Content
Growing tomatoes in open ground has its own secrets and rules. One of the important stages is bush formation or pinching side shoots. Not all summer residents use the method stepsons, as a result, either the crop does not have time to ripen, or the rows of tomatoes become too thick and begin to hurt.
Why pinching side shoots on tomato bushes is necessary, how to properly pinching tomatoes in open ground, and how formation methods depend on the type of plant and its variety - all in this article.
What is stepsoning
The tomato bush is very branched; new shoots, leaves, flowers and ovaries constantly appear on it. Stepchildren are usually called vegetative (dormant) buds that are located in the axils of the leaves. Up to a certain point, these buds usually sleep, but as soon as the tomato throws out all the ovaries and begins to form fruits, additional shoots begin to grow from these buds.
The stepchildren eventually produce full-fledged side stems with flowers and ovaries. It would seem that what’s bad here, because an increase in the number of fruits only benefits the gardener?
But it's not that simple. A large number of inflorescences and ovaries does not at all indicate an increase in yield. Quite the contrary: extra stepsons reduce the quality of the fruit and interfere with their ripening.
The damage caused by stepchildren on tomatoes is as follows:
- reduce productivity;
- help reduce the size of all fruits;
- extend the ripening period of tomatoes;
- thicken the plantings, leading to severe leaf growth of the bush, which leads to the development of infections and diseases of tomatoes;
- too many fruits can lead to breakage of shoots;
- they take away from the plant the forces it needs for the full ripening of the first fruits;
- lead to deformation and strong growth of bushes.
As a result, the tomato bushes that are not rooted produce a large number of fruits, but these tomatoes do not have time to ripen before the onset of autumn cold, since the plant does not have enough strength for such a volume of harvest. By autumn, the gardener will receive a bush with green and small fruits.
Is it always necessary to remove side shoots on tomatoes?
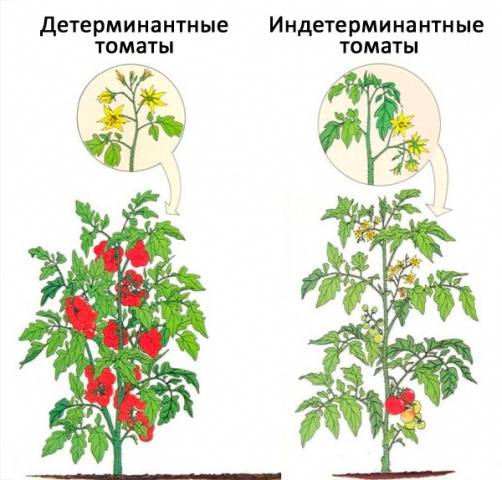
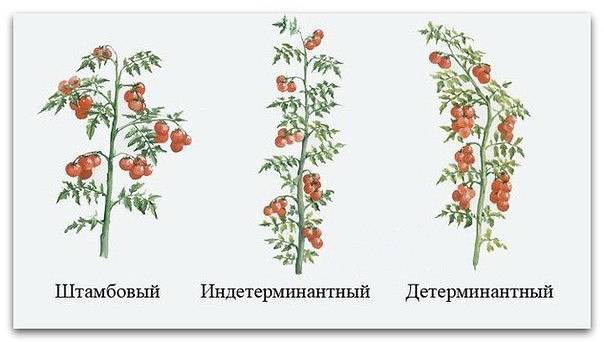
Forming tomatoes in open ground is not always necessary; a more thorough pinching procedure should be carried out in greenhouses. The fact is that domestic gardeners, as a rule, plant early-ripening determinate varieties of tomatoes in open ground.
Determinate varieties of tomatoes are characterized by the fact that after a certain number of ovaries appear on the bushes (usually from three to seven), the growth of side shoots stops automatically. Thus, tomatoes do not need to be shaped and controlled - as many stepsons will grow on the bushes as required to ensure a normal harvest.
However, this only applies to super early or early determinant varieties whose fruit ripening ends in mid-summer. The climate of most regions of Russia is such that already in August rains and a decrease in temperature begin, and in September there may be the first frosts.
In such climatic conditions, tomatoes do not ripen; they can only begin to get sick and drop their ovaries along with the green fruits. Therefore, there is an unspoken rule among the country’s gardeners: “Only those tomatoes that have formed before the first of August will have time to ripen.” What to do with the remaining shoots and inflorescences? They must be removed or broken off, that is, pinched. This is what it's all about pinching tomatoes in open ground for varieties with limited growth (determinant).
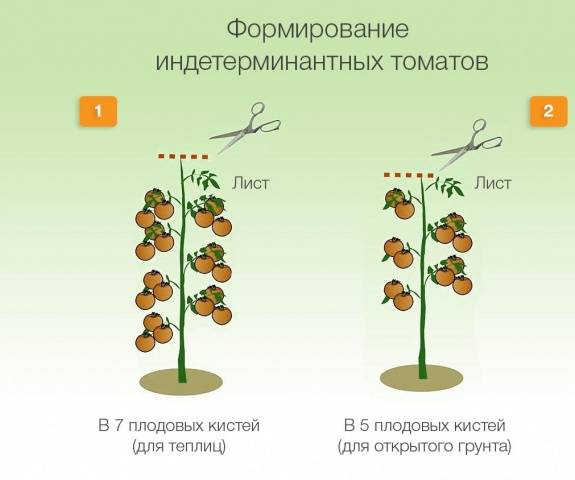
Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes have the following feature: stepsons and additional shoots on the bushes are constantly formed, and the main stem does not stop growing. To control the number of fruits and form a bush, you have to constantly pinch the shoots of such tomatoes.
Stepchildren begin to appear en masse when 5-7 ovaries are formed on the bushes (depending on the variety). From now on The gardener needs to periodically, once every 7-10 days, inspect the tomato bushes and break off the shoots.
Scheme of formation of indeterminate tomatoes in open ground is somewhat different from pinching determinate varieties.In this case, not only the lateral shoots under the tomato leaves are pinched, the tops of the main stems also need to be broken off. If this is not done, the bush will continue to grow upward, simultaneously forming inflorescences and ovaries - all this weakens the plant and inhibits the ripening of fruits.
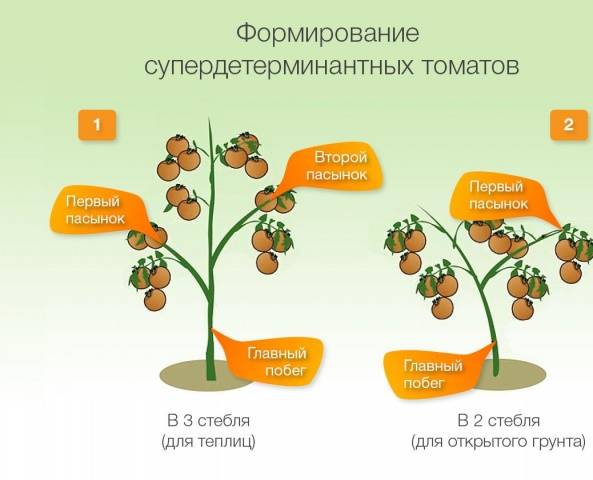
Today, breeders have developed many varieties of tomatoes that, in general, do not form stepsons. This, of course, makes caring for the beds much easier - you can plant such tomatoes and wait for the harvest, just by regularly watering the bushes.
These varieties include superdeterminate and hybrid tomatoes. These species are “programmed” to form a certain number of ovaries, after which the growth of the bushes stops.
How to remove stepsons
Proper pinching of tomatoes not only ensures an early harvest and large fruits, but the health of the entire plant directly depends on it.
Here are a few rules that a gardener should follow:
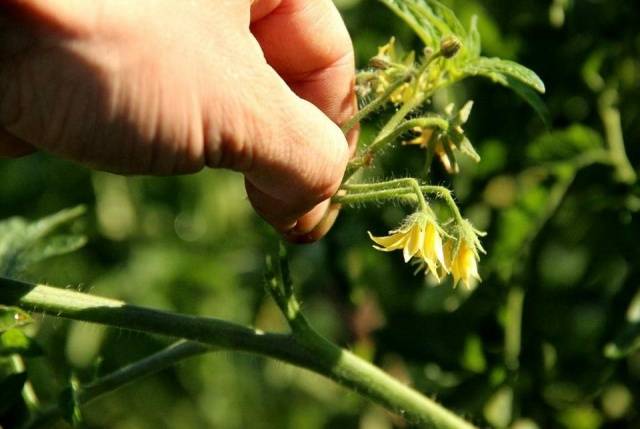
- The formation of tomatoes in open ground is carried out in the morning. It is in the morning that the tomato bushes are maximally saturated with moisture, the stems are elastic and fragile, so the stepson will break off more easily, and trauma to the plant will be minimal. In addition, by the end of the day and before the onset of a cold, damp night, the tomato will have enough time for the wounds to heal and dry out - the risk of infection of the broken areas of the shoots is minimal.
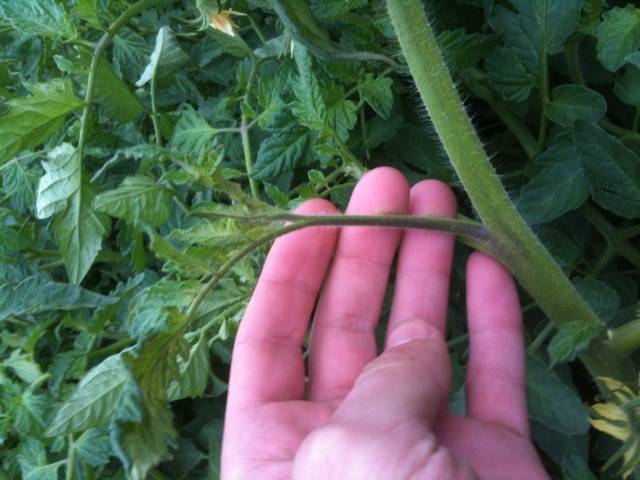
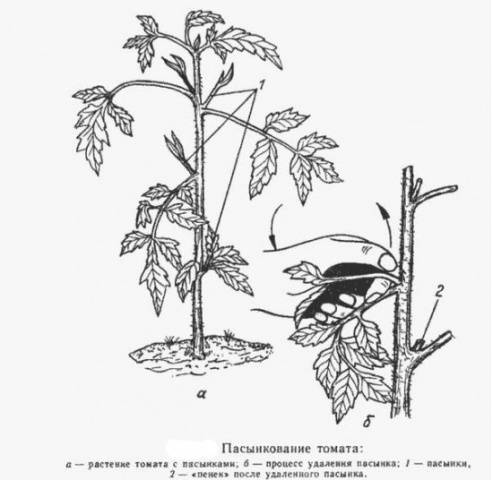
- The optimal time to remove shoots from a tomato is when the length of the shoots is from three to five centimeters. Such shoots have not yet had time to take away much strength from the tomato bush; the place where they break off will be inconspicuous, and the wound will be small.It is better not to break off larger shoots; if the gardener missed them or did not have time to remove them at a “young” age, you need to pinch the tops of these shoots.
- It is best to pick off the stepsons by hand, but it is recommended to wear rubber gloves to avoid introducing infection into the wounds. The stepson is pinched with two fingers and swung a little from side to side, gradually breaking off.
- If a knife or scissors is used to remove shoots, it is necessary to ensure the sharpness of the blades - they should be very thin in order to injure the tomatoes less. After processing each bush, the blade is disinfected with any means (for example, a one percent solution of potassium permarganate).
- You should not throw torn tomato shoots on the ground, they can become a source of infection. The shoots need to be collected and thrown away from the garden.
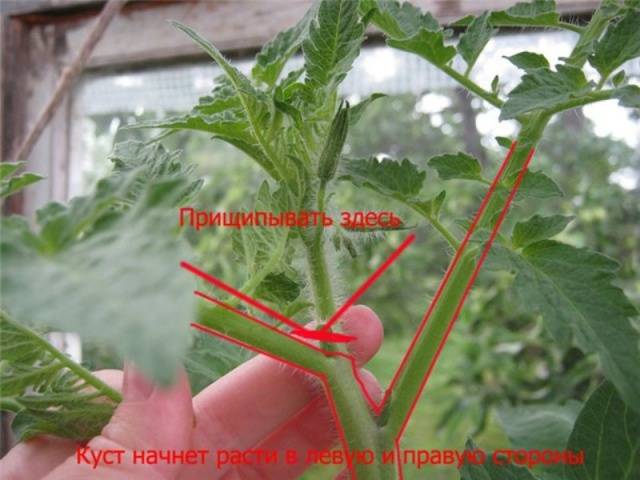
- The development point of tall tomatoes is pinched in the same way as the side shoots. You need to leave 3-4 sheets under the break point.
