Content
To get consistently high yields, you need to figure out who eats cucumber seedlings in a greenhouse. Pests are one of the main reasons for reduced yields in greenhouse conditions.
The most famous pests in greenhouses
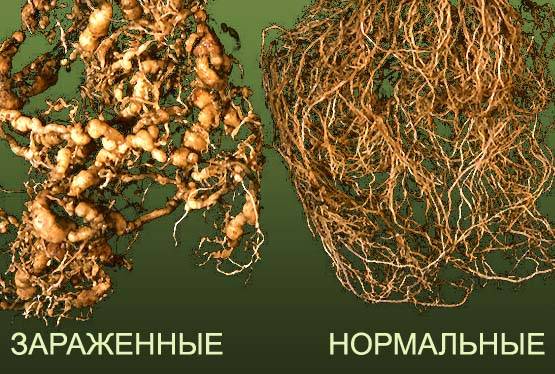
Root-knot nematodes
(Southern, Javan, peanut and northern) - harmful phytophages, belong to a large group of roundworms. The southern root-knot nematode is more common.
The female is easily recognized by her pear-shaped body, milky white in color, 0.5-1.9 mm long. Adults are located in the enlarged tissues of the injured root - in galls. They overwinter in the egg or larval phase. Penetration into the roots occurs during planting of seedlings. The pest's digestive enzymes provoke chaotic division of root cells. Nematodes develop in the resulting galls. Galls create obstacles to the flow of water and nutrients into the vegetative organs of plants. The leaves turn yellow and fall off.
Meloidogynosis is the name given to diseases caused by nematodes.As a result of the destructive activity of worms, the plant is depleted, the yield is sharply reduced, and premature death of the crop may occur. Diseases that penetrate through a damaged root (rot, fusarium wilt) develop due to nematode infection. Positive results are obtained from growing hybrids that are resistant to damage.
Pests of cucumbers in a greenhouse - mites - represent a large group of phytophages.
Common spider mite
It reproduces mainly on cucumbers. It settles on all vegetative organs of the crop: leaves, stems, fruits, entwining them with a web. Eating plant juice from cells causes irreversible changes in metabolism. Inhibition of plants leads to a significant reduction in yield. White spots on the leaves, at first isolated, eventually form a continuous marble pattern. Subsequently, the leaves dry out.
Tarzonemid mites
They rarely damage stems and roots, feeding mainly on leaves.
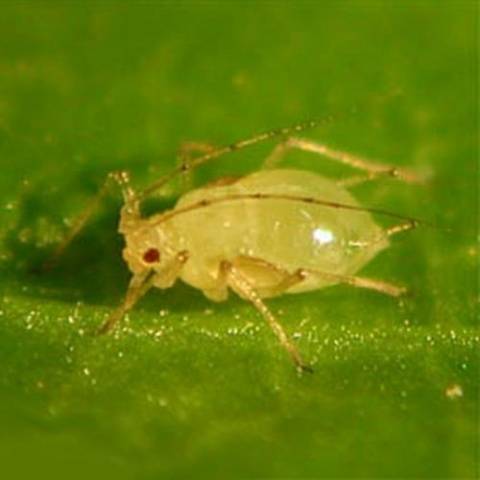
melon aphid
Tobacco and cucumber mosaic viruses are spread by aphids. Saprophytic fungi settle on its secretions. Cucumbers lag behind in growth and development, and product quality deteriorates. Photosynthesis is inhibited. With an ideal microclimate in the greenhouse - temperature +22...+25°C, relative humidity 80% - the population size increases sharply: 20 generations grow per season. In auxiliary greenhouses, the pest is sprayed with Actellik or Fosbecid, Intravir, TAB.
In greenhouses, natural enemies are used - predators, including:
- gall midge aphidimisa;
- parasitic riders of Lysophlebus;
- Cuban ladybug cycloneda.
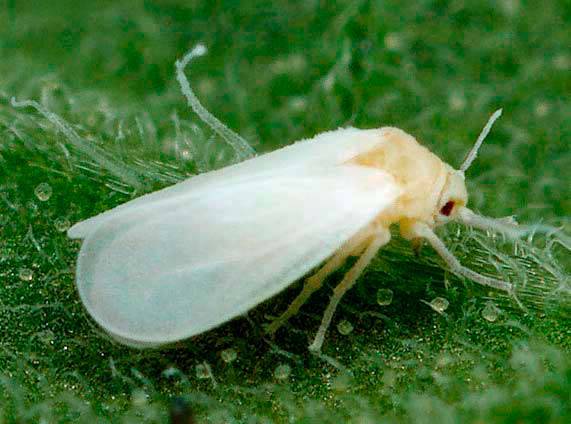
Greenhouse whitefly
On cucumbers, the reproduction rate, fertility and survival rate are higher than on other crops. It infects the leaves with honeydew, which is why a shine appears on them, and then black, or sooty fungus. The adult size is from 0.9 to 1.1 mm, yellowish in color. It has 2 pairs of wings, shrouded in white powdery pollen. Larvae and nymphs have a flat, round, undivided body, covered with spines. Wintering females can tolerate temperatures down to -12°C. During the season, 10-15 generations are formed. Protective measures:
- prevention - destruction weed- reserves;
- disinfection of containers and seedlings;
- use of Verticillin, Actellik or Fosbecid, Inta-Vira, TAB in auxiliary greenhouses.
Western flower or California thrips
Has quarantine value. Adult with a narrow body 1.3-1.4 mm long. Color ranges from light yellow to dark brown. There are 5 pairs of setae growing on the anterior and posterior margins of the pronotum. Has fringed wings. Adults overwinter on organic soil debris or in cracks in greenhouse structures. Appears after planting seedlings. Lays eggs in leaves and upper parts of stems. Females feed on plant sap for a month. During this time, they can lay up to 300 eggs.
The vital activity of thrips causes the appearance of yellow necrotic spots and significant weakening of plants. Ragged holes appear on the sheet. The tops of the stems curl. The flowers bear deformed fruits. Sterilization of soil, disinfection of containers and tools, and extermination of weeds give positive results.
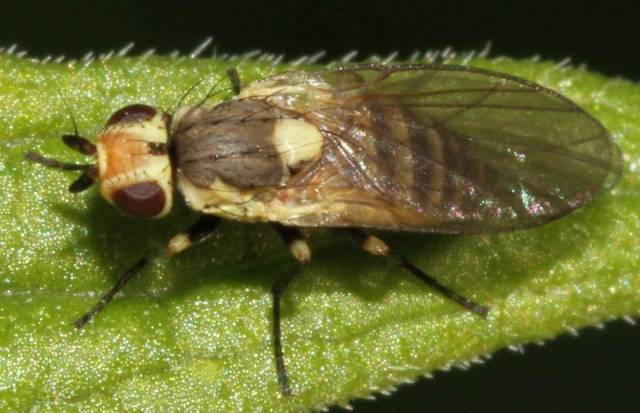
Nightshade miner
Harmful to cucumbers in spring. This is a fly with a black back, transparent wings, a yellow shield and light-colored halteres. Body length - 1.5-2.3 mm. False cocoons overwinter in the soil surface.It flies out at the time of planting seedlings. After mating, females lay eggs in leaf tissue. Then the emerging larvae gnaw through the passages, damaging the surface. Up to 5-7 generations can develop in a greenhouse. The function of photosynthesis is inhibited, the leaves turn yellow and fall off. Prevention - removal of weeds, soil disinfection. Actellik or Fosbecid, TAB, CE are used.
Cucumber mosquito
3-5 mm long, gray in color, with large compound eyes. Has one pair of membranous wings. The larva is white, legless, worm-shaped. It penetrates into the greenhouse with humus. The imago settles on cucumber seedlings. Oviposition occurs in the soil. The larvae gnaw tunnels at the base of the stems of seedlings and in the roots. The result of the feeding of the larvae is rotting and weakening of the lower part of the stem. Turgor is disrupted and the plant dies.
Protection of indoor plants
The fight against phytophages begins with the aim of prevention:
- before planting, the greenhouse (its main structures) is disinfected by gas-flame treatment;
- carry out thermal treatment of the soil;
- eliminate old plant residues;
- wash glass and greenhouse structures with disinfectant solutions;
- whitewash the greenhouse foundation.
A set of preventive measures leads to the death of the main number of phytophages.