Content
Of all fodder root crops, fodder carrots rank first. Its difference from the equally common fodder beet is that it is not only more nutritious, but also more unpretentious in care. One fodder carrot root contains almost all known vitamins and amino acids. Due to its rich vitamin composition, it is actively used in feed for animals and birds.
Composition and benefits of feed carrots
Feed carrots contain a large amount of vitamins and minerals. But what stands out in its composition are:
- carotene;
- vitamin C;
- B vitamins;
- vitamin E;
- calcium;
- boron;
- silicon and others.
It is worth noting that not only the root vegetable itself is rich in vitamins, but also its tops. It contains even more manganese, iodine and protein than carrots themselves.
Forage carrots and their tops are perfectly digestible by animals and birds.Their introduction into the diet promotes better digestion of other feeds. It is this fodder root vegetable that can enhance the formation of milk, which is especially important for dairy animals.
Characteristics of varieties
All varieties of fodder carrots are usually divided according to their color into three groups:
- white;
- yellow;
- red.
At the same time, it is difficult to single out an absolute leader among these fodder varieties. The most productive varieties will be white, then yellow and red. But in terms of dry matter content, the order of leadership will be reversed: red, yellow and only then white.
Let's look at the varieties of each of these groups.
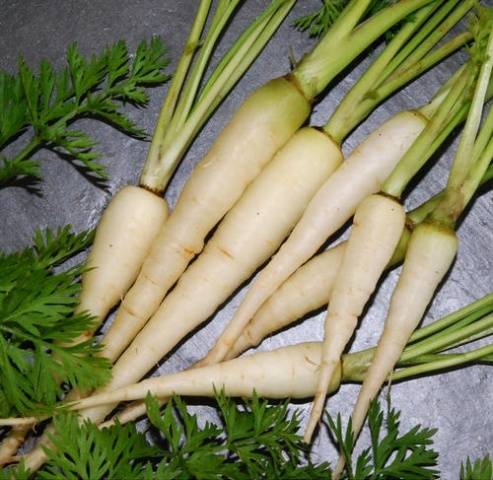
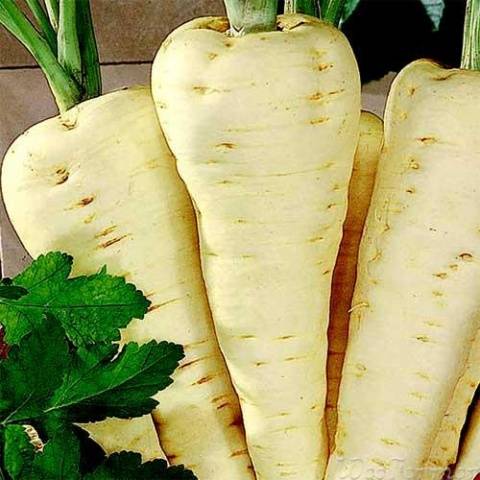
White varieties
These feed varieties are the most common and the largest - up to 4 kg. At the same time, the average length of a carrot can reach 50 cm, and its neck has a thickness of 8 cm. The percentage of dry matter in carrots of these varieties will not exceed 12%, sugar will be about 3%.
White Belgian
Only the tops of the White Belgian protrude above the surface. The long carrots of this forage variety are cone-shaped and hidden from view underground.
White greenhead
The lush tops of this forage variety are formed by dark green, erect leaves with green petioles.
But this can only happen when grown on heavy soils and with prolonged exposure to low temperatures.
White carrots This variety got its name because of the green color of its top. In its shape, it resembles an elongated cone, which is 2/3 hidden underground. The flesh of carrots is white and very juicy.
Gigantic white
The rich carrot tops consist of erect leaves on long petioles. Some plants have an underdeveloped stem part. Carrots of this variety have an elongated conical shape and are white in color with a green tip. The white flesh of Gigantic White is distinguished by its juiciness.
Arnimkrivenskaya white
The white roots of this forage variety are shaped like an elongated cone and are completely buried in the ground. They are skillfully hidden by thick tops of raised green leaves. The white pulp is characterized by medium juiciness.
White varieties of fodder carrots also include:
- White Weibul;
- Championship;
- Fat;
- Berlin giant.
