Content
All varieties of mint contain a significant amount of aromatic substances. Among them there are real record holders. One of them is menthol mint, which, as the name suggests, is characterized by a high menthol content.
Description of menthol mint
Menthol mint is considered a subspecies of peppermint, a widespread plant that is cultivated for industrial purposes. Its main characteristics:
Parameter | Meaning |
Plant type | Perennial herbaceous |
Root | Creeping, superficial, with a small lobe |
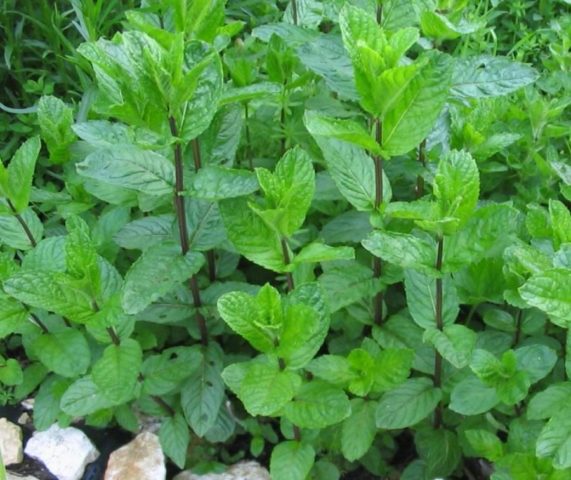
Stem | Straight, light green, becomes reddish with age, tetrahedral. Hollow inside. In good conditions it grows up to 1 m; in nature, the average height of a bush is 0.25-0.5 m |
Leaves | Green, ovate-elongated, pointed, with an uneven serrated edge. The upper leaves are sessile, the lower leaves grow on a short petiole. Opposite location |
Flowers | Small, light purple, grows in spike-shaped inflorescences |
Flowering time | July August |
Fruit | Nut-shaped coenobia, ripen in August-September |
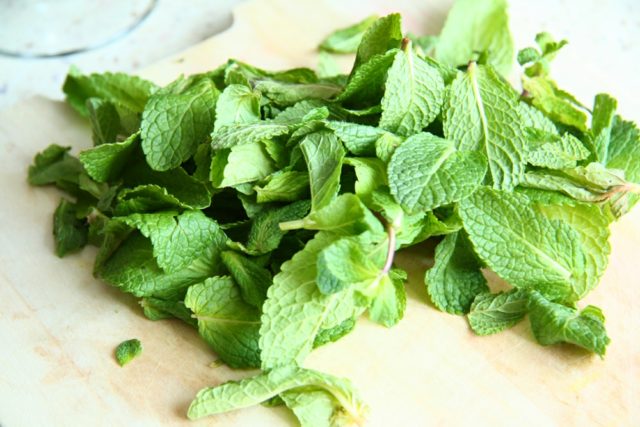
Pictured below is menthol mint:
What is the flavor of menthol mint?
A distinctive feature of menthol mint is its increased content of aromatic essential compounds, primarily menthol. This gives it a strong and lasting smell of freshness.
What is the difference between menthol and mint?
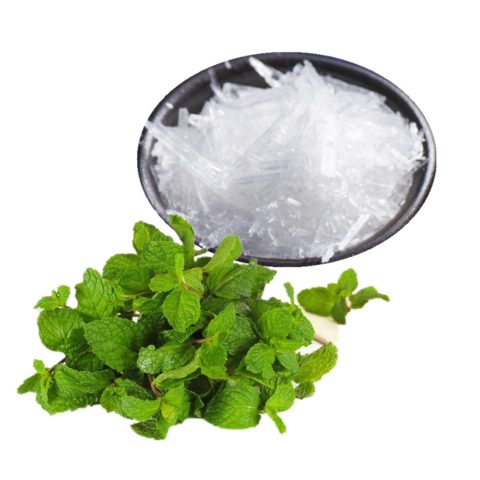
Unlike mint, which is a plant, menthol is a crystalline organic compound that is obtained from the leaves of plants in the Lamiaceae family. This substance is widely used in cosmetology and pharmacology, as well as in the food industry.
Menthol, obtained from mint extract, has a local anesthetic effect; upon contact with the skin and mucous membranes, its effect is manifested through irritation of cold receptors. This explains the characteristic refreshing effect of this substance.
A video on this topic can be viewed at the following link:
What are the benefits of menthol mint?
The aromatic substances that make up menthol mint have a positive effect on many body functions. They have a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system, and ease the course of colds. I also use infusions and decoctions of menthol mint externally as an antiseptic and cleanser.
Uses of menthol mint
Menthol mint has many beneficial properties, but it also has contraindications.It is used in cooking, cosmetology and medicine, as well as in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
In folk medicine
In folk medicine, mint has always been used as a sedative. Its decoction was taken for nervous disorders, increased excitability, and also as a sleeping pill. An extract from it is a good choleretic agent; it normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Mint lowers blood pressure and also has a mild analgesic effect. Inhalations with a decoction or tincture of this plant can be done to soften coughs and relieve throat irritation during colds. Drinking mint decoction is useful for women to reduce menstrual pain, as well as during menopause.
In cosmetology and perfumery
A decoction of menthol mint is widely used in cosmetology. It has antiseptic properties and can be used to treat small wounds, rub it on the face for cleansing, and also for the treatment and prevention of rashes. It is good to use it as a mouth rinse, it is not only refreshing, but is also an excellent prevention of gum disease. Mint decoction perfectly strengthens hair, improves its structure, and at the same time reduces itching of the scalp.
Among perfumes, there are quite a few that contain menthol - an extract from mint leaves. These are various lotions, ointments, creams. Menthol is widely used to make toothpaste and mouth rinses.
In pharmacology
There are quite a lot of medicines containing menthol.These are various herbal tinctures with a calming and vasodilating effect, drops, mixtures for inhalation, as well as local anesthetics. The most well-known pharmacological preparations obtained from menthol mint: Boromenthol, Valokormid, Zelenin Drops, Menovasin, Pectusin, Strepsils, Faringopils, Evamenol.
In cooking
Menthol-flavored mint is widely used in cooking. In one form or another, it is found in many dishes; as an ingredient or as part of spices, it is found in the recipes of many cuisines around the world. Green leaves are used to decorate and serve dishes, as a component of salads, to prepare sauces for meat and fish, and they are also included in alcoholic drinks and cocktails.
Menthol mint is used for preserving vegetable snacks, fruits and berries, for preparing compotes and soft drinks, and the most popular way of growing it is adding leaves to tea when brewing.
Restrictions and contraindications
In addition to its medicinal properties, menthol mint also has contraindications for use. For example, it is not recommended to use it for people whose work requires increased attention. In addition, mint can have a negative effect on male libido, reducing sexual desire. It should not be used by people with low blood pressure, as well as those who have allergic reactions to menthol or other substances contained in this plant.
A contraindication to the use of menthol mint is varicose veins.Women suffering from infertility or having difficulty conceiving should also avoid any dishes containing components of this plant.
How does menthol mint reproduce?
There are many ways to propagate menthol mint for planting in your garden. Here are the main ones.
- Seminal. The most optimal planting method is if this crop is planted on the site for the first time. Menthol mint seeds can be purchased at garden centers or online. It is best to plant it in seedlings. To do this, menthol mint seeds are sprouted at home, and then, after the onset of suitable weather conditions, the grown plants are planted in a permanent place.
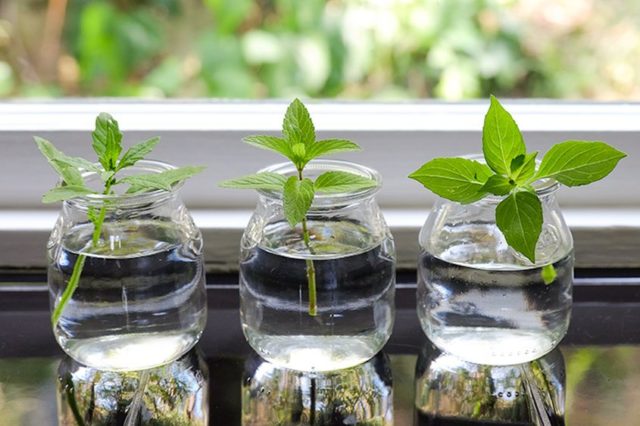
- Cuttings. This propagation method can be used if there are already mint bushes on the site. To make cuttings, you need to cut off the apical part of the plant 10-15 cm long and place it in water. After about 2 weeks, the cutting will begin to form its own root system at the cutting site. When the roots reach 2-3 cm in length, the young seedlings can be planted in open ground or in a pot.
