Content
All gardeners grow garlic, because it is not only an ingredient in many dishes, but also has healing properties. However, not everyone is able to get a good harvest of this spicy vegetable. The reason for this is crop diseases that affect garlic at different stages of development. And if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the losses will be significant. Therefore, every gardener should know the main diseases of garlic and their characteristic symptoms.

Weakened garlic can suffer from several diseases at the same time
Fungal diseases of garlic
Most often, the spicy vegetable suffers from fungal activity. They begin to actively reproduce in the presence of favorable conditions and can spread not only to plantings of garlic, but also onions. To successfully fight fungal diseases, you need to be able to recognize them at an early stage of development.
Rust
The causative agent is the fungus Puccinia alli.The disease does not cause rotting of the stem and head of garlic, so it can be successfully combated. When infected, white dots appear on the feathers of the spicy vegetable, which eventually turn red-brown as spores mature on the affected areas. This leads to disruption of the process of photosynthesis in the leaves. As a result, garlic lags behind in development, its underground part does not grow because it does not receive enough nutrition.
It is recommended to start treatment immediately when white spots appear on the leaves of garlic. To do this, you must first remove all damaged feathers and burn them, and then treat the plantings with Strobi, Topaz or Quadris fungicide. If necessary, repeat the procedure after 7-10 days.
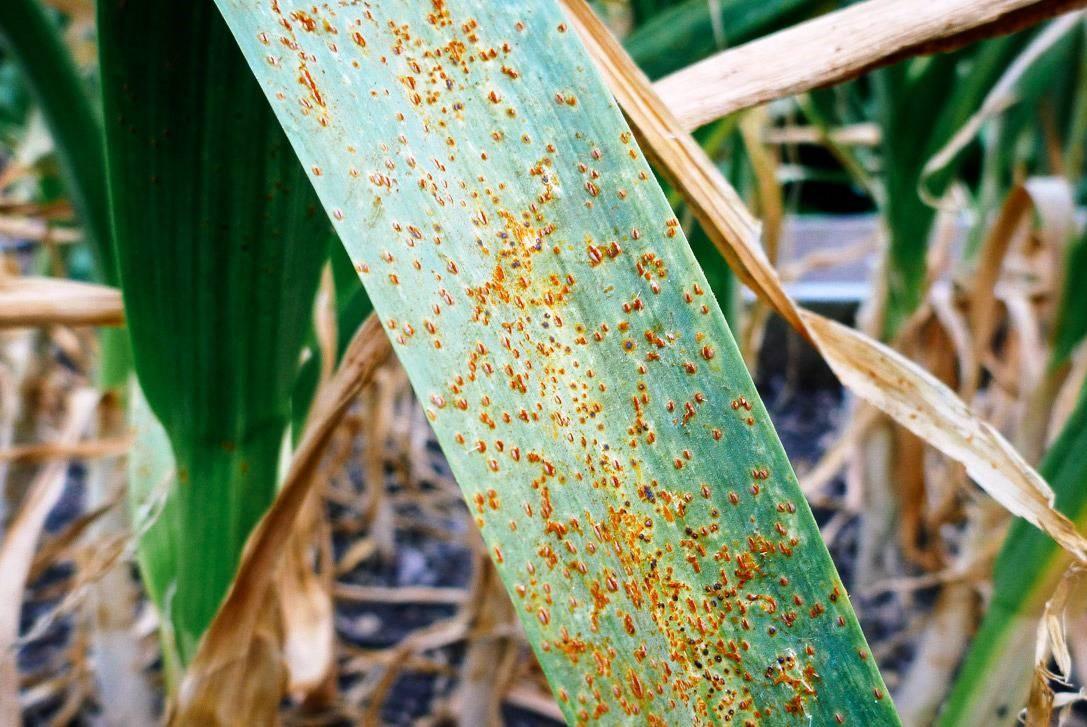

Garlic cloves affected by rust are edible
Downy mildew
Caused by the fungus Peronospora destructor Casp. The disease progresses rapidly with high air humidity and can lead to the loss of the entire crop. When affected, a gray-violet coating appears on the leaves of garlic, indicating conidial sporulation. Subsequently, the symptoms of the disease appear in the form of local yellowing spots. In the absence of control measures, the mycelium moves to the base of the leaf rosette and spreads to the bulb, which causes it to rot.
It is possible to successfully fight this garlic disease only at the initial stage. To do this, it is necessary to treat the plantings with the fungicide Ridomil Gold or a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture. You need to spray garlic several times until the signs of pathogenic microflora disappear.
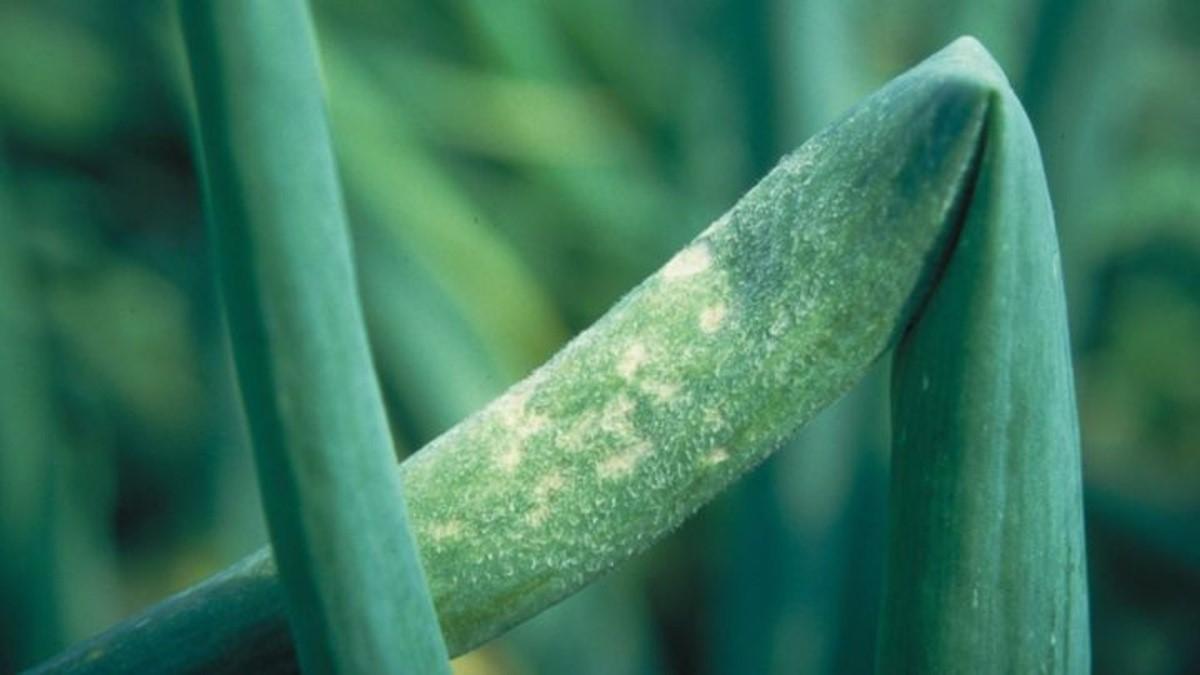

Downy mildew is also called peronosporosis
Fusarium
The disease is caused by Fusarium fungi. Pathogens enter the vascular system of the spicy vegetable through open wounds in the roots and then spread throughout the plant. The disease progresses in hot weather, reducing yields. When it develops, the development of the root system is disrupted, which ultimately leads to the death of garlic.
Fusarium can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- brown stripes on leaves;
- pink or purple bloom on the stem and in the axils of the plates;
- white speckles at the base of the head;
- the teeth soften;
- the peduncle fades;
- the roots rot.
This fungal disease of garlic is dangerous because it is impossible to recognize it at the initial stage of development. Therefore, you can only use preventive measures to prevent the appearance of fusarium in the garlic bed. To do this, it is necessary to water the soil before planting and spray the garlic against disease with the fungicide Maxim or Previkur Energy, and also treat the seed with Fundazol, soaking it in it for half an hour.