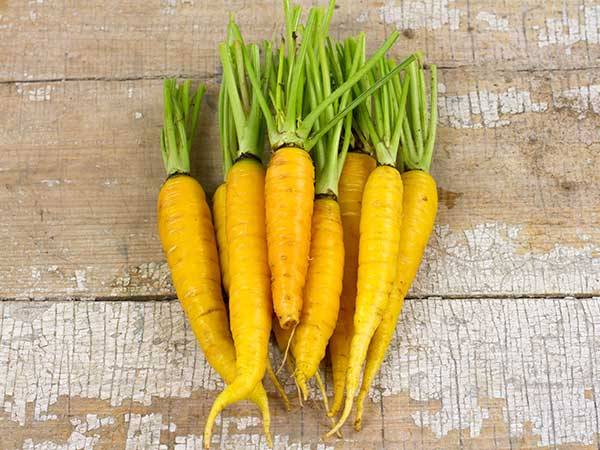
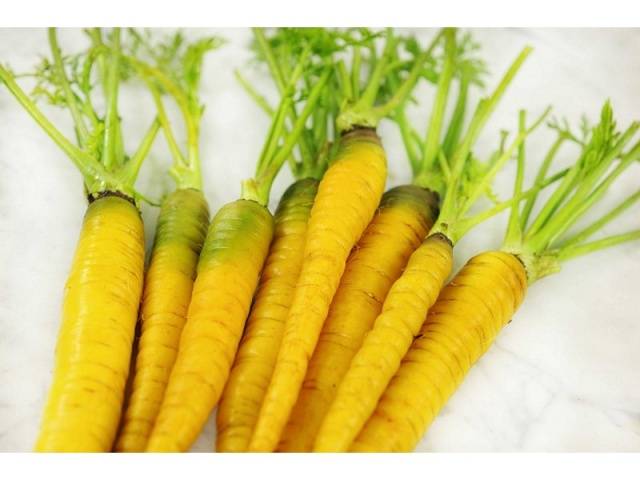
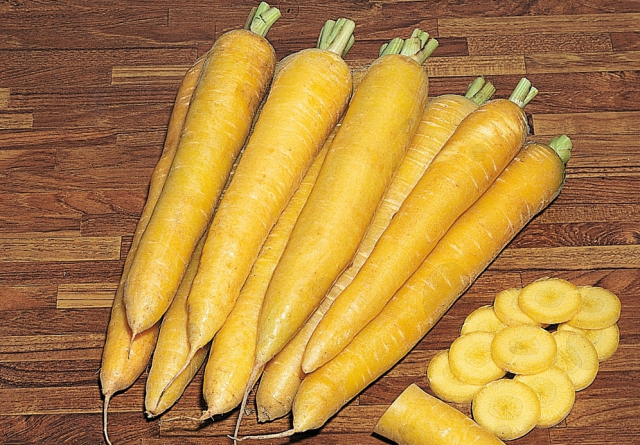
Yellow varieties
They are in second place in terms of yield and dry matter content - up to 13%. The sugar content of these feed varieties will be up to 5%.
Belgian yellow
Just like the Belgian White, it is very difficult to clean. The conical root crop of this variety has a slightly blunted bottom and is securely hidden under the abundant tops.
Lobberich yellow
The tops of this variety, in contrast to its stem part, are well developed. It consists of erect leaves on long petioles. Lobberich yellow carrots are quite long and very pointed. It practically does not protrude above the surface of the earth. The color of the root crop is heterogeneous: the dark green top smoothly flows into the yellow bottom. Its flesh is also yellow.
Saalfelder yellow
Unlike the previous variety, the shape of this fodder carrot is not so sharp, although it is also elongated. It is yellow and completely immersed in the soil. The light yellow pulp of the variety has medium juiciness.
Yellow varieties of fodder carrots also include:
- Long green-headed giant;
- Palatinate golden yellow;
- Flanders;
- Yellow giant Weibull.
Red varieties
These varieties are record holders for the dry matter content of all fodder carrot varieties - up to 15%. Sugar in them will not exceed 5%.
Bull's heart
Bull's heart has almost no tops and does not produce flower shoots in the first year of the growing season. The root crop of this variety has an oval shape, slightly narrowed downward. Its lower part is slightly rounded. The surface of the root crop, as well as its pulp, are red.
Gigantic red
This variety cannot boast of lush tops of erect leaves with green petioles. In addition, its stem part is not developed.
Almost entirely hidden underground, the root crop of this variety has the shape of an elongated cone. In this case, only its upper part, painted green, will be visible. The lower part of the root crop is red in color. The flesh of the Gigantic Red has a pleasant yellow color.
