Content
The method of propagating honeysuckle by cuttings is considered one of the most popular. Only the method of dividing the bush competes with it, but it has its drawbacks. With this type of propagation, the entire plant is exposed to stress. If the procedure is performed incorrectly, the berry plant can die. Propagation by cuttings is completely safe for the mother bush. Cutting branches will not cause the plant to die.
Features of planting honeysuckle cuttings
The popular method of propagating edible honeysuckle has its own characteristics. You need to know them for the process to complete successfully. First of all, it is important to choose cuttings that have the best survival rate. These include pieces of twigs taken from honeysuckle during the beginning of fruiting. Moreover, for reproduction they are always chosen by young ones, who are the growth of this year.
The harvesting time for the highest quality materials depends on the climate of the region and the type of honeysuckle. In late crops, berry ripening begins in early July. Early varieties delight with their harvest in the first ten days of June.
Summer harvest cuttings are called green because their bark has not yet matured to brown. You can propagate the crop using lignified branches, but they are collected in late autumn or spring before the buds open. There is also a third option. It involves cuttings of edible honeysuckle in the summer, but the branches are prepared in combination. The shoot is cut so that one part of it has green bark, and the other is woody.

Cut green cuttings are immediately rooted
The popularity of the rapid propagation method is also explained by the possibility of preserving the variety you like and receiving free seedlings. It is enough to ask your friends to cut ten cuttings from different honeysuckle bushes and root them immediately in open ground or a box with substrate.
However, if there is a shortage of material for reproduction, it is better to do it in a different way. If you managed to get several branches, then for maximum savings it is better to root them in separate containers. The popularity of the reproduction method is explained by the following facts:
- If it gets colder outside, the pots with seedlings can be moved indoors or to a greenhouse. During hot weather, plantings are brought into the shade.
- There is no need to closely monitor soil moisture. In the hot summer, the soil in the garden dries out quickly, which is dangerous for the cuttings. The soil in a flower pot retains moisture longer.Advice! Germination of freshly cut green cuttings can be done in water. Then there will be no problems with watering at all.
- It is easier to plant a rooted honeysuckle seedling from a separate container in open ground. The plant's root system is not damaged, which contributes to better survival.
The method of growing honeysuckle from cuttings is simple for the gardener and does not require any costs. If propagation does not work the first time, the next season you can cut more branches and try to root them.
How to propagate honeysuckle from cuttings
Having decided on this method of propagation, the gardener should know that it is easier to do this in the spring. If there was no opportunity, then in the summer and, finally, in the fall. The principle is almost the same, but there are nuances. They are associated with the extraction of cuttings, storage and rooting.
The video shows an example of reproduction technology:
How to propagate honeysuckle by cuttings in spring
There are three options for propagating berries in the spring:
- lignified brown cuttings harvested in the fall;
- lignified brown cuttings cut from honeysuckle in the spring before the buds swell;
- green fresh shoots cut in late spring or early summer.
The first two options are also suitable for autumn propagation, so they will be discussed later. Now it’s worth familiarizing yourself with the rooting of green shoots.