- Root cuttings. The superficial roots of mint resemble long vines. They contain a large number of dormant buds. For propagation, a part of the root 10-12 cm long is cut off and planted in moist, fertile soil.
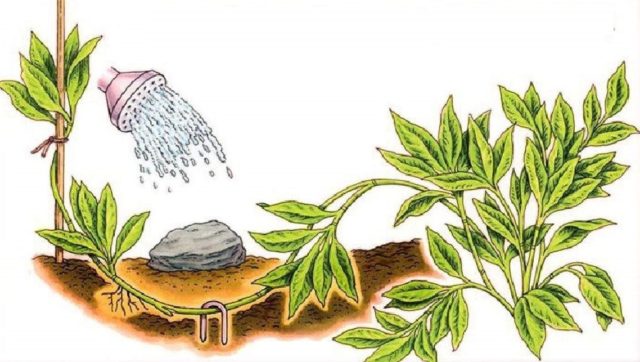
- Air layering. To obtain them, a side shoot of a mint bush is bent to the ground and sprinkled with soil. Quite quickly, a root system of its own will begin to form in the internodes, and a chain of sprouts will appear along the entire length of the buried shoot.In the future, they need to be cut off from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.
- Dividing the bush. The plant can be dug out of the ground and cut into several parts so that each contains a sufficient number of roots and a stem with buds. In this way, you can divide an adult mint bush into several small ones and plant them around the area.
Landing rules
For growing menthol mint, an open sunny area with loose, fertile soil is best suited. If there are not enough nutrients, additional nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers, as well as humus, must be added. Seedlings are planted in open ground in May, when the ground has warmed up and the night temperature no longer drops below + 5 °C. Menthol mint is planted in rows, keeping a distance of 25-30 cm between neighboring plants.
Features of growing menthol mint
After planting, young plants are watered regularly. After the seedlings take root well and greenery begins to develop, the frequency and volume of watering must be reduced. Menthol mint loves breathable soil, so after watering the top layer of soil must be carefully loosened, ensuring air access to the surface roots of the bush. Weeds must be removed in a timely manner so that mint crops do not compete with them for light and nutrients.
Fertilizing menthol mint should be done very carefully. Excess nitrogen, as well as an excessive amount of fresh organic matter (manure or chicken droppings), have a beneficial effect on the growth of green mass, but the concentration of menthol in the leaves also increases, which negatively affects their taste. They just become bitter.In addition, an increased nitrogen content in the soil is a risk factor for the appearance of such a dangerous fungal disease as rust.
For the winter, menthol mint bushes are left in the ground. This perennial plant has good winter hardiness and freezes out quite rarely, except in the most severe frosts. In autumn, the bushes must be cut, leaving small stumps 5-7 cm high, and then covered with fallen leaves or dry grass, and with the onset of winter, additionally covered with a layer of snow.
Another feature of growing menthol mint is its proliferation. If no measures are taken to limit its spread, the creeping roots of plants will take over more and more new territories. For this reason, over time, mint can turn into a nasty weed. To artificially limit the growth of the root system, a fence is dug around the mint bed to a depth of 0.2-0.25 m from metal sheets or slate. This problem can be avoided if you plant mint in special pots or containers dug at the same level as the beds.
Pests and diseases
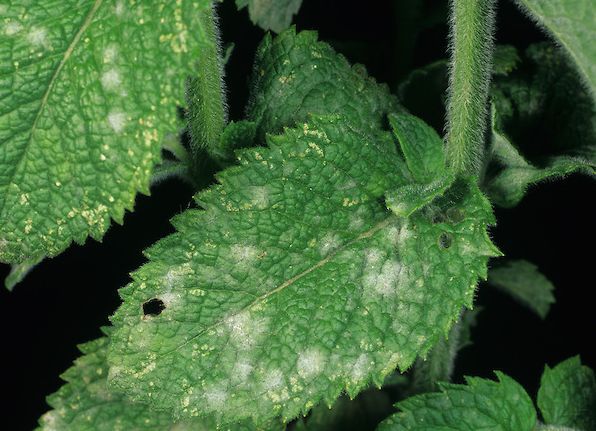
In unfavorable weather conditions or improper care, menthol mint can be susceptible to various diseases, mainly fungal. These include the following:
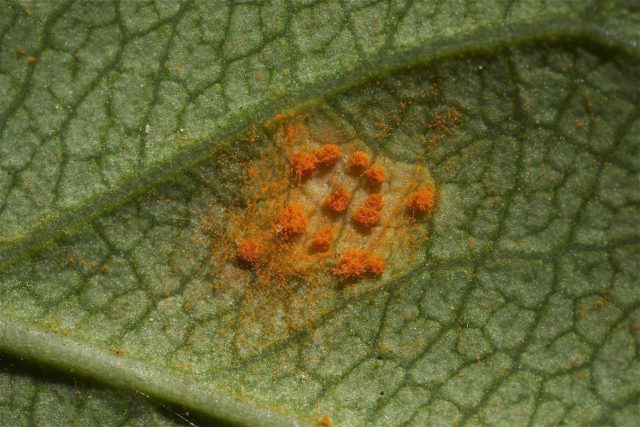
- Rust
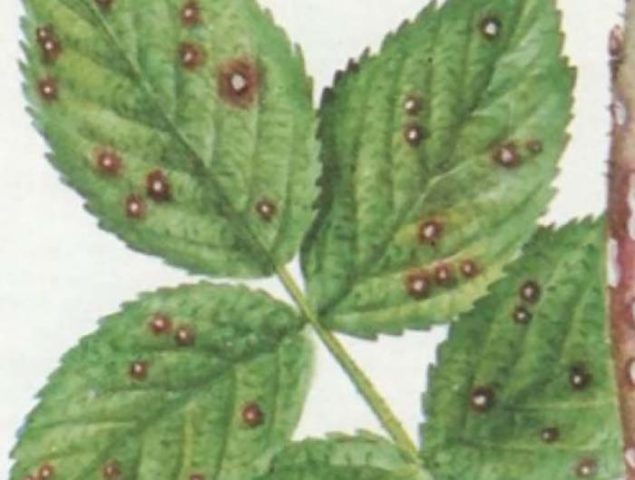
- Anthractosis
- Septoria
- Powdery mildew
- Verticillium
Diseased mint bushes must be promptly identified and destroyed. There is no point in spraying the remaining plantings with various preparations, otherwise it will be unsafe to eat them.
Prevention of the appearance of fungal diseases of menthol mint is high-quality weeding, timely disposal of plant waste, and deep autumn plowing before planting.
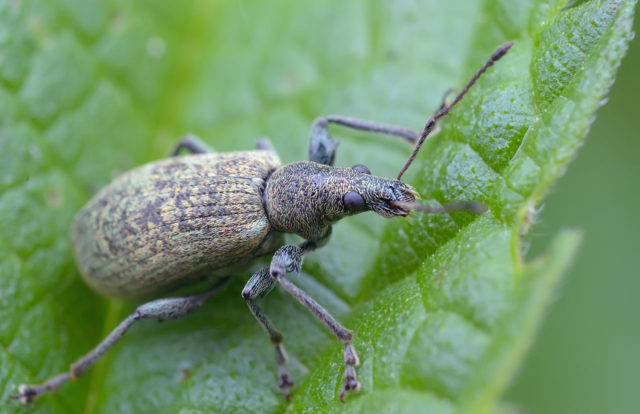
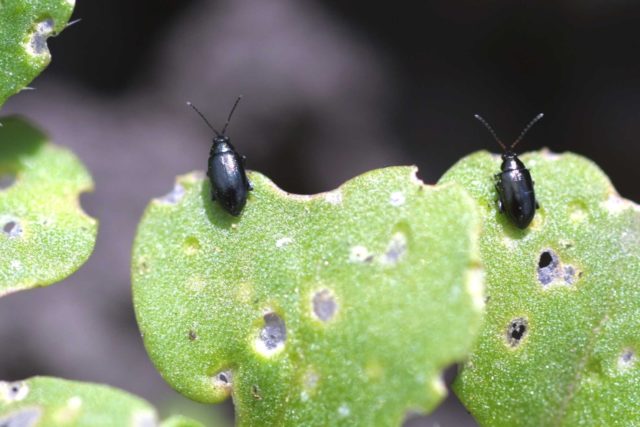
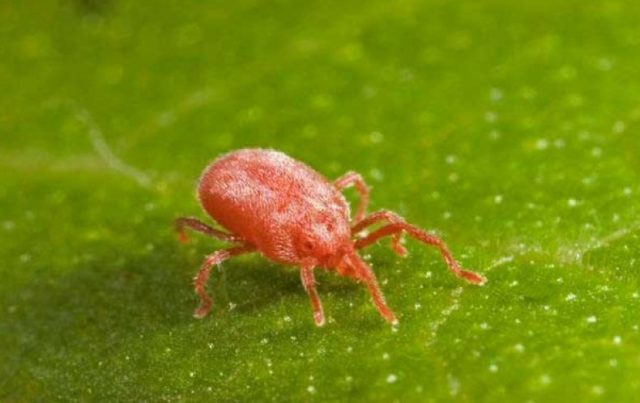
Pests can also appear on menthol mint, despite the fact that its greens contain a large number of aromatic compounds and have a specific taste. The following insect pests pose a danger to this plant:
- Weevil
- Peppermint flea beetle
- Peppermint mite
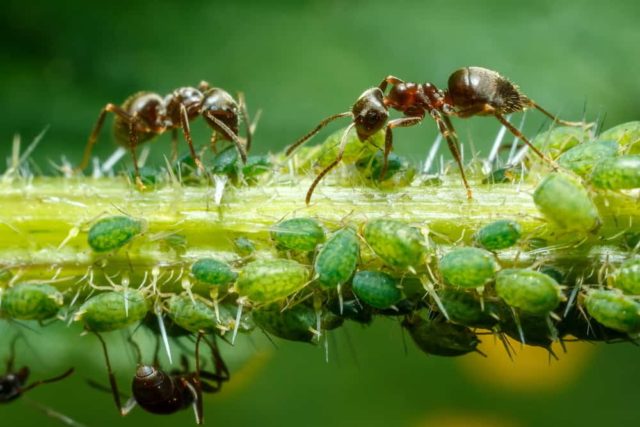
- Aphid
- Wireworm.
- Medvedka
Pest control is carried out in various ways, from shaking off plants and manually collecting insects to treating plantings with various means. The use of chemicals for menthol mint in this case is not always justified, so various folk remedies, for example, celandine infusion, are often used for spraying.
When and how to collect menthol mint
The best time to collect menthol mint leaves is mid-July. It is during this period that its flowering begins. The concentration of essential oils in green plants reaches a maximum. You cannot start collecting early in the morning; the bushes must have time to dry from dew. Menthol mint is collected both with individual leaves and branches, tying them into bunches.
How to dry menthol mint correctly
Menthol mint is dried in open areas or in rooms with good air exchange: in attics, terraces, gazebos or under a canopy. At the same time, the greenery should not be exposed to direct sunlight.Bunches of menthol mint are usually hung-dried, and the leaves are laid out in a thin layer on clean paper or cardboard, covered with gauze on top to prevent insects.
Dried greens become brittle and rustle to the touch. It is crushed and stored in glass or ceramic jars with tight-fitting lids. In this form, menthol mint can be stored for up to six months.
Another way to store fresh mint is to deep freeze it. In this case, fresh leaves are washed, dried and placed, without compacting, in a small, tightly closed container. Then the containers with the leaves are placed in the freezer and stored at a temperature of - 18 ° C. In this form they can remain without loss of properties for up to 7-9 months.
Conclusion
Menthol mint is a fairly easy to cultivate plant that does not require special care. It has a lot of useful properties and can be used for culinary, hygienic or medical purposes. However, we should not forget that over time the plant can grow greatly and literally fill the entire area.