrees. If you plant tomatoes in too cold soil, the development of the plants will stop, and subsequently they may even die or this will affect the yield of the tomatoes. On the day of transplantation, the weather should not be too hot; it is good if it is cloudy or rainy outside.
You can speed up soil warming by using black plastic film. They simply cover the ground in the greenhouse with it until the desired temperature is reached. As a last resort, you can use hot water to water the holes before planting tomatoes.
Before doing this, the walls and structures of the greenhouse need to be thoroughly washed and treated with an antiseptic. It is recommended to use new soil every year, but you can simply disinfect it.
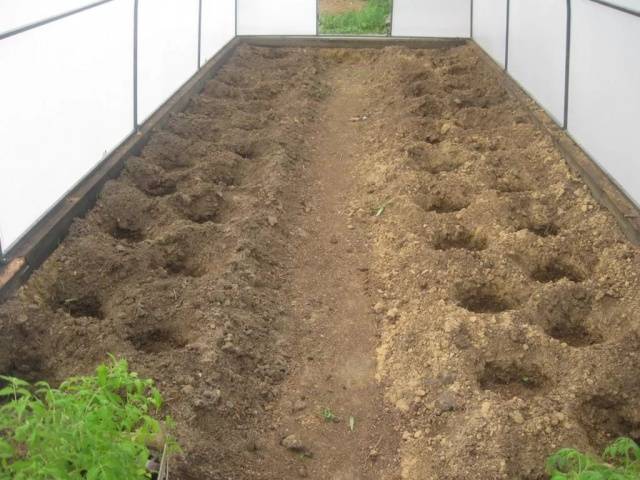
Fertilizing the soil before planting tomato seedlings is mandatory - for this, superphosphate and potash fertilizers are used. Peat, humus or rotted sawdust will help loosen the soil; the amount of such additives should be about a bucket per square meter. When everything is ready, make holes for tomato seedlings.
The scheme for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse, of course, depends on the type of plant and variety. So:
- low-growing, early-ripening tomatoes are planted in the greenhouse in two rows, observing a checkerboard order of holes. The distance between adjacent tomatoes should be 35-40 cm, leaving at least 55 cm between rows.
- Low-growing (determinant) and standard varieties of tomatoes, which are usually grown in one stem, can be planted a little thicker: 30 cm between bushes, rows half a meter apart.
- Indeterminate tomatoes are also planted in a checkerboard pattern. An interval of 80 cm is maintained between the rows, the distance between neighboring bushes must be at least 70 cm.
The most important thing is that the tomato plantings do not become thickened. If such a tendency is observed, it is necessary to remove side shoots. But there shouldn’t be too much distance between the tomato bushes, otherwise the plants will start to fall.
The process of planting a tomato is no different from planting seedlings in the ground: about a liter of warm water is poured into the hole, the seedlings are removed from the pot, the roots are straightened and placed in place, covered with soil and lightly compacted.
Do not deepen the seedlings too deeply, this will lead to the formation of lateral roots, which will slow down the growth of plants. Only overgrown tomatoes can be planted a little deeper, but it is better to avoid this.
Experienced gardeners recommend removing cotyledon leaves before planting tomatoes in a greenhouse. The same is done with yellowed or damaged leaves.
Do not touch the tomatoes for 10-12 days after transplanting into the greenhouse: at this time they are acclimatized, so it is not worth watering or fertilizing the seedlings in the greenhouse yet.
Tying and pinching tomatoes in a greenhouse
Two weeks after planting the seedlings in the greenhouse, you can start tying up the stems. Tall tomatoes in a greenhouse need to be tied up, usually trellises about 180-200 cm high are used for this. With low-growing varieties, everything is much simpler - their stems do not need to be tied up (only when there are too many fruits on the bushes, it is better to install supports).
For tying, you should use a thread that is not too thin, otherwise the tomato stems may be cut. It is better to use bandages or thin strips of cotton fabric for this. The free end of the rope is tied around the bottom of the bush and carefully wrapped around the entire stem. As the tomatoes develop, the stems are tied up additionally.
