Content
Tomatoes easily catch all sorts of pathogens, especially if the weather is favorable for this, and the gardener chooses the wrong planting site and/or makes serious mistakes in care. Fungicides for tomatoes help to cope with diseases caused by fungi. They are also used as a preventive measure. The range of such preparations is quite large, so you need to be able to choose and use them correctly, otherwise they will be useless at best, and harm the plants at worst.
What are the different fungicides for tomatoes?
The main classification of fungicides for tomatoes is based on their mechanism of action. Also among the basic criteria is the type of active ingredient that ensures the effectiveness of the drug.
Systemic fungicides for tomatoes
Systemic tomato fungicides are absorbed into the plant tissue after they reach the leaves and stems, forming a protective layer on the surface.Most of these drugs have a broad spectrum of action, but with regular use for several seasons in a row, pathogens can develop resistance to them.

To protect the tomato crop, systemic fungicides must be alternated with other agents.
Organic
Unlike inorganic fungicides for tomatoes, the effectiveness of which is ensured by copper or sulfur compounds (copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, colloidal sulfur), organic ones have a more complex composition. They work using derivatives of complex multicomponent organic acids or polycyclic compounds.
Biological fungicides for tomatoes
Fungicides for tomatoes of biological origin, which contain one or more strains of fungi and/or bacteria hostile to pathogens. They either destroy pathogenic microflora, or inhibit the process of its reproduction and parasitize on it.

Many biological fungicides for tomatoes simultaneously improve the quality of the substrate and have a beneficial effect on the immunity of tomatoes
Complex
These tomato fungicides contain more than one active ingredient. They are characterized by a wide spectrum and duration of protection. They are used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of fungal diseases.
The best fungicides for tomatoes
It is impossible to list the best fungicides for tomatoes.The optimally suitable drug in each case is determined individually, taking into account the stage of plant development, the need for treatment or prevention, the specific diagnosis, its severity and other factors.
Fungicides for tomatoes in a greenhouse
The experience of gardeners shows that tomatoes indoors suffer from diseases more often and they spread faster. In a confined space, this is almost inevitable if you do not follow the planting scheme, creating crowding in the beds and do not ventilate the greenhouse, getting rid of stale, humid air.
Thanos
A drug with two active ingredients (famoxadone and cymoxanil). The first destroys the pathogen on the surface of leaves and stems, forms a protective film, the second penetrates into tissues and encapsulates infected cells. It is used to protect tomatoes, potatoes, grapes, onions, sunflowers from fusarium and prevent infection with the corresponding fungus.
Bushes can be treated with Thanos throughout most of the season. The first spraying is 10-12 days after planting in the greenhouse, then at intervals of 8-12 days. The waiting period before harvesting the fruits is 14 days.
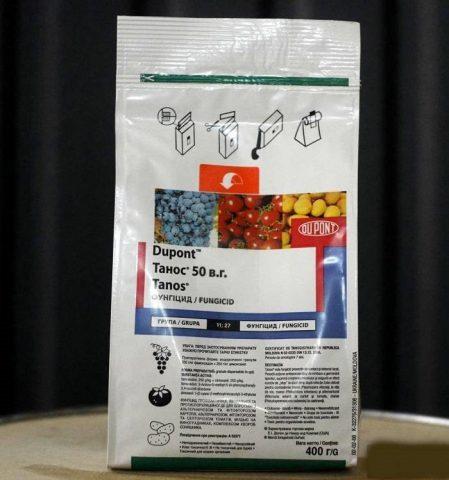

Among the undoubted advantages of the drug Thanos is its minimal danger to bees (Class III)
Agat-25K
Fungicide of biological origin for tomatoes in a greenhouse. At the same time, it works as a biostimulant to activate development processes and increase overall endurance. Also used for pre-planting seed treatment and spraying of adult plants. Used to protect against:
- root and other types of rot;
- late blight;
- Alternaria;
- true and downy mildew.

Treatment with Agat-25K improves the taste of tomatoes and increases their keeping quality
Baktofort
A bacterial fungicide used for the prevention and treatment of the vast majority of fungal and bacterial diseases of tomatoes, including:
- different types of rot;
- fusarium;
- late blight;
- Alternaria blight;
- cercospora;
- true and downy mildew;
- moniliosis;
- scab;
- blackleg;
- bacteriosis;
- bacterial cancer.
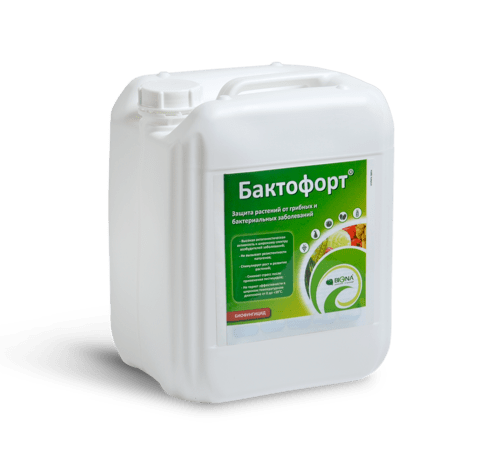

If the instructions are followed, Baktofort is harmless to human health and the environment and does not lead to sanitary pollution.
Fungicides for open ground tomatoes
In open ground, it is easier to provide tomatoes with normal aeration and follow the planting scheme recommended by the manufacturer. But there is much more contact with potential carriers of pathogens (wind gusts, precipitation, weeds, insects).
Profit Gold
A two-component (famoxadone and cymoxanil) systemic fungicide used to protect tomatoes, potatoes, onions and grapes from stem rot, late blight and anthracnose. Suitable for use in open ground due to maintaining efficiency despite frequent and heavy rains. The desired result is achieved for approximately 15 days.
The concentration of the drug Profit Gold in solution is determined depending on the degree of neglect of the disease (3 g per 2.5-5 liters of water). 3-4 treatments are allowed per season.

The waiting period before harvesting tomatoes after treatment with Profit Gold fungicide is 14 days.
Score
A complex fungicide with systemic action, suitable not only for tomatoes, but also for the vast majority of garden crops. On tomatoes it is mainly used to protect against Alternaria blight. The active ingredient is difenoconazole.
The drug Skor works not only as a fungicide, it increases the yield of tomatoes and has a positive effect on the taste of the fruit. There is also an increase in keeping quality, transportability, and overall stress resistance.
No more than two treatments are allowed per season. Scor begins to act within 2-3 hours after spraying. The effect lasts for 1-3 weeks. The interval before harvest is at least seven days.

Skor cannot be used in water protection zones of reservoirs.
Gamair
Systemic fungicide of biological origin. It is used to prevent damage to tomatoes by various types of rot and spots, late blight, Alternaria, powdery mildew and for the treatment of these diseases. Available in different forms - powder, concentrated suspension, tablets.
After treatment, Gamair begins to act immediately. The protective effect lasts for 7-20 days. The procedure can be repeated 2-3 times during the season with an interval of 2-4 weeks. There is no waiting period before harvest.

Gamair is suitable for pre-planting treatment of tomato seeds and spilling soil for seedlings
Fungicides for tomato seedlings
Treatment of tomato seedlings with fungicides helps strengthen the immunity of seedlings and activates the development of their root system. It is not advisable to use aggressive chemicals on young plants; it is better to use biological products.
Fitosporin-M Tomatoes
Microbiological fungicide to protect tomatoes from various types of rot and late blight. Provides a powerful immunostimulating and anti-stress effect. In addition to spraying shortly before planting in a permanent place, it is practiced to soak the roots in a solution immediately before transferring them to the garden bed.
Fitosporin begins to act from the moment the plants are treated
Trichodermin
Fungicide for protecting tomato seedlings from the vast majority of soil-borne diseases. Suppresses pathogens by releasing specific enzymes and antibiotics, competition for soil and direct parasitism. It is used for pre-planting treatment of seeds, soil, and spraying of seedlings.
In addition to fungal strains, Trichodermin contains a complex of organic acids. They have a beneficial effect on the immunity and overall endurance of seedlings.

The number of treatments with Trichodermin is not limited, there is no waiting period before harvesting
Fitolavin
Bacterial fungicide with antibiotic properties. On tomatoes it is used to prevent diseases caused by the corresponding microorganisms:
- bacteriosis;
- black bacterial spot;
- bacterial wilt;
- bacterial cancer;
- crown rot;
- necrosis of the stem core.
Fitolavin is used for watering and spraying seedlings. Begins to act within 12-24 hours. The protective effect lasts for 10-38 days.

After treating seeds with Fitolavin, there is an increase in the percentage of their germination and faster germination
Which to choose
When choosing a fungicide for tomatoes, you need to consider several basic criteria:
- Stage of development.Not all fungicides suitable for mature plants are used on tomato seedlings. Young seedlings need gentle preparations. In addition, there are specialized products for pre-planting seed treatment.
- Diagnosis and confidence in it. If the symptoms can be identified accurately, you can use a drug that is effective specifically against this disease.
- The degree of neglect of the problem. When the disease is noticed at an early stage and/or the pathogen affects only individual bushes, milder means (for example, of biological origin) can be used. In severe cases, only agrochemicals help, starting to act immediately and aggressively.
- Place of cultivation. If tomatoes are planted in a greenhouse, they can be treated with contact fungicides that remain exclusively on the surface of the leaves and stems. When planted in open ground, their validity period varies greatly depending on the frequency and intensity of precipitation and air temperature, so it is more advisable to use systemic preparations in outdoor beds.

When there is no complete certainty in the diagnosis, broad-spectrum drugs are used that destroy different types of pathogens
Rules of application
Before using any tomato fungicide, you must read and follow the manufacturer's instructions.The most common mistakes gardeners make are arbitrarily increasing the concentration of the drug in the solution and/or shortening the intervals between treatments, hoping to get a faster and more pronounced effect. It is likely that such actions will make the crop unsuitable for food or even destroy the bushes.
Each fungicide for tomatoes has its own nuances of use. But there are also general rules for their use:
- Treat not only the bushes themselves, but also the soil in the garden bed. The causative agents of many diseases enter plants when leaves come into contact with the substrate.
- Carry out continuous spraying of plantings. Not only obviously infected, but also visually healthy tomatoes are treated with a fungicide solution. It is possible that the pathogen is also present on them, but symptoms have not yet appeared due to the long incubation period.
- Use a fine spray bottle. It allows you to spray the bushes as evenly as possible.
- Prepare the solution immediately before the procedure. Most fungicides for tomatoes have a minimum shelf life and lose their beneficial properties within a few hours.
- All work with the drug, starting from the moment of preparing the solution, should be carried out without removing at least the minimum set of personal protective equipment.
- Carry out the treatment in the evening, after sunset. During the day, the drug evaporates faster and may not have time to be absorbed into the tissue. In addition, burns from direct sunlight are possible.

When spraying bushes, you need to wear closed, waterproof shoes and clothes with long sleeves and trousers.
Conclusion
Fungicides for tomatoes are one of the most effective means for the prevention and treatment of fungal diseases. Such preparations are presented in a wide range in stores, so it can be difficult for novice gardeners to make a choice. The most important criteria to consider are the main active ingredient, the mechanism of action, the specific diagnosis, its severity and the age of the plant.








