Content
- 1 Description of the medicinal product
- 2 Application in landscape design
- 3 Reproduction methods
- 4 Landing dates and rules
- 5 Features of care
- 6 Chemical composition in plant value
- 7 Medicinal properties of kupena
- 8 Recipes based on the roots of the purchased medicinal plant
- 9 The use of medicinal products in folk medicine
- 10 Application in cosmetology
- 11 Restrictions and contraindications
- 12 Collection and procurement of raw materials
- 13 Interesting facts about the pharmacy store
- 14 Conclusion
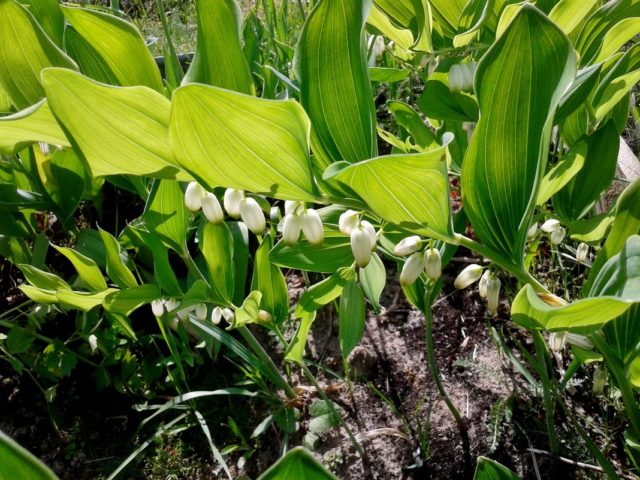
Kupena officinalis is a well-known plant from the Lily of the Valley family (Convallariaceae), which in appearance resembles garden lilies of the valley. Due to its decorative appearance, the crop is widely used for landscaping areas. Various parts of the plant are harvested for the preparation of medicinal infusions and decoctions.
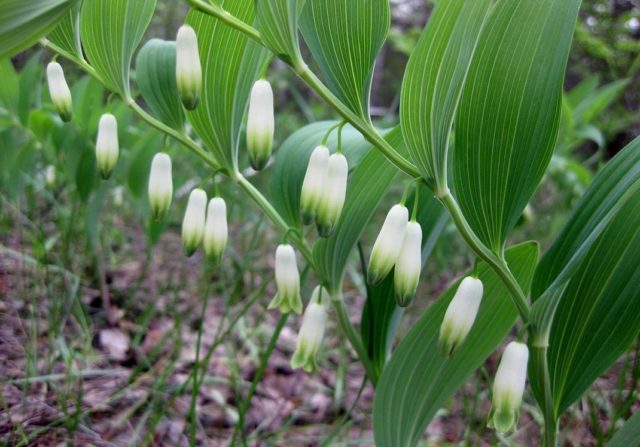

The medicinal product has many names: core, wolf grass, signet, blind lily of the valley, crow berries, wolf fang, Solomon's seal
Description of the medicinal product
The perennial belongs to the herbaceous group.The description of the plant Kupena officinalis allows us to form a general idea of the ornamental crop:
- thick, multi-jointed, woody rhizome over time;
- bush height up to 60 cm;
- stems are bare, drooping, with edges;
- leaves are alternate, oblong elliptical or ovate, stem-embracing;
- leaf length up to 14 cm;
- leaf width up to 5 cm;
- the color of the upper part of the leaf blades is green;
- the color of the lower part of the leaves is matte, grayish-green;
- drooping pedicels emerging from the axils of the leaf blades;
- perianth tubular, white;
- the perianth has six teeth of a greenish tint;
- the fruit is a round berry, up to 1.2 cm in diameter;
- The color of the berries is black and blue.
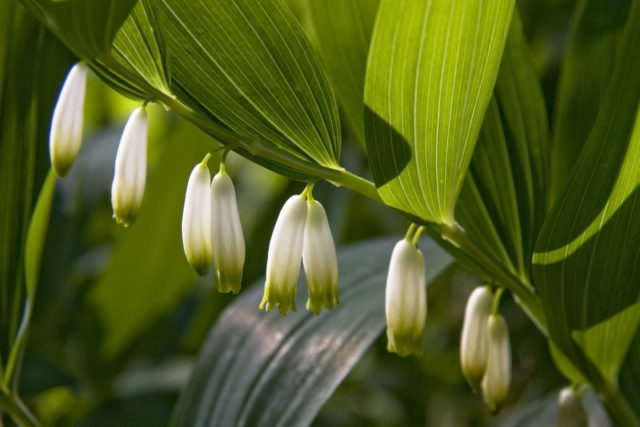