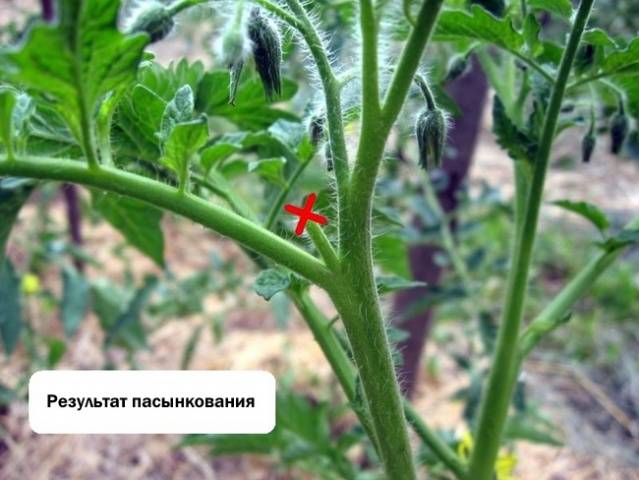
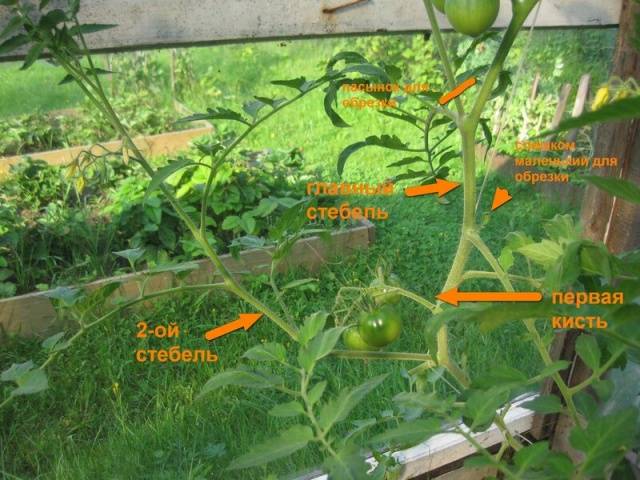
An approximate diagram of tomato pinching is shown in the photo below.
How to form tomatoes in open ground
The method or scheme for forming tomato bushes depends on several factors:
- type of plant (determinate or indeterminate);
- tomato varieties (stunted or not);
- speed of tomato ripening;
- weather conditions (in cloudy and cool summers, even determinate varieties run the risk of not having time to produce the entire harvest, so the bushes are “thinned out” a little, removing several stepsons);
- climatic features of the region (if in the southern regions even indeterminate varieties can bear fruit until November, in the northern part of the country only those ovaries that have managed to take shape in the first half of summer are left);
- the requirements of the gardener himself: for some, the quantity of fruits is important, while for others, the quality and size of the tomatoes is a priority.
If the owner of the plot puts productivity first, it is necessary to grow tomatoes with several stems.
Forming tomatoes into one stem
The method of growing tomatoes with one stem is most often used in greenhouse conditions, but it can also be used in open ground, especially when tall indeterminate varieties are planted.
This principle obliges the gardener to remove absolutely all the stepsons, leaving only one central stem. As a result, only a certain number of ovaries will be formed, which is regulated by the tomato variety.
The complexity of the method lies in the fact that you have to constantly monitor the condition of the bush and remove new shoots in a timely manner. In addition, formation into one stem sharply reduces the total number of fruits - there will be 3-5 ovaries on the bushes.
This method is suitable for those who grow early tomatoes for sale, because the plant, not weakened by its stepsons, devotes all its strength to ripening the first (and last) fruits. It is possible to get the harvest 10-14 days earlier, and the cost of tomatoes, as you know, is very high during this period. In addition, the fruits will be large and beautiful.
Forming tomatoes into two stems
Much more often, domestic gardeners use methods of forming bushes with several stems, because this way they can increase the yield of tomatoes.
In order to get two trunks on the bushes, it is necessary to remove all the stepsons, leaving only the one located under the very first brush. This side shoot will become a full-fledged stem, and almost as many fruits will ripen on it as on the central stem.
Thus, it will be possible to almost double the tomato yield, while the speed of their ripening will be slightly less than in the first case. The tomatoes themselves may also turn out to be somewhat smaller than if the bush were formed into only one stem.
Forming bushes into three stems
This is the most optimal option for forming tomato bushes, which is why it is most often used when growing tomatoes in open ground.
To form a bush with three stems, it is necessary to determine the central shoot and select the first ovary. Now it remains to monitor the formation of leaves below this ovary: you need to leave the stepsons growing from the axils of the first and second leaves after the ovary.
Since the leaves on tomatoes appear alternately, the left stepsons should be directed in opposite directions - this will preserve the shape and balance of the bush (as in the photo).
Forming tomatoes into three stems allows you to get maximum yield; the fruits will be quite large and ripe. Only in the northern regions or in some areas of the middle zone may a few unripe fruits remain on the bushes. In this case, green tomatoes are picked and left to ripen in a dry and warm place (for example, on a windowsill).
Results
Having heard about pinching tomatoes and forming bushes into several stems, you don’t need to immediately rush to your seedlings with scissors. It is not necessary to remove and pinch shoots in every case; this procedure is required only for indeterminate varieties with uncontrolled growth. In other cases, the gardener must independently decide on the need for pinching, based on the condition of the plants, the number of ovaries on them and weather conditions in his region.
You can learn more about planting tomatoes in open ground from the video: