Content
good cucumber seedlings grown at home in a greenhouse in compliance with all rules. Cucumbers are a capricious crop of the pumpkin family that can be grown in open or closed ground. In the second case, the likelihood of improving the quality of the harvest and obtaining earlier fruits increases than when grown in a garden bed. To achieve the desired results, you need to grow strong and healthy seedlings.
Growing seedlings in a home or apartment
Proper cultivation of cucumber seedlings involves the following steps:
- preparing soil and containers for growing;
- preparation and sowing of seeds;
- seedling care;
- landing at a permanent place.
In many regions, conditions for growing cucumbers in open ground are not always optimal, so cucumber seedlings are often planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse. In this case, the choice is made in favor of self-pollinating varieties, which do not require any insects for pollination. It is important that cucumber seedlings are not planted too early. In this case, the risk of its outgrowth and weakening increases. The sprouts will be thin and elongated, pale green in color and too fragile. Such plants will not be able to produce a high-quality harvest.Late planting threatens the growth of small and weak shoots, which take a long time to take root after transplantation, increasing the likelihood of a later harvest. It is better to sow seeds for seedlings 3-3.5 weeks before transplanting to a permanent place.
Preparing soil and seeds
It is important to prepare the soil or buy ready-made ones. This will speed up and facilitate the period of adaptation of the plant to new conditions. For cucumber sprouts, you can prepare a mixture of peat, turf, manure and sawdust (4:4:1:1) or humus mixed with turf and sand (6:3:1).
The soil substrate is pre-disinfected. For this purpose, use boiling water, a solution of potassium permanganate, or calcination in the oven. Then the soil is distributed into a container, which is also subjected to preliminary disinfection. It is important that the containers for each sprout are individual, since cucumber seedlings do not tolerate picking. Each cup should have a drainage hole to remove excess moisture. The container is filled halfway with soil.
Seed material can be regular or processed. The regular one needs to be sorted first. To do this, they are dipped in a strong saline solution: good seeds will sink, bad seeds will float. After this, the seeds are washed, dried or processed. Treated seeds can be immediately sown in the soil; they are covered with a protective layer that prevents the development of fungi and microbes. This layer also contains a number of nutrients that help the seedlings grow stronger.
Preliminary preparation of seeds for planting involves their disinfection and stimulation.
To solve the first problem, use a saturated solution of potassium permanganate, in which the seeds are soaked for half an hour.After this, they are dried and soaked for about 12 hours in a solution of ash, taken in an amount of 2 tbsp. l. for 1 liter of water. Then they are wrapped in damp material and left in a warm place.
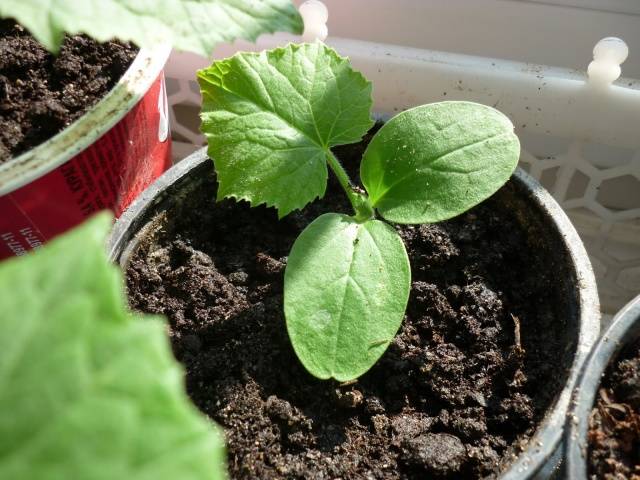
After a small root appears, the seeds are placed in prepared containers and sprinkled with about 2 cm of soil. Plant growth is stimulated with a special solution, for example, Epin. The soil is then covered with a transparent material to create a greenhouse effect. Growing high-quality seedlings requires establishing an optimal regime.