Red thick
This is one of those forage varieties that only has half the leaves. The remaining half is in a reclining position. Moreover, both halves of the tops have long green petioles. The red-pink elongated root crop of a conical shape practically does not protrude above the surface of the earth.The pulp of this variety is red in color. It is quite juicy and without visible damage.
Red varieties of fodder carrots also include:
- A long orange-red giant;
- Orange-yellow Dippe;
- Long red Brunswick;
- A long, thick, blunt-nosed giant.
Table varieties grown for feed purposes
There are not many such varieties used in Russia, about 10 pieces. This is due, first of all, to their increased productivity. Let's look at the most common of them.
Biryuchekutskaya 415
An excellent unpretentious and high-yielding variety. Able to actively bear fruit even in dry areas. The harvest of Biryuchekutskaya 415 can be harvested within 2.5 months from the first shoots. The orange root vegetable is cone-shaped, up to 16 cm long and weighs up to 120 grams. The pulp is also orange and has good flavor characteristics. A distinctive feature of these root vegetables is their excellent preservation even after long-term storage.
Vitamin 6
The main characteristic of Vitamin 6 carrots is their high carotene content, up to 28 mg. The carrot itself, as well as its pulp and core, are orange in color. In its shape, it is similar to a blunt-ended cylinder with a length of up to 20 cm and a diameter of up to 4 cm. There are small grooves on its surface, but in general it is smooth. Perfect for long-term storage.
Incomparable
The long, bright orange carrots of this variety are cylindrical in shape with a blunt tip. Its length will be about 20 cm, and its weight will be up to 200 grams. It is incredibly productive and has good immunity to many diseases. In addition, the gardener will not see its flower shoots until the second year of the growing season.
Recommendations for cultivation
Forage carrots are a fairly unpretentious crop.Most often it is grown on an industrial scale, but there are frequent cases of its planting in ordinary areas. Especially where all kinds of livestock are kept.
This root crop is undemanding to the planting site. It grows especially well on well-lit loamy and sandy loam soils of fertile composition.
If the soil is heavy, adding peat, sand or mature compost will help improve its composition.
If crop rotation is organized on the site, then the best predecessors for this crop will be:
- beet;
- potato;
- grains and legumes.
Planting fodder carrots after green manure shows excellent results. Fodder carrots can also be successfully planted in beds of winter crops after they have been harvested.
In addition, they are perfect as mulch and green fertilizer for garden beds. The most common are rapeseed, flax and mustard.
This fodder root crop cannot be planted in one area for more than 5 years in a row. This ban is associated with significant soil depletion. If you plant this crop in one place for a long time, its yield will drop sharply. It will be susceptible to various diseases and pests.
To avoid this, it is recommended to take a break every 3 years and plant other crops in the carrot bed. Moreover, carrots are an excellent precursor for many of them.
Before sowing fodder carrot seeds, you need to prepare the bed:
- When digging the soil in the fall, there is no need to prepare the bed in the spring.It is enough to lightly loosen it with a hoe.
- If the soil was not dug up in the fall, then this is done in the spring. In this case, it is advisable to choose the roots of other plants.
Feed carrot seeds are sown in early spring, as soon as the soil thaws. This crop is cold-resistant, so you don’t have to worry about sudden spring frosts.
For those who sow seeds according to the lunar calendar, the best time to plant this root crop will be the waning moon. For others, it is recommended to meet the deadlines from April 20 to May 10.
When the soil is prepared, the gardener can begin sowing:
- Furrows must be made in the designated area. The optimal distance between furrows is 20 cm, and the depth should not exceed 1 cm.
- The furrows are shed with warm water.
- After the soil has absorbed the water, you can sow the seeds. Sowing is done no more often than every 1 cm.
- The top of the furrow is sprinkled with soil. You can also use peat.
Further care for root crops is quite simple. They only need:
- Moderate regular watering. As a rule, this crop needs to be watered no more than once every 2 days in normal weather. In dry weather, watering is done daily, and in cloudy weather - once a week.Advice! It is better to water in the evening.
- Thinning. It is produced twice: after 14 days and after 8 weeks from emergence. In the first thinning, no more than 3 cm is left between young plants, in the second - no more than 5 cm. All empty holes from torn out plants must be filled with earth.
- Feeding. To do this, use any nitrogen mineral fertilizers, urea and potassium sulfate.
Harvesting fodder carrots can be done either by hand or by machine, depending on the volume of sowing.
Only whole, undamaged root vegetables are left for storage. For better preservation, it is necessary to provide them with a temperature no higher than +2 degrees and a humidity of 90-95%.
You can learn about the best way to store carrots from the video: