Content
Raspberry Octavia is one of the varieties with late ripening berries. Popular in Europe, where it is cultivated on an industrial scale. In Russia, the variety is not so in demand; you cannot find it in the fields of agricultural complexes. Raspberries are grown in summer cottages or garden plots.
History of origin
Octavia's homeland is England. A hybrid form of culture was created in 1996 on the basis of East Malling Station. The originators of the Octavia variety are a group of breeders led by Victoria Knight, Master of Science in Genetics.
Raspberries were bred by cross-pollination of the complex hybrid EM 5928-114 and Scottish Glen Ampl. After experimental cultivation in 2002, Octavia raspberries went on sale, first in England and Europe, and four years later they were exported to the Russian market.
Description of Octavia raspberries
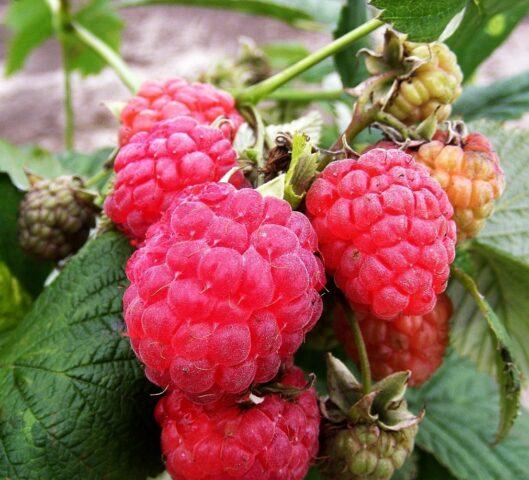

Octavia is named after the eighth month of the year, because in August the crop begins its fruiting period
Externally, Octavia raspberries are not much different from the usual varietal variety. But it produces larger fruits with a pronounced aroma. Octavia inherited this quality from her predecessor Glen Ampl. The complex hybrid endowed the culture with strong immunity and a high ability to form new shoots.
Berries
Octavia raspberries bear fruit with a minimal concentration of acids. If the taste of other varieties is affected by the sufficiency of heat and lighting, then the nutritional value of the Octavia hybrid does not change due to changeable weather conditions.
Characteristic:
- raspberries of regular conical shape;
- large-fruited variety, weight – 5.5-6 g, leveled, small specimens are not found, commercial product yield – 98%;
- the drupes are densely located, the grip is strong, the seeds are small, the berries do not fall off after ripening;
- Up to eight viable ovaries are formed on the fruit cluster;
- the color is light crimson, matte, without a glossy coating.
Octavia was created for commercial cultivation, so the possibility of transportation and long-term storage was high on the list of priority qualities.
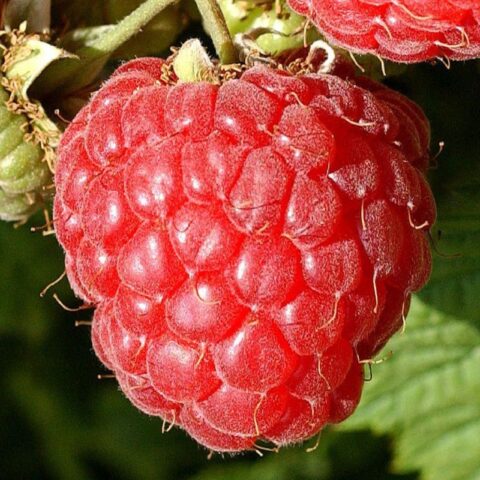