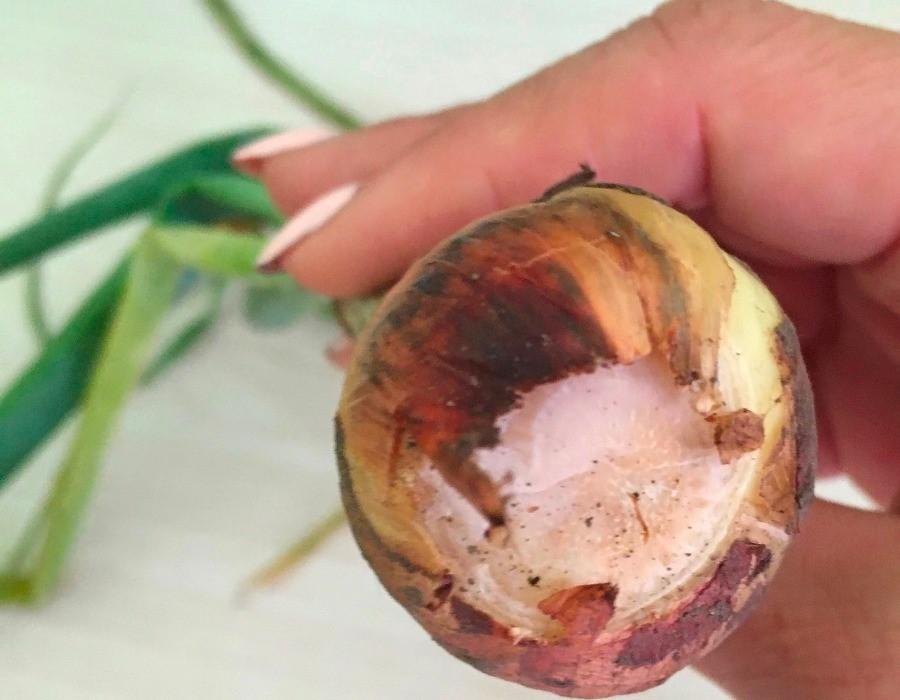

Fusarium is also called bottom rot
Cervical rot
The most common disease not only of garlic, but also of onions. Its causative agent is the fungus Botrytis allii Munn. Pathogenic microflora begins to actively multiply even before harvesting at the stage of lodging of leaves. The causative agent of the disease penetrates the plant tissue through open wounds as a result of mechanical damage, as well as through a loosely closed neck. The lesion cannot be detected immediately, so diseased heads, along with healthy ones, end up in storage. The affected areas soften, become yellow-pink, watery, and begin to emit an unpleasant putrid odor. As a result, diseased garlic becomes covered with thick gray mold.
To prevent the massive spread of this disease in garlic plantings, it is recommended to treat them several times per season with Fundazol, Quadris, and Skor.

Increased nitrogen content in the soil provokes the development of neck rot.
White rot
The disease can affect garlic during the growing season and storage. It is caused by the insidious marsupial fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, which can make the soil unsuitable for growing crops for many years. White rot begins to appear clearly in the middle of the season until harvest.
Main signs of damage:
- yellowing and dying of leaves;
- roots and scales are covered with thick white mycelium;
- the teeth become watery and rot.
For the treatment and prevention of white rot of garlic, it is recommended to treat plantings with copper-containing preparations - Abiga-Peak, Bordeaux mixture, as well as systemic agents, including Previkur Energy, Profit Gold, Ordan.
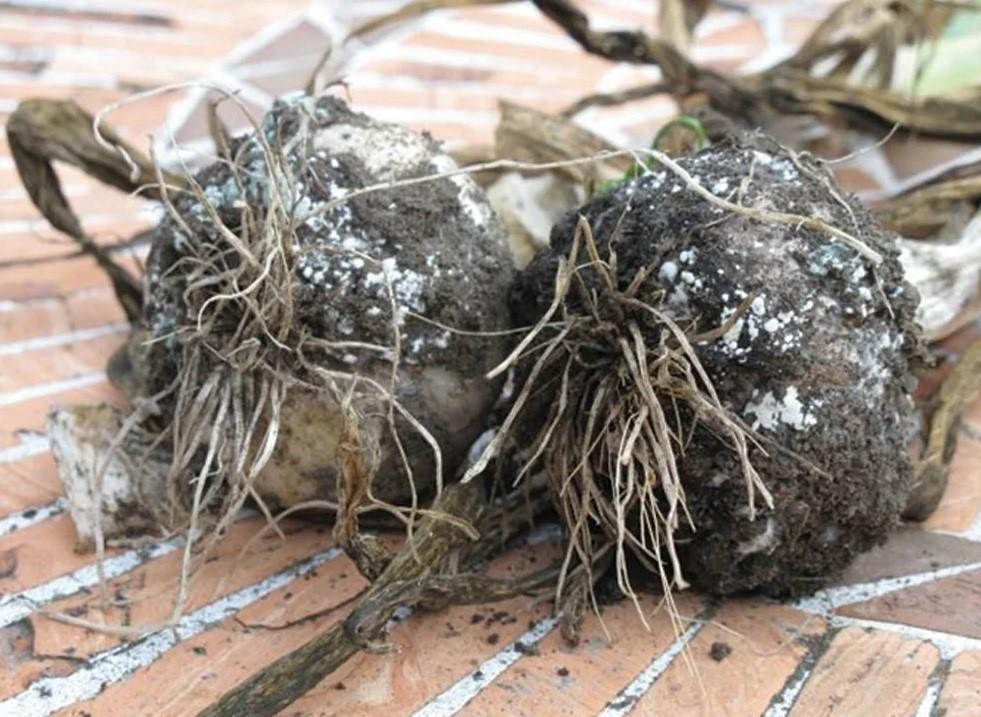

White rot progresses against the backdrop of a sharp cold snap and high humidity
Black mold or aspergillosis
The disease is caused by certain types of Aspergillus fungi. Black mold appears when garlic is stored at temperatures above +18 °C. Initially, signs of the disease appear on top of the heads, and then it penetrates inside the cloves. As a result, the affected areas soften and become covered with black mushroom growths. The causative agent of the disease spreads quickly through the air, as well as through contact between diseased and healthy heads of garlic.
Black rot can only be dealt with by removing infected specimens and treating the crop with Maxim.Also, to prevent damage, it is necessary to feed the spicy vegetable in a timely manner to strengthen its immunity and spray the plantings with Ridomil Gold.
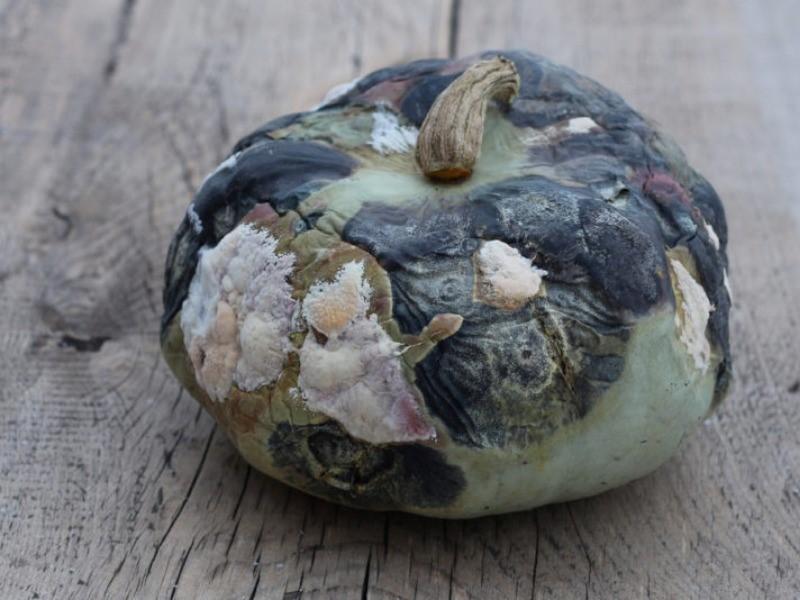

Unripe and poorly dried heads are especially susceptible to aspergillosis.
Green or blue rot
The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Penicillium. Symptoms of damage become noticeable during the storage period of the crop, namely two months after planting. First of all, the fungus penetrates into damaged, frozen heads, and then spreads to healthy specimens. Humidity above 90%, temperature within +1-3 °C and lack of ventilation in the storage contribute to the rapid progression of green or blue rot.
When infected, watery brown spots appear on the bottom of the garlic and on the side scales. Subsequently, the affected tissue softens and becomes covered with a gray coating, which eventually becomes green or blue, indicating sporulation of the fungus. As a result, the garlic becomes dark in color and empty inside. It breaks apart easily when pressed.
For treatment, it is necessary to water the plantings with Maxim during the growing season, and spray the vegetative part with copper-containing products.