The temperature at which seedlings do not grow should not be lower than 25 °C.
Cucumbers love a lot of light, so it is important to take this feature into account and install additional lighting if it is insufficient. Under such conditions, cucumber seedlings for the greenhouse will grow strong.
Seedling care
After the sprouts appear, remove the transparent coating and ensure good lighting. In this case, the temperature needs to be lowered by 3-5 °C during the day; at night, 18 °C will be enough. Further care for seedlings is as follows:
- Watering - abundant, regular. You can check the degree of soil moisture by taking a little soil: if it crumbles, then it needs watering, but if a lump forms, then you can skip the moistening procedure. For irrigation, use only warm water with a temperature of 25 °C. This condition allows roots to develop better. In the first days, until the first leaves fully open, watering should be done frequently; with the appearance of the second true leaf, watering should be done less frequently, but a little more. It is important to prevent the soil from drying out, which can lead to a depressed state of the root system of the crop.
- Top dressing - every 10 days.It is better to use liquid fertilizers, alternating mineral fertilizers with organic ones. The first ones are diluted according to the instructions, and the second ones - in the amount of 2 tbsp. into a bucket of settled warm water. It is advisable to feed in the evening, and in cloudy weather - in the morning.
- Disease Control - another stage of care. Seedlings are often infected with powdery mildew; its appearance is provoked by cold watering and a thickened planting pattern. Yellowing of cucumber seedlings can occur due to incorrect temperature conditions or a decrease in soil fertility. Withering of foliage is promoted by high temperatures and lack of moisture, as well as a lack of mineral elements in the soil. To prevent all factors, it is important to apply fertilizers on time, ensure normal moisture and regular ventilation. Without this, cultivation will not be effective.
Preparation and planting in the greenhouse
In order to prepare the crop for planting in a permanent place, it is hardened off. Plants grown at home are very pampered and sensitive to any environmental changes. Three-week-old seedlings begin to harden 2 weeks before transplanting. The procedure involves gradually lowering the temperature and regularly ventilating the room. It is important to adhere to the following points when hardening:
- hardening time increases by 1-2 hours every day;
- In the first days, the sprouts must be shaded to save them from possible burning under the influence of direct sunlight.
The seedlings can be gradually taken into the greenhouse, where they will grow in the future. The hardening process helps strengthen the sprouts and improve survival after transplantation.Before transplanting to a permanent location, high-quality cucumber seedlings are characterized by:
- the presence of at least 2 pairs of true leaves;
- strong short stem;
- bright green foliage;
- developed roots.
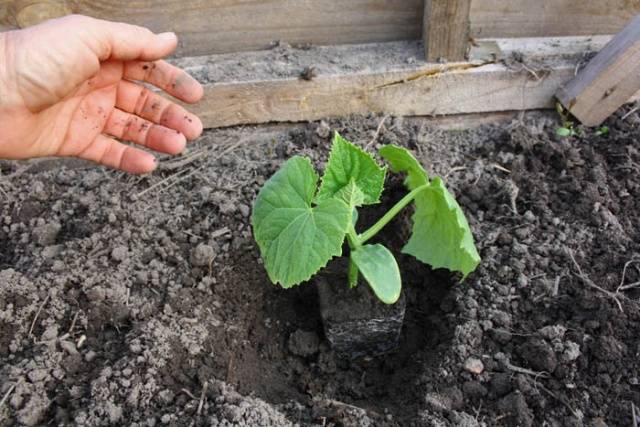
Cucumber seedlings are planted on prepared soil in a checkerboard pattern. The planting depth should be equal to the depth of the container in which the sprout grew. When replanting flowering plants, it is better to remove the color to improve survival. When transferring sprouts with a lump of earth from the container into the holes, it is important to prevent injury to the root system. There is no need to bury the seedlings; after planting, they are spilled with warm water. Further cultivation involves proper care, on which the yield and quality of the fruit will depend.