The berries are aromatic and versatile in use.
In addition to fresh consumption, Octavia is suitable for all processing methods
Bush
Raspberries are tall and compact. In order not to overload the plant, it is formed with 6-8 perennial stems.
What does the Octavia bush look like:
- The bearing shoots are dark gray with a brown tint, up to 2 m long.
- Intensive growth of green mass begins in the second year after planting. The young shoots are flexible, light green in color, and numerous.
- The thorns of Octavia raspberries are located in the lower part of perennial shoots at the tops in the form of rudiments.
- The fruit clusters are long (up to 15 cm), the fruiting zone is 40 cm (starting from the crown).
- The flowers are self-pollinating, light cream closer to white, small, simple.
- Raspberry Octavia forms complex leaves consisting of three rounded lobes located on short thick petioles.
- The leaf blades are corrugated, with teeth along the edge, light green, with fine edges.
The root system of the Octavia raspberry is branched, powerful, and mixed.
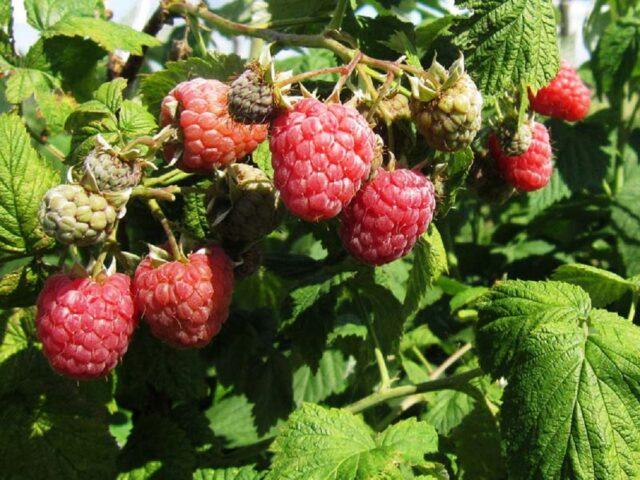

Octavia's stems are flexible, unstable, and droop under the weight of the fruit.
The culture requires installation of support.
Characteristic
Octavia is a light-loving raspberry, but does not tolerate prolonged drought. It was created for growing in damp climates, so the berries do not lose their shape and are not prone to rotting, but can be baked in the sun. Raspberries bear fruit consistently and are not affected by temperature changes. The plant is not afraid of prolonged rains in the cold season. Raspberry Octavia feels much more comfortable in temperate and temperate continental climates than in the subtropical zone.
Ripening time and yield of Octavia raspberries
The berries do not ripen at the same time, the fruiting cycle is extended. Raspberries begin to ripen in the second half of July. The last berries are harvested at the end of August. Depending on the climatic conditions of the region, the dates may shift, but only slightly.
Octavia raspberries are not remontant, so the yield is average; it directly depends on the timely application of fertilizing. Subject to the conditions of agricultural technology, 3.5 kg is harvested from one raspberry bush.Octavia's peak yield is observed in the fourth year of growth.
Frost resistance
The frost resistance indicator is not bad, but not the best. Raspberries overwinter without shelter at -250 C. If the indicator is lower, then Octavia requires insulation of the root system. Young plants are less resistant. They are completely covered. In spring, the variety is not at all afraid of return frosts. Raspberries are characterized by a relatively late onset of sap flow, so sub-zero temperatures do not harm the structure of the stems.
Disease resistance
Octavia practically does not get sick if you follow the feeding regime and timely watering. Raspberries are immune to anthracnose, all types of rot, septoria, and purple spot.
Raspberries are not affected by glass midge, stem gall midge, or weevil. Without preventive treatment and with a massive spread of the pest, the raspberry beetle can be found on the Octavia variety.
Advantages and disadvantages
Raspberries ripen during the period when the early and middle varieties have already been harvested, and the remontant varieties have just formed the ovaries of the second wave. Therefore, the variety fills an empty niche in berry production.
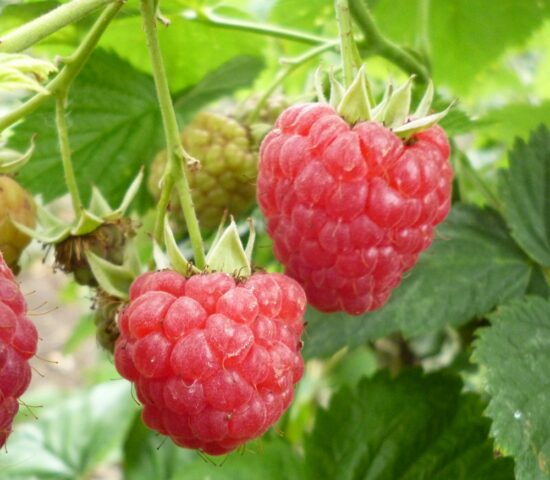

Raspberry Octavia is characterized by one but long fruiting cycle (1.5 months)
Pros:
- pronounced aroma;
- balanced taste;
- leveled fruits;
- high nutritional value;
- the berries do not fall off after ripening;
- good frost resistance;
- stable immunity;
- versatility in use;
- maintains its presentation during transportation;
- stress resistance.
Minuses:
- average yield;
- requires fixation to a support;
- poor drought resistance;
- berries can bake in the sun.
The variety requires constant feeding with mineral fertilizers and organic matter.
Features of growing Octavia raspberries
Planting is carried out in the spring before the buds open. Choose a flat area without stagnant water, in a subtropical climate - with periodic shading, in a temperate zone - in an open place. Raspberries grow only on slightly alkaline or neutral, aerated, fertile soil with good moisture-holding capacity.
How to plant
If there are several raspberry seedlings, they are distributed in a checkerboard pattern. The interval between holes is 2.5-3 m. Material 1-2 years old is purchased at a nursery.
Planting algorithm:
- They dig up the place, add organic matter and ash.
- Dig a hole with a diameter of 50*50, 15 cm deep than the root system.
- The bottom is covered with compost mixed with peat and part of the turf soil.
- Place the raspberry in the center and cover it with soil so that the neck is about 5 cm under the ground.

After planting, Octavia raspberries are watered with Kornevin solution and the trunk circle is mulched
Octavia raspberry care
Watering the variety depends on the frequency of precipitation; the soil should always be moist. They maintain soil aeration by loosening and remove weeds at the same time.
Feed the raspberry variety:
- in the spring before buds open with nitrogen;
- after two weeks - liquid organic matter;
- after 14 days, add “Nitroammofoska”:
- at the time of budding, microelements (iron, phosphorus, manganese) and the “Bud” product are effective;
- when the berries are formed, fertilize with superphosphate and potassium sulfate;
- After harvesting, complex mineral fertilizer and organic matter are applied.
For a plant of reproductive age, perennial stems are completely cut out in the fall, leaving only the shoots of the current season. They are shortened by 1/3.Raspberries require insulation of the root system for the winter. The plant is hilled up and mulched, and if necessary, the bush is covered completely.
Reproduction
Raspberries form a sufficient amount of root shoots - this is the most common method of propagating the Octavia variety. During loosening, strong sprouts are left, the rest are cut off. The following year, in the spring, the material is planted on the site.
You can propagate raspberries by layering. To do this, bend a lateral perennial shoot to the ground, fix it and cover it with soil. They are well insulated for the winter; at the beginning of the season, plots are cut and planted.
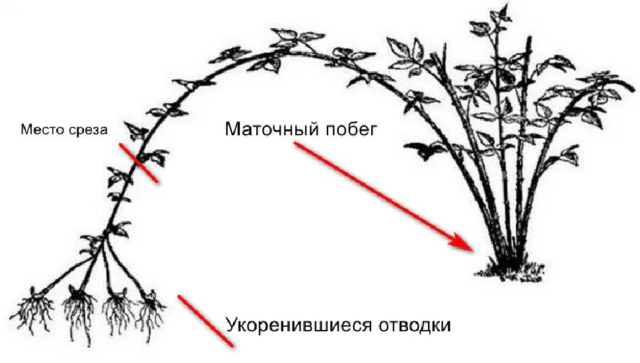
The layering method is quite effective in growing raspberries.
A less productive way to propagate a crop is by cuttings taken from annual shoots. They are planted in a container with a substrate and brought indoors for the winter. In the spring, the rooted material is determined to a permanent place of growth.
Prevention of diseases and pests
At the end of the season, remove all plant debris and dig up the soil around the bush to kill overwintering pests and pathogen spores. In the spring, treat the raspberries and soil with Topaz and cover the surface of the root circle with ash. During budding, the plant is sprayed with Energen. In the fall, before frost, they fumigate with colloidal sulfur and water the soil with Karbofos.
Conclusion
Raspberry Octavia is a late hybrid of English selection. The yield is average, but stable, the plant is stress-resistant, tolerates low temperatures well, and develops quickly. The variety responds poorly to moisture deficiency. In subtropical climates, it requires regular watering.
Reviews from gardeners about Octavia raspberries