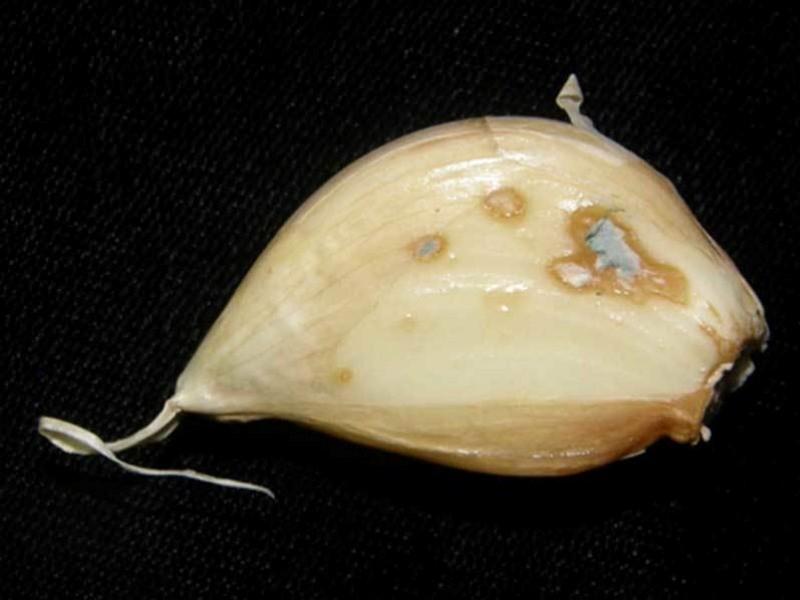

Green or blue rot develops due to a lack of potassium in the soil
Bacterial diseases of garlic
Garlic is also affected by bacterial diseases. Most often, infection occurs through an infected instrument and when using low-quality planting material. The danger of such diseases is that they are difficult to cure. Therefore, experienced gardeners recommend getting rid of them when individual infected specimens appear.
Bacterial rot
This disease most often affects onion and sometimes garlic plantings. It can be recognized by small brown spots randomly located on the teeth. Also, one of the signs of damage may be glazing of the heads, as if they were frozen or boiled. Sometimes, due to bacterial rot, garlic cloves acquire a pearlescent yellow tint and begin to emit a putrid odor.
The development of the disease is facilitated by growing crops on depleted soil, insufficient care and getting burns during the growing season. During storage, bacterial rot begins to progress in conditions of high humidity and insufficient ventilation of the room. To prevent damage, it is recommended to feed garlic with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers in a timely manner.
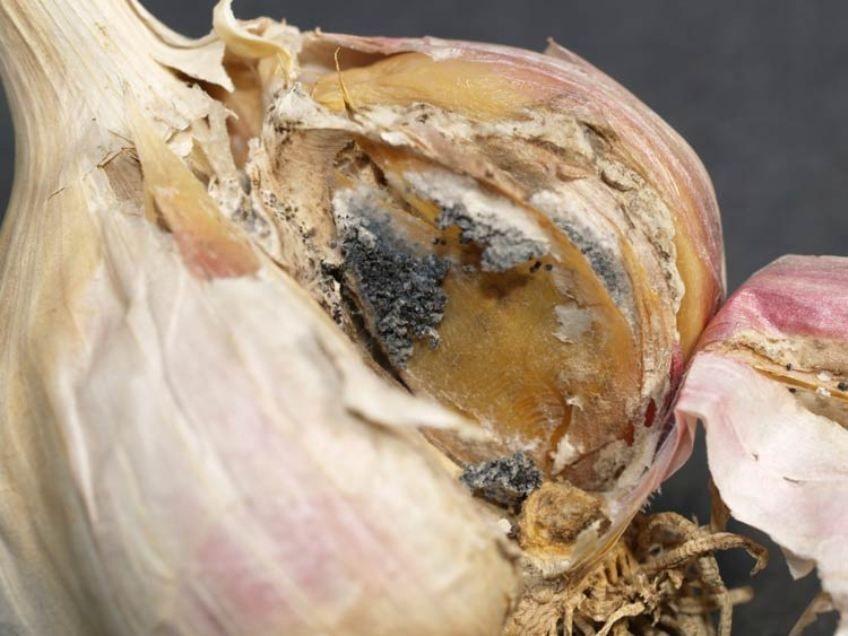
The causative agent of bacterial rot overwinters in plant debris
Viral diseases of garlic
These are diseases of winter and spring garlic; there are no effective treatments. However, this crop suffers from viruses much less frequently than other vegetables. If signs of damage appear, diseased specimens must be immediately uprooted and burned.
Mosaic
The disease begins to progress in summer with high humidity and high temperatures.
Signs of damage:
- light spots and stripes on feathers;
- causeless wilting of leaves;
- corrugation of plates;
- deformation of inflorescences.
The mosaic virus interferes with the maturation of the heads. Therefore, they are poorly stored in the future.