The plant blooms in late May, early June, bears fruit in August
Where and how does fragrant kupena grow?
Kupena officinalis, the photo and description of which is presented above, grows naturally in the European part of Eurasia. The plant is widespread in forests, meadows, and mountain slopes. Medicinal or fragrant kupena prefers well-shaded places.
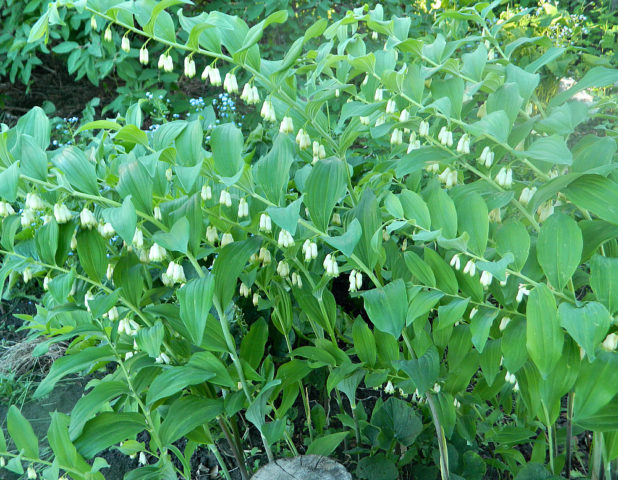

The creeping rhizomes of the plant grow, forming vast clearings
Poisonous medicinal product or not
Based on the description of the fragrant plant (Polygonatum odoratum Druce), pharmaceutical or medicinal, one can draw conclusions about the poisonous properties of almost all parts of the plant. Stems, foliage, roots, flowers have an emetic effect. An overdose of any drug prepared from aromatic medicine can cause a sharp deterioration in health. Various parts of the plant should absolutely not be used for the prevention and treatment of diseases in children and pregnant women.Berries and seeds have the most pronounced toxic properties.
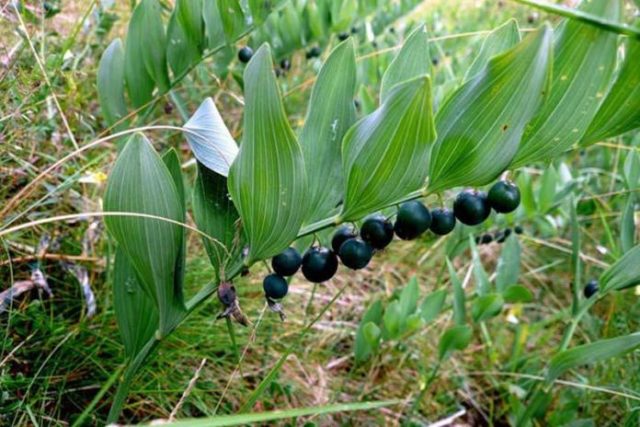

The bright color of the fruits of the medicinal plant signals danger
Application in landscape design
Modern fashionable landscape designers widely use perennial medicinal flowers to decorate areas. Even after flowering ends in June, until late autumn, fragrant bushes do not lose their decorative appeal. Another advantage of the culture is that the medicinal plant takes root well and grows in shaded areas where other flowers die from lack of sunlight.
The fragrant medicinal plant can be placed anywhere in the garden:
- in the shade of trees, buildings and other small architectural forms;
- in sunny meadows;
- around picturesque stones, driftwood;
- in rockeries;
- near a pond or swimming pool.
Kupena officinalis harmonizes very beautifully with moss, loosestrife, periwinkle, beetleweed or ajuga, garden mantle, filamentous speedwell, and bulbous primroses (narcissus, tulip, crocus, scylla).
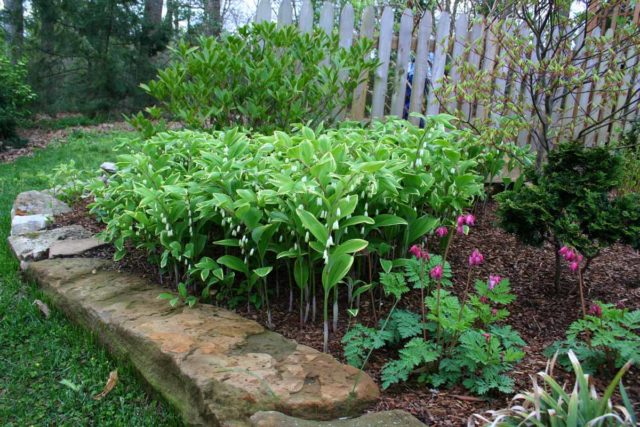