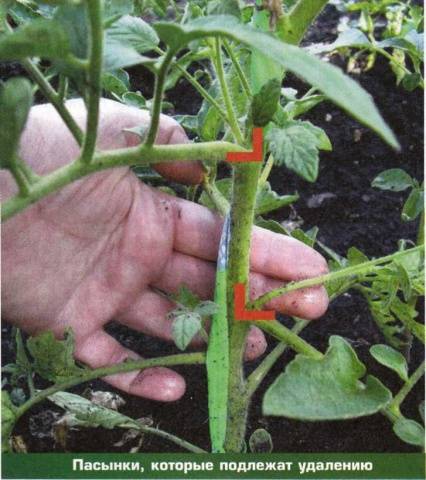
Stepping is the formation of a bush by breaking off unnecessary shoots. This procedure is also not performed with all varieties of tomatoes, for example, standard tomatoes already produce few lateral shoots, the bush itself is compact and not spreading.
In other cases, it is necessary to regularly remove the stepsons to prevent the formation of an excessive number of ovaries - this will deplete the plants and reduce the yield.
Tomato bushes are formed into one, two or three stems. In the case when only one stem is left, it is possible to collect the earliest harvest, but there will be few fruits, because only 4-5 clusters will remain.
Therefore, most often tomatoes are formed into two or three stems - this way the yield will be high and the fruits will ripen quite early. 7-8 brushes are left on each stem; all other shoots must be removed before their length reaches more than five centimeters.
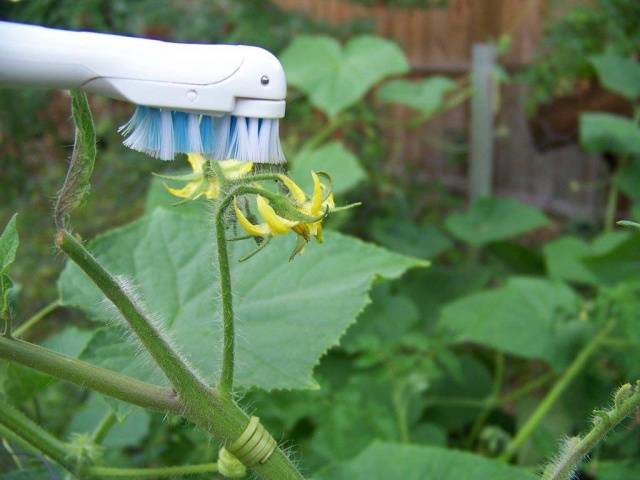
Pollination of tomatoes in a greenhouse
As mentioned above, not all tomato varieties require pollination - for a greenhouse it is better to use tomatoes that do not require the participation of insects. But many gardeners note a more pronounced taste and aroma in varieties that require pollination.
In this case you will have to seriously tinker with greenhouse tomatoes:
- One option is to install a bee trap directly into the greenhouse. This should be done only at the flowering stage of the bushes. But this method is good only for summer residents who breed bees.
- Another method is suitable for those who live next to an apiary or have a neighbor who is a beekeeper: you need to attract beneficial insects to the greenhouse.For this purpose, fragrant flowers are planted at the entrance to the greenhouse; small containers with sweet syrup can be placed in the greenhouse itself or tomato bushes can be irrigated with this solution.
- For some varieties of tomatoes, intensive ventilation of the greenhouse is enough: this way pollen is transferred from flower to flower by air flow. During the flowering phase in the greenhouse, you need to open all the windows and doors to create a draft. Before this procedure, you need to reduce the air humidity in the greenhouse, again, using ventilation and stopping watering. The pollen should be crumbly and dry. But irrigating the bushes with a sprayer will help to consolidate the result - this will help the pollen to germinate on the pistils of the flowers.
- The most labor-intensive method is to transfer the pollen by hand using a paint brush. This option will suit summer residents who have small greenhouses with several dozen plants.