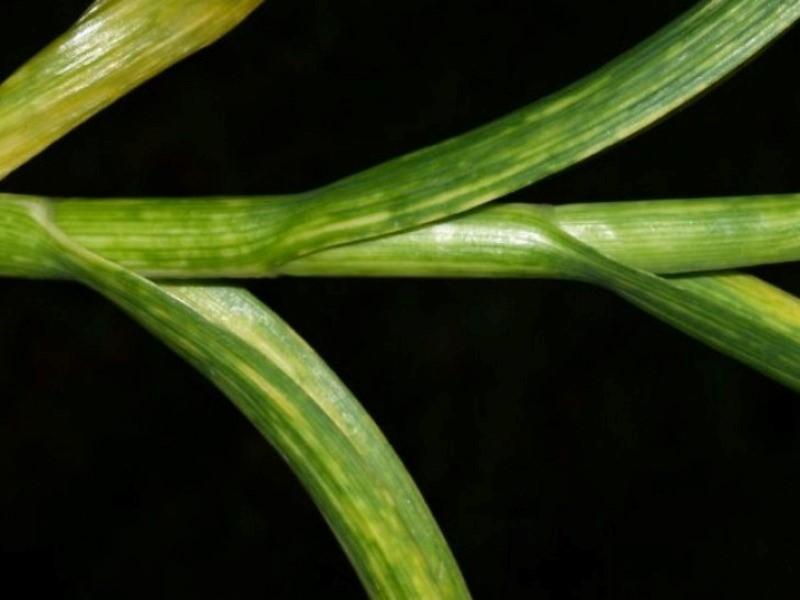

Ticks carry mosaic virus
Yellow dwarfism
The incubation period of the disease is 1-2 weeks. The virus does not persist in the soil and is found only in the heads. When affected, the leaves lose turgor, curl and lie down.As a result, the affected specimens stop developing and are stunted in growth. Yield losses can be 25-50%.
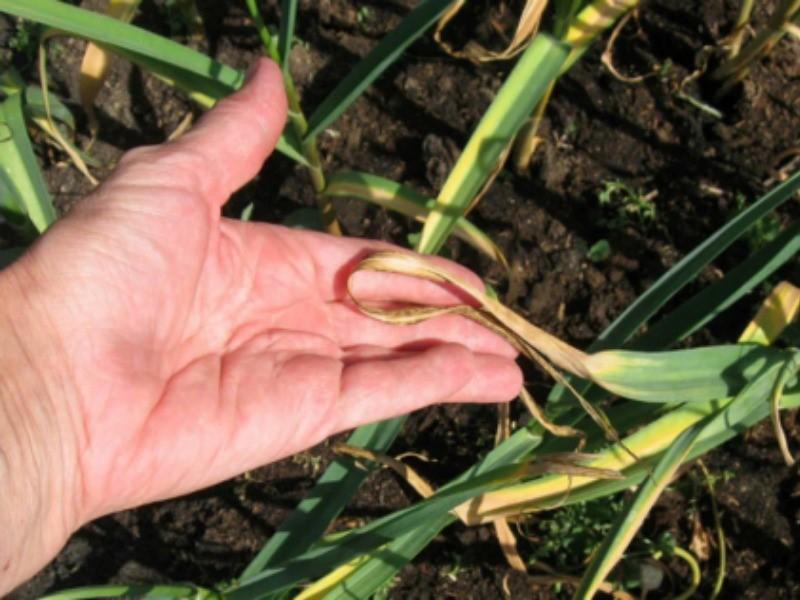

Yellow dwarfism often affects not only garlic, but also shallots
Non-communicable diseases
Sometimes garlic diseases develop due to improper care or inappropriate growing conditions. In this case, the problem does not lead to the loss of the crop, and it is easy to correct if measures are taken in a timely manner.
Yellowing
Most often, yellowing of garlic leaves occurs due to a lack of nutrients in the soil and moisture. This symptom also appears when the spicy vegetable is grown in heavy clay soil.
To eliminate the problem, it is recommended in hot weather to water once every 5-7 days, soaking the soil to a depth of 7-10 cm. In the case of heavy soil in the garden bed, which has led to stagnation of moisture, it is necessary to add sand and loosen the soil. And if yellowing occurs due to lack of nitrogen, it is recommended to water the plantings with ammonium nitrate at the rate of 30 g per 10 liters of water.
