Content
Central Russia, and especially the south, are quite close in basic conditions to those regions where peanuts grow. On an industrial scale, the crop can be grown in areas where there are no early autumn frosts. At home, amateurs grow peanuts even on windowsills.
What family does peanut belong to?
The plant is classified as belonging to the legume family, genus Peanut. In everyday life, the crop is also called groundnut due to the characteristics of the final phase of its development. To ripen, the resulting pods, or beans in botanical terminology, with future grains bend towards the ground and gradually penetrate the soil. When harvesting, the beans are dug up.
Description of the peanut plant
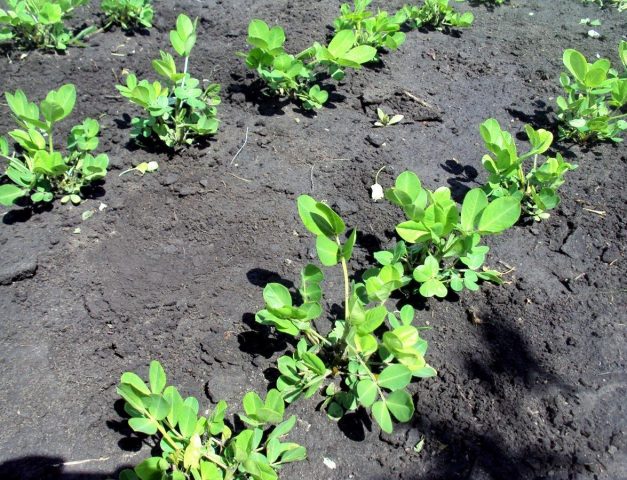
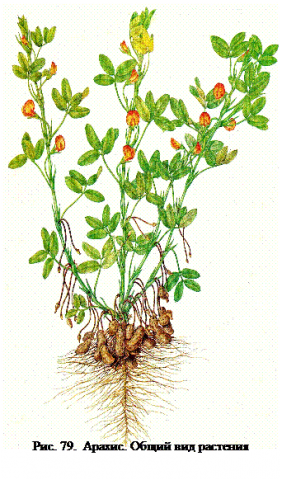
An annual vegetable plant that self-pollinates, rises above the soil as a lush green bush up to 60-70 cm. Taproots with many shoots provide sufficient nutrition to the erect stems, which in different varieties of peanuts are:
- hairy or hairless;
- with slightly protruding edges;
- with branches that go upward during flowering or descend after the formation of bean buds.
Alternate, pubescent leaves of different lengths: 3-5 or even 10-11 cm.They consist of several pairs of oval leaf blades, with a slightly pointed tip.
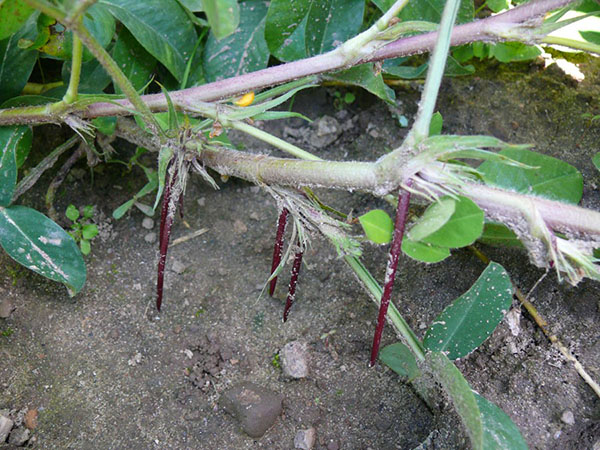
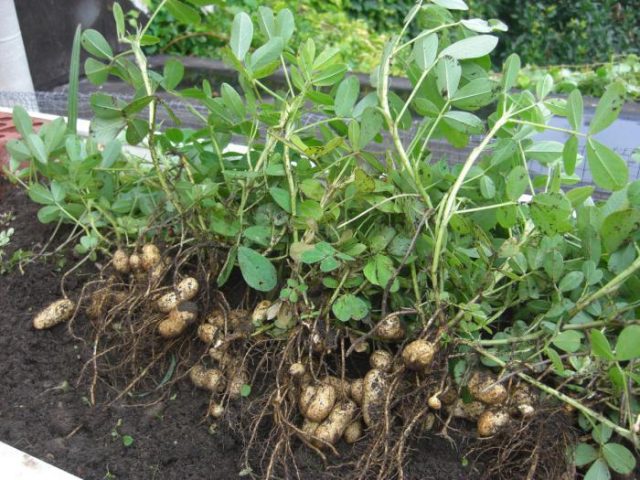
The pedicels emerge from the axils of the leaves and bear 4-7 flowers of the moth type, which is typical for leguminous grasses, which include peanuts. The petals are whitish or deep yellow. The peanut flower only blooms for a day. If pollination has occurred, bean ovaries begin to form. At the same time, the growth of the gynophore occurs, a section of the receptacle, which increases and, as the branch tilts, grows into the ground, pulling with it the miniature ovary of the bean to a depth of 8-9 cm. Schematic pictures show how peanuts grow. One bush can produce up to 40 or more beans.