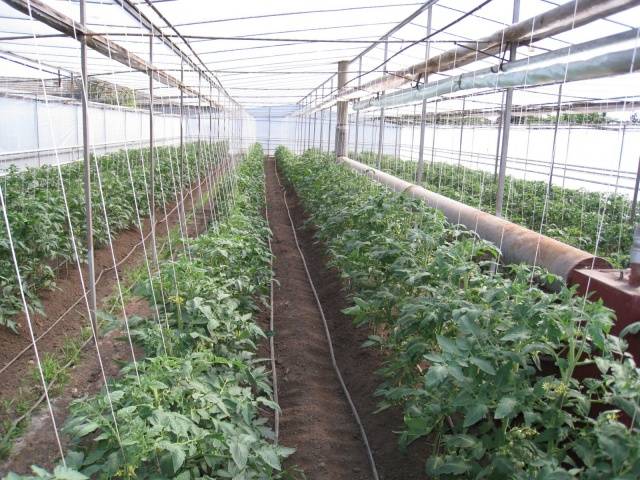
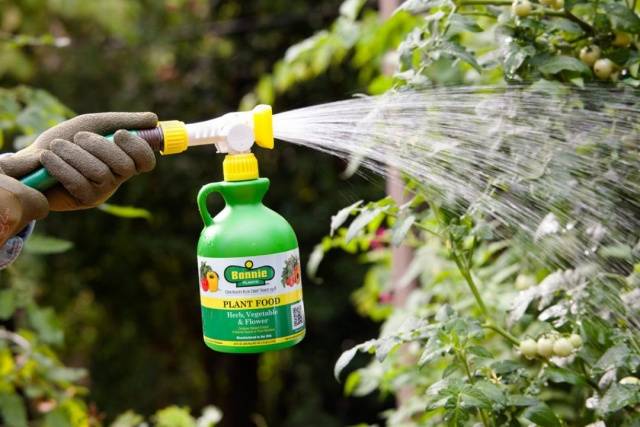
Watering and fertilizing tomatoes
Care in the greenhouse consists of feeding and watering the tomatoes.
Tomatoes need to be watered rarely, but abundantly. – this rule applies to both ground and greenhouse plants. High humidity is detrimental to tomatoes, especially in a closed greenhouse. This provokes the development of fungal infections, which can lead to the loss of the entire crop.
To prevent this situation, you should remove the lower leaves, monitor the density of the plantings, and regularly ventilate the greenhouse. And the main thing is to water the tomatoes only at the roots, avoiding getting the stems and leaves wet. Drip irrigation of tomatoes in greenhouses is very effective, so if possible, this system should be installed.
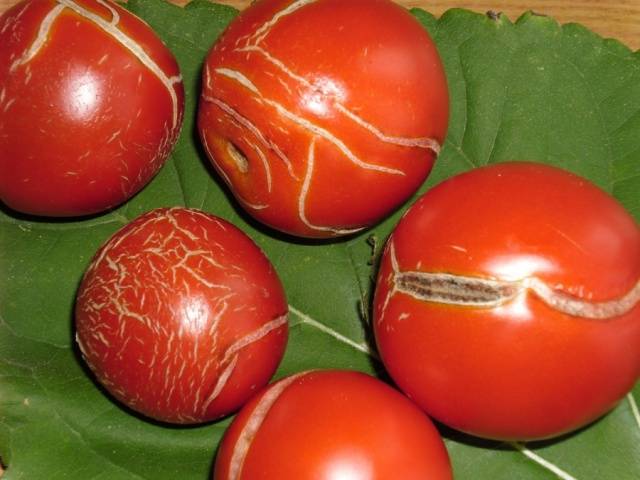
Greenhouse tomatoes should be watered no more than twice a week.The amount of water for each bush varies depending on the phase of plant development: at first, watering should be more abundant, and by the phase of ovary formation and fruit ripening, the amount of water should be gradually reduced. If this is not done, the fruits will crack, and the plants themselves may develop late blight or another infection.
During the entire growing season, tomatoes are fed at least three times. The feeding schedule is approximately as follows:
- The first feeding is carried out three weeks after planting the seedlings in the ground. At this stage, plants need nitrogen. Therefore, they take nitroammophoska and liquid mullein, dilute them in water and pour a liter of this solution under each tomato bush.
- After another 10 days, the tomatoes need to be fed with complex mineral fertilizer. The “Fertility” composition is effective, to which you can add a little potassium fertilizer.
- Two weeks after the second feeding, the next stage begins. For this they take superphosphate, wood ash or sodium humate with nitrophoska. The components are dissolved in water; about five liters of the composition need to be poured for each square meter.
It is very important not to overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers, because their excess will only lead to an increase in green mass - this will not increase the yield. To understand what tomatoes are missing, you should observe the color of the leaves and the general condition of the plants.
Another mandatory component of care is ventilation. Tomatoes are not afraid of drafts, so you can ventilate the greenhouse in any way. Windows and doors must be opened for at least a couple of hours after each watering.In addition, the greenhouse is ventilated daily in too hot weather, or when the temperature “outside” rises above 23 degrees. At night, the temperature in the greenhouse should be about 16-18 degrees Celsius.
Harvesting and storage
Growing a tomato in a greenhouse takes 1.5-2 months. During this time, the fruits have time to ripen and turn red. This means it's time to start harvesting.
Tips for growing and harvesting tomatoes in a greenhouse are as follows:
- in heated greenhouses, the fruits can ripen in the spring - in this case, ripe tomatoes are harvested every two to three days. In the summer-autumn period, harvesting will have to be done daily.
- It is necessary to pick the fruits so that the stalks remain on the bushes.
- Place the tomatoes in small boxes, in several layers, so that the fruits do not get wrinkled or crushed.
- You can pick both pink and red tomatoes: unripe fruits will have time to ripen if they are expected to be transported for a long time.
- If you pick tomatoes unripe, you can increase the yield, because neighboring tomatoes will begin to fill faster and more abundantly.
- It is recommended to alternate tomatoes folded in several layers with soft layers of peat, hay or sawdust.
- If you need to preserve the fruits for a long time, each tomato should be wrapped in soft paper.
- It is better to harvest early in the morning or wait until the evening.
Let's summarize
Growing and caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse differs little from cultivating this crop in open ground. To achieve high yields, you will have to follow the rules of tomato agricultural technology and thoroughly understand the characteristics of the capricious crop.
Tomatoes grown in a greenhouse can be no worse, or even better, than their garden relatives. Excellent taste and a standard smell are necessarily present if the watering rules are followed, the necessary fertilizers are applied, and normal pollination of flowers occurs.
Video about growing tomatoes in the greenhouse will help you sort out the remaining subtleties and understand all the nuances of this difficult matter:
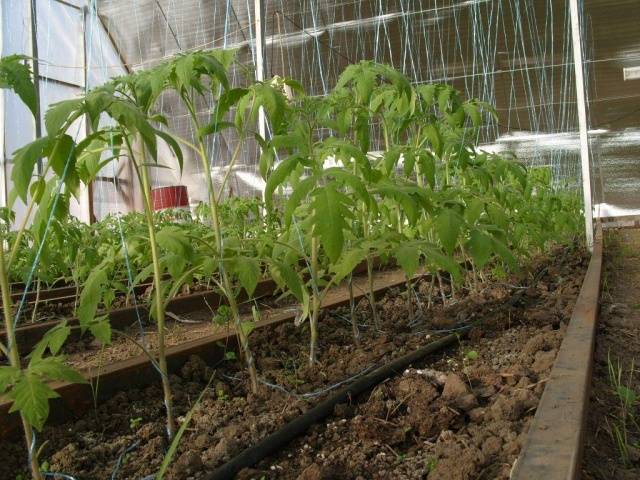






























Leaf curling. Two weeks have passed since planting the greenhouse.