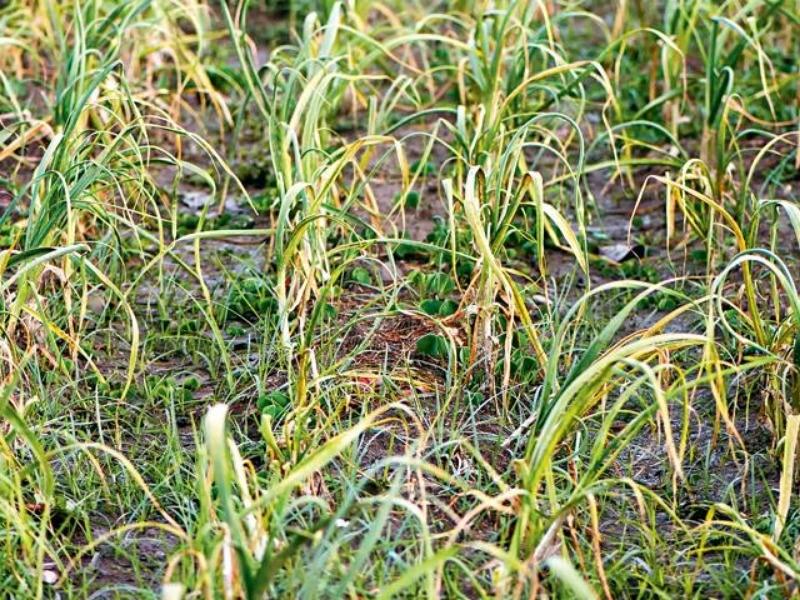

Yellowing of the leaves of a winter crop may be caused by insufficient planting depth
Drying
The problem arises when planting garlic in depleted soil with insufficient moisture levels. In this case, spraying the plantings with growth stimulants - Zircon, Energen, Epin, followed by fertilizing with ammonium nitrate will help correct the situation. It is also recommended to adjust the watering so that the top soil in the garden bed dries out only 2 cm between waterings.
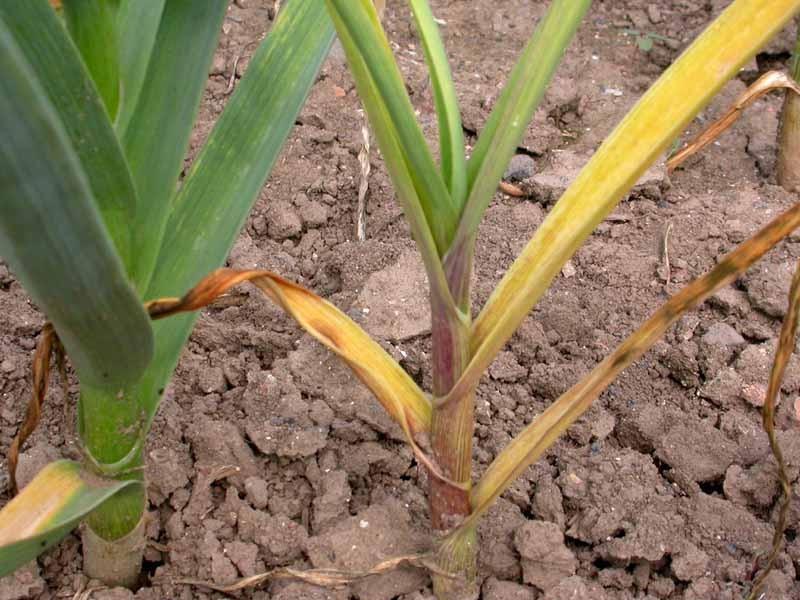

Drying of garlic can occur due to pest damage
Prevention of garlic diseases
To guarantee a good harvest of spicy vegetables every year, it is necessary to pay increased attention to preventive measures. They are unable to completely eliminate damage, but reduce this likelihood to a minimum.
Prevention of garlic diseases includes:
- careful selection and processing of planting material;
- compliance with crop rotation;
- timely removal of plant residues from the site and burning them;
- fertilizing with mineral fertilizers taking into account the stage of plant development;
- regular weeding and loosening of the soil
- thoroughly drying the crop before storing;
- ensuring optimal savings conditions;
- periodic disinfection of garden tools.
Conclusion
Knowing the main diseases of garlic and their characteristic symptoms, you can count on timely measures taken to help protect the harvest. However, it is still worth paying increased attention to the selection of varieties that have increased resistance to negative factors. This will significantly reduce storage losses of garlic and the likelihood of damage during the growing season.