Typically, beans are produced only from the peanut flowers located at the bottom of the bush. And also from the so-called cleistogamous flowers that the plant creates underground. The apical flowers, above 20 cm from the ground surface, do not produce fruit. Not all gynophores with bean ovaries grow into the ground; some simply dry out.
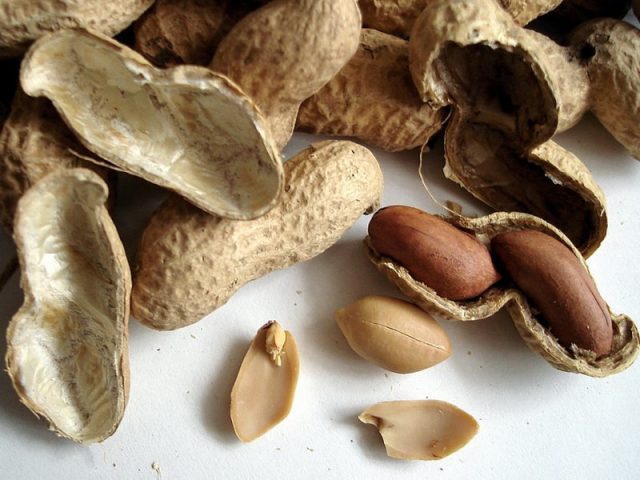
The fruits are oblong, swollen beans, with bandages, 2-6 cm long, with a wrinkled skin of an inconspicuous sand color. Each contains from 1 to 3-4 voluminous seeds. The grains are from 1 to 2 cm, oval, with a reddish-brown husk that easily separates after processing. The seeds consist of two hard, cream-colored cotyledons.
Where do peanuts grow?
The original legume plant spread throughout the world from South American territory, where Bolivia and Argentina are now located.
Where do peanuts grow in Russia?
The culture is becoming increasingly popular, including in temperate regions.The ripening period for different varieties of peanuts, from 120 to 160 days, is acceptable for some Russian regions. The main conditions for growing legumes are sufficient light, heat, and moderate humidity. Where summer temperatures do not fall below + 20 °C, and there are no early autumn frosts, peanuts grow well. If the thermometer readings are lower than recommended, development slows down until the plant dies. Hobbyists also grow peanuts in harsher conditions, using various effective shelters. In areas with warm summers, peanut seeds will ripen by the end of September, beginning of October, showing a yield of 1-2 t/ha, depending on the agricultural technology used.
In the world
Peanuts grow in many countries on large agricultural areas. First brought to Spain, the crop takes root in tropical Africa, where it becomes a valuable nutritious product. Here, in the territory of modern Congo, Senegal, and Nigeria, they learned to extract vegetable oil from peanut seeds. Gradually, peanuts from the legume family, which grow well in poor soils, spread throughout the countries of Southeast Asia and came to North America. Peanuts have gained particular popularity in the United States since the beginning of the 19th century. After 100 years, many areas previously occupied by cotton turned out to be under peanuts, which are also processed for technical purposes.
The largest areas cultivated for peanuts belong to India, China, Indonesia and other countries in this region. Culture also plays a leading role in the economies of a number of African countries.Peanuts grow on an industrial scale in the USA, Mexico, Argentina, and Brazil. Specific agricultural technology has been developed in the form of various fertilizers and growth stimulants, which helps accelerate the development of gynophore, reduces the number of underdeveloped ovaries and increases the volume of the harvest.
How do groundnuts grow?
For successful cultivation of a legume crop of tropical origin, choose the sunniest place on the site without the slightest shadow. You can see how peanuts grow in the photo. In the nature of Russia, the plant does not spread on its own. A short warm period with temperatures above + 20 °C forces lovers of exotic vegetables to grow them through seedlings. Heat-loving peanuts also grow in Russia.
