Content
Tomatoes are not only everyone’s favorite, but also a very healthy vegetable. A considerable amount of vitamins and minerals makes them useful in the treatment of many diseases. And the lycopene they contain is not only a powerful antioxidant. It is also an antidepressant, comparable in its effect to the well-known chocolate. Such a vegetable has every right to take pride of place in any garden. All gardeners want to grow it, but, unfortunately, this does not always work out. The tomato is susceptible to many diseases, the most dangerous of which is late blight. Treatment of tomatoes with boric acid helps to combat it, as well as to increase fruit set.
Tomatoes love warmth, but not heat; they need watering, but excessive moisture provokes the appearance of late blight. In a word, to grow these whims you need to work hard. And the weather is not always suitable for growing this vegetable. Regardless of the weather (and why, if it’s always warm there), only wild tomatoes grow in their homeland without any care. But their fruits are no larger than currants, and we want to grow a hefty vegetable so we can admire it ourselves and show off to our neighbors.To achieve this result, you need to monitor the health of your pets.
Precisely preventive, they should begin long before the possible occurrence of the disease. The most popular and effective immunostimulants are: epin, succinic acid, immunocytophyte, HB 101. They will be most beneficial for tomatoes if all the necessary components of proper nutrition, both macro and microelements, are available to the plants.
A balanced diet is the key to a healthy and strong plant. Bor is not a macronutrient for tomatoes, but its deficiency can have a catastrophic effect on plant development. Tomatoes are one of the crops that are especially sensitive to a lack of boron in the soil. It is very important for the proper development and abundant fruiting of this vegetable.
The role of boron in the growing season of tomatoes
- Participates in the formation of tomato cell walls.
- Regulates the supply of calcium to plants. Lack of calcium is the cause of a physiological disease of tomatoes - blossom end rot.
- Boron is necessary for the rapid growth of all parts of plants, since it is responsible for the growth of the tips of stems, leaves and roots. Accelerates the formation of new cells.
- It is responsible for transporting sugar from mature parts of the plant to developing organs.
- Promotes the process of laying new buds, the growth of tomato fruits, and most importantly, is responsible for the number of flowers and their preservation, ensures successful pollination of plants and the formation ovaries.
- Participates in the process of photosynthesis.
With a deficiency of this element, not only the growth of plants is impaired, but also their ability to form a full-fledged harvest.
How does boron deficiency manifest in tomatoes?
- The root and stem stop growing.
- Chlorosis appears at the top of the plant - yellowing and reduction in size; if the deficiency of this important element persists, it dies completely.
- The number of flowers decreases sharply, they are not fertilized, do not form an ovary and fall off.
- The tomatoes become ugly, with suberized inclusions appearing inside them.
Prolonged precipitation and intensive application of organic and mineral substances without boron also contribute to it. To grow tomatoes on sandy, alkaline soils, it is necessary to apply increased doses of boron fertilizers, since their content in such soil is low.
Spraying tomatoes with fertilizers containing boron
There are a lot of boron-containing fertilizers, but the vast majority of them are applied at the planting stage in dry form, so they act slowly.
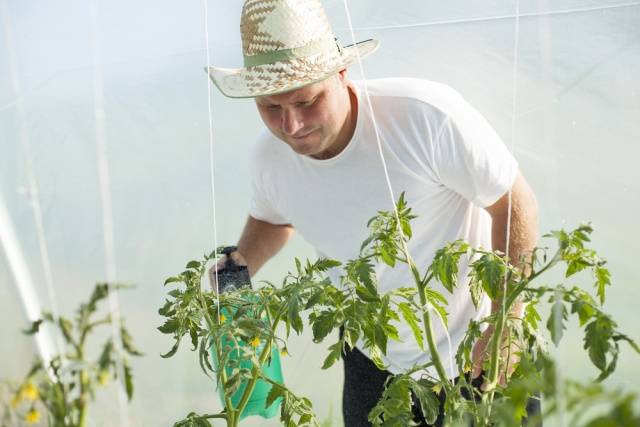
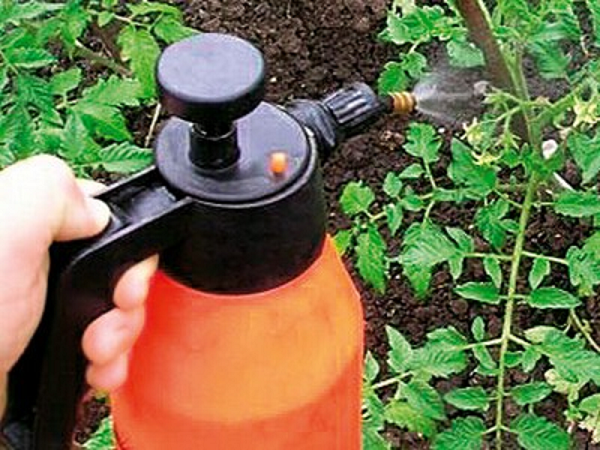
The easiest way to enrich tomatoes with boron is by spraying or watering with boric acid. When it is dissolved in water, boron becomes available to plants. Such treatment of tomatoes with boric acid will not only eliminate its deficiency, but will also be a preventive treatment of tomatoes against late blight and a number of other diseases.