The snow-white tears of the inflorescences of Kupena officinalis look magnificent and solemn next to brightly flowering plants
Reproduction methods
Medicinal or pharmacy kupena reproduces in two main ways:
- seminal;
- vegetative (by dividing the bush).
Growing a plant from seeds is a troublesome and time-consuming task.
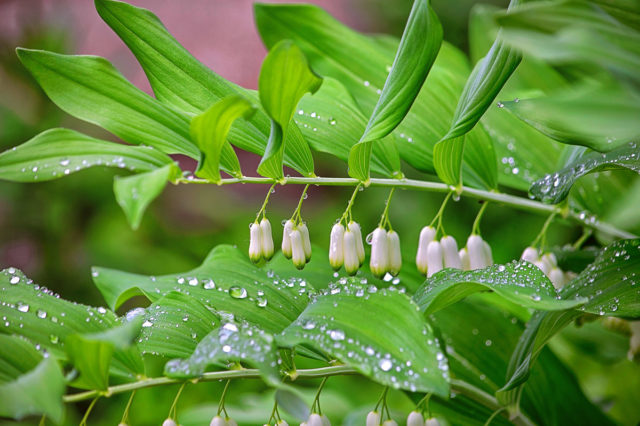

Propagation by dividing the bush is the simplest and most affordable way to purchase fragrant medicinal plants.
Seed propagation
To propagate fragrant or medicinal flowers from seeds, you can use purchased or home-collected planting material.Seeds should be pre-stratified for a month on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator.
A soil mixture of equal parts of river sand and peat is placed in the container for seedlings. The seeds are sown, the planting containers are removed for 90 days in a cool place with an air temperature of + 5 ⁰C.
Then the crops are kept in a room for 3-4 months at temperatures up to + 23 ⁰С, after which they are again put in a cool place (up to + 5 ⁰С) for 30-60 days.
At the last stage of growing seedlings, the air temperature should be up to + 23 ⁰C.
At this time, medicinal plant crops need diffused light, watering as the soil mixture dries out. The seedlings of the fragrant plant, transplanted into open ground at the end of May, take root at a fairly slow pace.
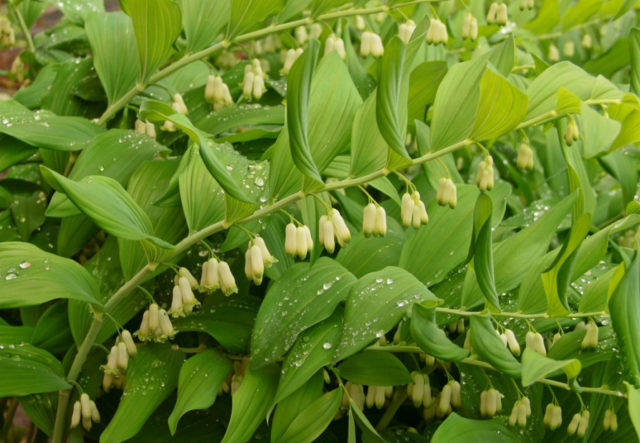

The first flowering of medicinal plants grown from seeds occurs only in the fourth year of life.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
The bush is divided at the end of summer or early autumn, or in early spring before the shoots begin to grow. The mother bush is removed from the ground, the root system is divided into several plots so that the root segment contains a viable growth point.
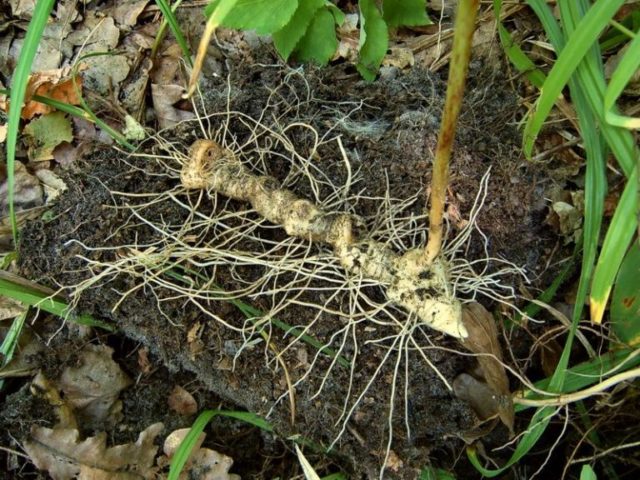

Experts recommend dividing the bushes once every five years to prevent the medicinal plant from growing
Landing dates and rules
Kupena is not distinguished by complex agricultural technology. The medicinal plant grows well in the wild without human intervention.
Deadlines
Seedlings of medicinal plant, or medicinal plant, are transplanted into open ground at the end of May.
The plots obtained from the mother bush are moved to a new place in early spring, late summer or at the very beginning of autumn.

To carry out the work of transplanting the fragrant medicinal plant to a permanent place, you must choose a cloudy day.
Place
Well-shaded areas are considered the optimal place to place a pharmaceutical or medicinal purchase. In the shade of trees and architectural forms, the graceful forest beauty will feel great.
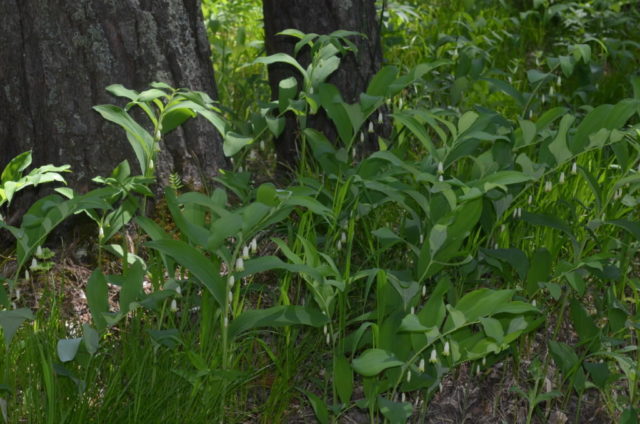

The medicinal crop grows actively in well-fertilized soils
Landing algorithm
Planting holes for transplanting seedlings or plots of medicinal products into open ground are prepared in advance.
The rhizome is carefully placed in the hole, straightened, deepening up to 8 cm into the soil.
The distance between individual plots should be at least 20 cm.
Transplanted medicinal plants are watered, the holes are sprinkled with dry soil and a layer of mulch.

In the first two years, young bushes of the medicinal crop take root, then the flowering period begins
Features of care
Minimal care is required for medicinal perennials:
- watering as the soil dries out, no more than once a week;
- mulching to prevent the soil from drying out near the bushes;
- gentle loosening;
- two-stage fertilization (the first time in early spring, fertilizing with complex mineral or organic preparations, the second time - during flowering);
- monitoring of diseases and pests;
- preparation for wintering (mulching with sawdust, compost or peat, covering with spruce branches).
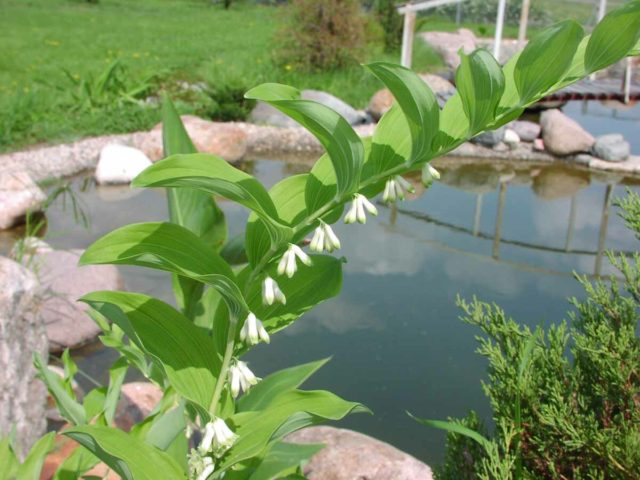

When loosening the soil, it is important not to damage the rhizomes of the plant, which are located close to the surface of the earth.
Chemical composition in plant value
Almost all parts of a medicinal or pharmaceutical purchase are endowed with a unique chemical composition, which explains the value of the ornamental crop for the human body:
- roots are a source of fructose, alkaloids, mucous substances, starch, glycokenin, trace elements (zinc, copper, manganese), carotene, ascorbic acid, nitrogen-containing compounds, tannins;
- leaves and stems are sources of alkaloids, flavonoids (vitexin, quercetin), steroid saponin (diostegin), vitamin C and PP;
- fruits are sources of cardiac glycosides (convallarin, convallatoxin, convallaramine).
Allantoin is found in almost all parts of the fragrant plant and promotes a powerful anti-inflammatory, antitumor and wound-healing effect.
To treat some diseases (ulcers, wounds on the surface of the skin), fresh juice is used in certain proportions. For the treatment and prevention of other ailments, decoctions, infusions, and tinctures are prepared. When deciding to use traditional methods, you should consult in detail with a specialized specialist.
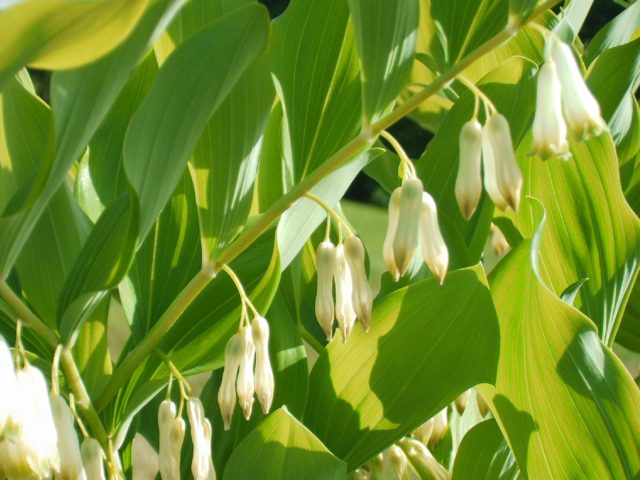

Thanks to the active substances contained in the leaves, fruits, roots, kupena officinalis is used in official medicine
Medicinal properties of kupena
The following medicinal properties of the plant are widely used:
- expectorant effect, since the foliage and stems of the kupena help get rid of cough, relieve inflammation of the lower respiratory tract, and thin mucus;
- analgesic effect, since the tincture of various parts of the officinalis is suitable for rubbing for rheumatism, joint pain, pain syndromes due to arthritis, gout, migraine;
- decongestant, diuretic and blood purifying effect helps in the complex treatment of dropsy, various edema, diabetes;
- antitumor, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing effects;
- hemostatic and enveloping effect in the complex treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers, inflammatory processes in gynecology;
- tonic effect, thereby relieving the symptoms of heart disease;
- restoration and lightening of the skin for acne, freckles, pigmentation;
- emetic effect in case of poisoning;
- reducing the risk of hallucinations in disorders of the nervous system.
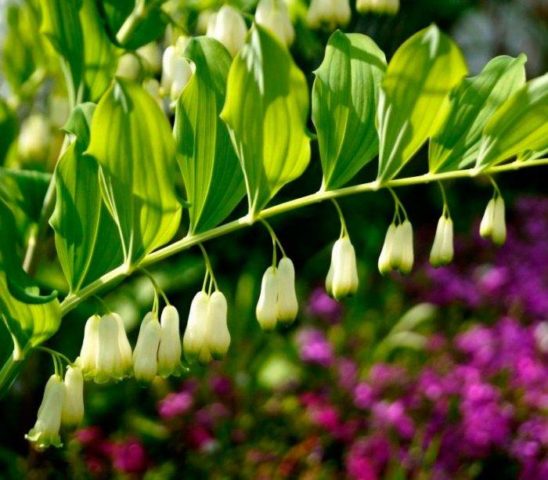

Since ancient times, “deaf lily of the valley” has been used to prepare medicinal potions for numerous ailments
Recipes based on the roots of the purchased medicinal plant
A special niche in the prevention and treatment of various diseases is occupied by the rhizomes of medicinal or fragrant kupena. The compositions are prepared from dried roots, following a proven recipe that is passed down from generation to generation.
Decoction
A decoction of the rhizome has the form of an enveloping mucous liquid that does not irritate the walls of the digestive tract. For this reason, the remedy from kupena can be used internally for such ailments as diseases of the lower respiratory tract (cough, bronchitis), gastritis, gout. Use the decoction regardless of meals, 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
There are several ways to prepare the decoction. In the first way, the decoction is prepared as follows:
- young roots are selected, dried, crushed;
- one tablespoon of roots is poured with one glass of boiling water;
- under the lid, the mixture is infused in a water bath;
- the mixture is filtered and left for one hour.
The second method of preparing a decoction of kupena rhizomes:
- the crushed raw materials are poured with cold water in an enamel pan;
- Heat the liquid over low heat without bringing it to a boil;
- the mixture is filtered and infused for one hour.

Before using the “deaf lily of the valley” decoction internally, you should first consult with your doctor.
Milk decoction
A decoction of the drug in milk is used for problems with the pancreas and various forms of hernia. The mixture effectively and gently reduces blood sugar levels. Take 1-2 tbsp of decoction from the pharmacy with milk orally. l. 3 times a day.
Cooking method:
- dried root crushed into powder (2 tbsp) is poured with cow's milk (3 liters);
- Bring the mixture to a boil over low heat;
- stirring occasionally, the broth is left on the fire to evaporate approximately one liter of milk;
- the mixture is filtered while hot.

A decoction of kupena officinalis in cow's milk has been used in Rus' for a long time.
Infusion
An infusion, unlike a decoction, is a longer-aging composition that contains the maximum concentration of beneficial substances. Used to treat inflammatory processes of the respiratory tract, ulcers, hernias, and relieve pain. The algorithm for making an infusion is similar to preparing a decoction, but the healing agent should be infused for at least three hours. Application regimen: 2 tbsp. l. 2-3 times a day.

Herbalists recommend steaming the infusion by wrapping the container in a warm blanket
Tincture
Tincture of fragrant rosemary is prepared using alcohol. Suitable for outdoor and indoor use.Internal use of tincture of the root of the plant is prescribed for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, bronchitis, diseases of the intestines, prostate and female reproductive organs. Oral dosage regimen - up to ten drops of alcohol tincture per glass of water, green tea or rosehip infusion once a day for 14 days. After ten days, the two-week course is repeated.
An alcohol tincture of medicinal product is prepared as follows:
- fresh root is grated;
- 100 g of crushed raw materials are poured with a liter of 70% alcohol;
- the composition is infused for 20 days in a dark place at room temperature.

Alcohol tincture is used to treat problem areas of the skin (acne, age spots, freckles, growths, bruises, abrasions, bruises)
Juice
Fresh juice from the leaves of Kupena officinalis is used for compresses, lotions, and applications. The leaves are picked, washed, ground in a meat grinder, and the juice is squeezed out through gauze.

An elixir of fresh leaves of the aromatic plant is used to treat dermatological problems.
The use of medicinal products in folk medicine
Bought pharmaceutical, or medicinal, is the raw material for the preparation of traditional medicine compositions. From generation to generation, herbalists have passed down invaluable recipes that many still use today, along with medications as part of a comprehensive treatment for various diseases.
For stomach pain
For stomach pain, after consultation with your doctor, you can use a decoction of a pharmacy or medicinal product. For chronic stomach problems, a decoction of Solomon's root in milk is most effective.

Decoctions, infusions and tinctures of kupena officinalis are used to treat various gastrointestinal diseases.
For abrasions and cuts
The greatest effectiveness for abrasions, bruises, wounds, cuts, and other damage to the skin is shown by fresh juice from the leaves, decoctions and infusions from the roots of the aromatic plant. A bandage soaked in the medicinal composition is tied to the damaged areas of the skin for an hour, twice a day for seven days. Such compresses and applications relieve pain, swelling, and inflammation.

In emergency cases, you can tear off a leaf, scald it with boiling water and tape it to the wound.
For gout and joint pain
You can relieve joint pain and unpleasant symptoms of gout with the help of an infusion of Solomon's seal rhizomes. The healing mixture is taken orally, 0.5 ml twice a day for seven days.

The infusion of the rhizome is rubbed into sore spots twice a day for one week.
For hemorrhoids
“Pochchechuy” is what they called hemorrhoids in Rus'. The disease was cured with the help of a decoction of the roots of the medicinal plant. The recipe for a decoction for the treatment of hemorrhoids is slightly different from the classic one:
- take two tablespoons of crushed root of the pharmacy;
- pour 400 ml of boiling water;
- leave covered in a warm place for four hours;
- strain through several layers of gauze until a clear solution forms.
The course of treatment is at least five procedures until the symptoms disappear.
Tampons soaked in a decoction of fragrant root are inserted into the rectum overnight
Application in cosmetology
Thanks to its unique natural composition, kupena is widely used for the production of cosmetics for face and body care. The plant is included in creams, tonics, lotions, and masks. Kupena officinalis essential oil is very effective in combating freckles and other skin pigmentation.A homemade decoction of the roots has a beneficial effect on problematic facial skin:
- for red spots with smallpox, measles and acne, use the decoction as the main lotion after washing and removing makeup;
- to lighten pigmentation, use rhizome juice diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio;
- for pigmentation and redness, use the essential oil of kupena officinalis, which is also diluted with water.

Traditional medicine should only be used after consultation with a dermatologist or cosmetologist.
Restrictions and contraindications
As you know, kupena medicinal, or medicinal, is a poisonous plant. In order to choose the right dose, you should consult with herbalists and homeopaths.
There are categorical contraindications for the use of any compositions from the medicinal product:
- children under 16 years of age;
- pregnant women;
- women during breastfeeding;
- people suffering from seasonal allergies.
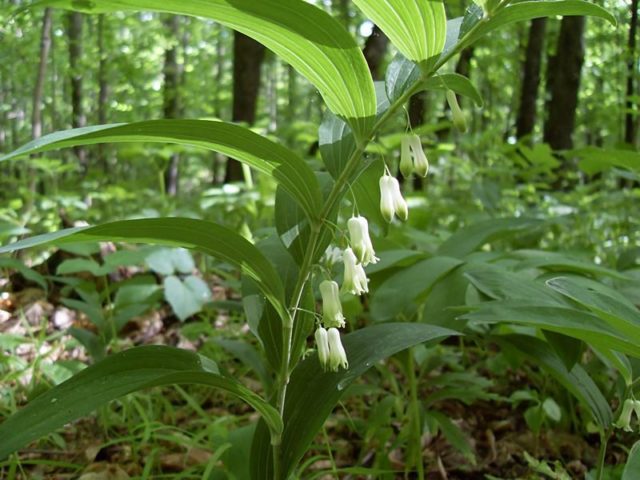

In case of overdose in adults, symptoms of poisoning and vomiting are observed.
Collection and procurement of raw materials
The grass (leaves, stems, flowers) is collected from May to June during flowering. The roots are harvested in September. The berries are harvested after full ripening. The raw materials are dried in air, in ventilated areas. After drying, store in paper or wooden containers in a dark and dry place. Experts recommend collecting raw materials in the forest, away from roads and industrial facilities.

The dry parts of the medicinal product retain their beneficial properties for two years.
Interesting facts about the pharmacy store
Since ancient times, the root of the fragrant aromatic plant has been used for economic purposes:
- treatment of cattle infected with gadfly larvae;
- as an anthelmintic for the treatment of domestic animals;
- to increase appetite in ruminants.
In addition, in the old days, young men and women rubbed their cheeks with kupena berries to give a natural blush.
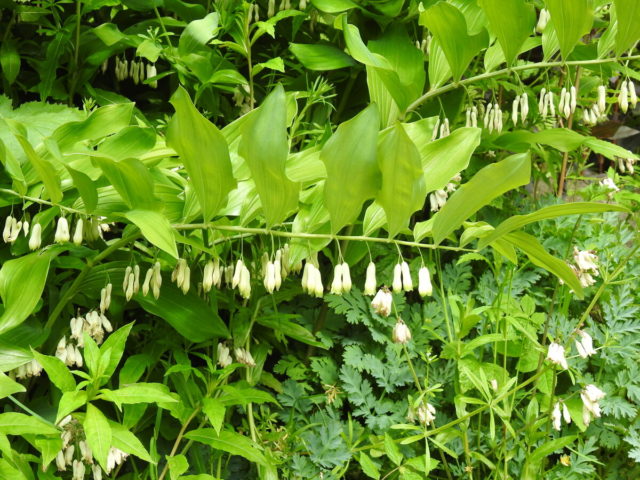

Deer and red deer in the wild willingly eat medicinal tea to naturally expel worms and other parasites
Conclusion
Kupena officinalis is a unique, amazing plant that can be found throughout almost the entire European part of the continent. The herb, which produces delicate inflorescences in the shape of crystal bells in early summer, heals many diseases. According to ancient legend, King Solomon appreciated the beneficial properties of fragrant bath. He gave the plant his mark, which can be seen on the curved roots. Therefore, people call the healing herb “Solomon’s seal.”