Landing
In the south, the seeds of the crop are sown when the soil warms up to 14-15 °C. According to the phytocalendar, this period coincides with the flowering of acacia. Sprouts develop quickly in warmth at a temperature of + 25-30 °C.
For successful cultivation in a temperate climate, the following requirements are adhered to:
- Light soils are preferable - sandy loam, loam, with good aeration, neutral acidity;
- nutrition for the plant is provided by the autumn application of humus or rotted compost;
- do not plant in areas where other legumes grew last year;
- holes for peanut seedlings are prepared 10 cm deep;
- Between the lush bushes of the legume plant, an interval of up to 50 cm is maintained.
When industrially planted in the south, row spacings of up to 60-70 cm are maintained, with a distance between plants of 20 cm. Peanut seeds are planted to a depth of 6-8 cm.
Experienced vegetable growers select legume varieties zoned for the steppe and southern parts of the forest-steppe strip of the European continent of the Black Sea zone. In the Russian climate, the following peanut varieties grow successfully:
- Klinsky;
- Stepnyak;
- Accordion;
- Krasnodar;
- Adyg;
- Valencia Ukrainian;
- Virginia Nova.
Care
From the beginning of the growth of peanut seedlings, the crops are watered once every 2 weeks. In caring for groundnuts in dry weather during the flowering and ovary formation phases, regular watering every other day with mandatory subsequent loosening of the soil plays an important role. In the evening, the plants come to life after spraying the bushes with warm water, which is carried out every other day. The best solution would be to organize drip irrigation. If it rains, even irregularly, the zoned varieties grow well without watering, since groundnuts are initially drought-resistant. But during periods of heavy rains or prolonged continuous precipitation in the middle zone, the crops are covered with a transparent film. Soil that is wet for a long time can cause fruit to rot. Peanuts stop watering a month before harvesting.
An important point in agricultural technology is hilling, which makes it possible not to lose that part of the crop that may dry out before reaching the ground. The soil is raked under the plant to a height of 5-6 cm. The reception is carried out the next day after watering or rain several times during the growing season:
- 9-12 days after the appearance of the first flower;
- 2 or 3 more times with an interval of 10 days.
In farms where peanuts grow as an industrial crop, they are fed:
- In the spring, before sowing or planting young shoots, the area is fertilized with 50 g of nitrophoska per square meter. m;
- twice during the summer they are supported with complex potassium-phosphorus preparations.
Harvesting
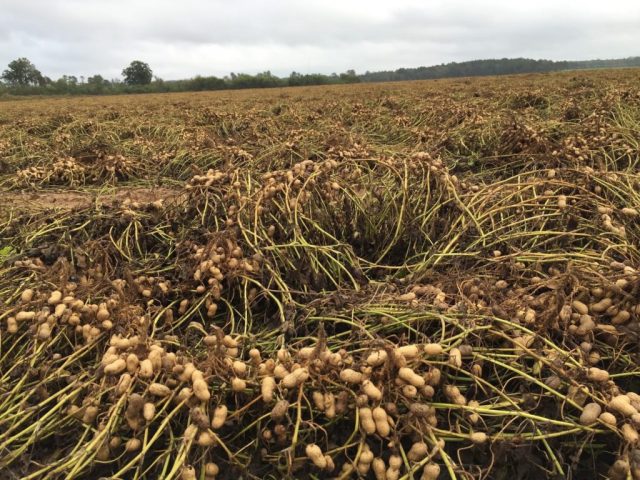
With the beginning of autumn, the leaves on the peanuts turn yellow. This is a sign of grain ripeness. It is necessary to collect the beans before the air temperature drops below 10 °C. If early frosts occur, the seeds are tasteless and bitter. In households, the crop is dug with a pitchfork to keep the beans undamaged. They are dried in the sun for several hours, then torn from the stems and roots and dried in air. In bad weather, the nuts are placed under a canopy where air flows. Store beans in boxes or bags in a dry, warm room where the thermometer does not show below + 10 °C.
Peanuts are susceptible to many fungal diseases. Preventatively adhere to recommendations for watering plantings. If symptoms occur, treat with broad-spectrum fungicides. Groundnuts also have many pests that feed on delicate leaves and flowers: caterpillars, aphids, thrips. Wireworms damage fruits. They get rid of them by placing bait in the holes and inspecting them regularly.
Conclusion
Few regions of Russia have a similar climate to the regions where peanuts usually grow. And yet, enthusiasts can grow groundnuts in the middle zone. The seedling method will speed up the ripening time, and maintaining the moisture regime in the soil will save the harvest.