Boron fertilizer is added to the holes during planting. It is better if it is in the form of a solution and at least a day will pass between its application and planting of seedlings.
Boron is a sedentary element. It practically cannot move from one part of the plant to another. As tomatoes grow, the growing vegetative mass needs new supplies of this nutrient. Therefore, tomatoes are sprayed with boric acid dissolved in water. It must be remembered that boron is very slowly removed from the human body, and its increased content in tomatoes can simply be harmful. Therefore, in this matter you need to find a middle ground.
Preparation of boric acid solution for processing tomatoes
How much boric acid is needed to prepare the solution so that the tomatoes have enough of this nutrient, and the health of the gardener who will eat the processed tomatoes is not at risk?
It is optimal for the plant and safe for humans to fertilize with a 0.1% solution of boric acid in warm, clean, non-chlorinated water. That is, a standard packet of boric acid weighing ten grams must be dissolved in ten liters of water. In practice, this much solution will be too much for a single treatment. You can prepare half the amount or store the finished solution until the next processing, since its properties do not change during storage.
Therefore, a ten-gram packet of powder is added to a liter of hot water, mixed thoroughly until the crystals are completely dissolved, and then the mixture is added to the remaining nine liters of water.
When and how to treat
Root feeding, that is, watering at the root, is needed by tomatoes during the period of active growth of root mass. They will promote the regrowth of young roots. Therefore, it is advisable to carry them out during planting and in the initial stage of growth, but not more than once every two weeks.
Tomatoes need foliar feeding most of all during the period of flower cluster formation, bud formation, flowering and ovary formation. Therefore, the first spraying of tomato with boric acid is carried out during the formation of the first flower cluster. To spray plants in open ground, it is better to choose a windless and dry day. You need to process so that the solution completely wets the flower brush.
All the subtleties of such processing in a greenhouse can be seen in the video.
Spraying a tomato with boric acid for the ovary on the second cluster is carried out when buds form on it, about two weeks after the first. In total, three to four treatments need to be carried out. By spraying the tomatoes correctly and on time, you can be sure that almost all the tomatoes set, the flowers and ovaries do not fall off.
Boric acid is not only a necessary fertilizer for tomatoes; spraying it during the growing season of plants is an effective remedy against late blight.
Therefore, to prepare the working solution, use a ten-gram bag of boric acid per five liters of water.
The effect of such a solution on tomatoes is enhanced by the addition of iodine - up to ten drops per bucket of solution.
If you want to increase the yield of tomatoes, speed up their ripening, and also improve the taste and beneficial properties of the fruit, spray them with a solution of boric acid, observing the timing and processing standards.















So should you spray your tomatoes with 1% or 0.1%?
0,1%
Hello, there is a mistake in the advice, you write: It is optimal for the plant and safe for humans to fertilize with a one percent solution of boric acid in warm, clean, non-chlorinated water.That is, a standard packet of boric acid weighing ten grams must be dissolved in ten liters of water. BUT THIS IS NOT 1% RR, BUT 0.1% RR.
So which is correct??????
then below is your advice: - Attention!
Only a 0.2% solution of boric acid in water has a protective effect against late blight. who is right?????
Hello Anna! You are right, if you dissolve 10 g of the drug in 10 liters of water, you will get a 0.1% solution. This is what is used for prevention and feeding. And a 0.2% solution is already therapeutic, a last resort.
How long can boric acid solution be stored?