The green tops of the branches are harvested for propagation after the end of honeysuckle flowering.
In warm southern regions, early varieties of honeysuckle can be propagated with green shoots from late spring. The bush should already bloom and begin to form berries. Before harvesting cuttings, the vine is checked for maturity. When bent, the green twig should break easily.
Only the middle part of the cut green branches is left. The lower cut is made oblique at an angle of 45°, and the upper cut is made straight above the bud by 1.5 cm. The lower leaf on the shoot is removed, and the rest are shortened to half.
In this form, it is difficult to plant honeysuckle with a branch directly into open ground. First, cuttings require rooting. They do this in water or soil. When choosing the second option, prepare a substrate from 3 parts sand and 1 part peat. If desired, the soil mixture can be purchased at the store. Sometimes it is replaced with perlite or vermiculite.
The prepared substrate is loaded into flower pots and moistened abundantly. The lower part of the cuttings is immersed in the soil, covered with film, jars or cut PET bottles to create a greenhouse. Throughout the entire process, the seedlings are kept at a temperature of 20-25 oC. After about 1.5 weeks, the cuttings should take root. They can be planted immediately or left to grow until next spring in a house or greenhouse.
How to root honeysuckle with cuttings in summer
In cold regions, it is better to propagate the berry plant in the summer. There are two options here. The first is to cut honeysuckle with green cuttings and try to root it, as discussed above. The second option involves preparing combined shoots. Such branches have a green upper part and a woody lower part. Cuttings with one or two side shoots are taken.
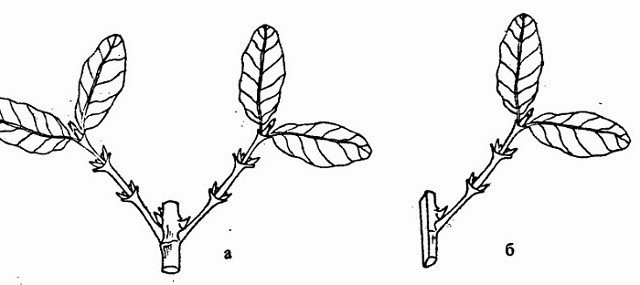
A combined cutting may have one or two green side shoots
Using combined cuttings has two great advantages. Firstly, according to statistics, the survival rate of such material is 30% higher than lignified shoots. Secondly, the green part of the branch contributes to almost 100% rooting of the woody part under favorable conditions.
Cuttings are done after flowering.The branch is cut so that the green shoot below has a lignified part about 2 cm long. The blanks are immersed in the prepared substrate to a depth of 3-5 cm, and a greenhouse is set up. The soil is constantly kept moist. After about 15 days, rooting will occur. It is impossible to grow strong honeysuckle seedlings from summer combined cuttings. Before the onset of spring next year, they are grown indoors.
How to propagate honeysuckle by cuttings in the fall
With the onset of autumn, gardeners stock up on lignified branches for further propagation of the berry plant. It is important to set the timing correctly here. It is unwise to carry out cuttings of honeysuckle in the summer after the berries, since the lignified material has not yet matured. They do this in late autumn, when the bush has shed its leaves.

In the fall, lignified cuttings are not germinated, but are rooted with the onset of spring.
One-year-old lignified growth 1 cm thick is cut in the fall. The cuttings are cut 20 cm long so that each has 5 internodes. For storage, the harvested material is sent to the cellar, wrapped in burlap or covered with sand and sawdust. Be sure to remember to treat with a fungicide to prevent the development of fungus.
They begin to reproduce only in the spring. The prepared substrate is moistened and treated with fungicides against rot. The blanks are immersed in the ground at an angle of 45°, maintaining a distance of about 12 cm. In the south, they can be planted directly on the street. For cold regions, it is optimal to use nurseries.
After the woody branch is buried, one bud should remain above the ground. A greenhouse is being built above the plantings. Rooting will occur around the third week.Honeysuckle seedlings growing outside are freed from the greenhouse. If you used a nursery, then harden the plants before planting them in open ground.
How to take honeysuckle cuttings
Cutting the planting material is done with sharp pruning shears. If reproduction occurs in summer, green branches can be cut off with a sharp knife. In any case, the tool must be disinfected before use.

Green branches are easier to cut with a knife
Green shoots are cut early in the morning or during the day if the weather is cloudy. The length of the workpiece is from 7 to 12 cm. There must be at least three internodes with full buds and leaves. The bottom of the leaf is torn off, and the rest is cut with scissors by 50%. The lower oblique cut of the branches is immersed for a day in a solution with any drug to stimulate root growth.

Lignified honeysuckle branches are cut with pruning shears
It is possible to stock up on lignified cuttings in the spring before the buds swell or in the fall after the leaves have dropped. In the second option, this is the period from September to October, which depends on the weather conditions of the region. The branches that are ripe from the current year are used. Each workpiece should have from 3 to 5 internodes.
When harvesting in spring, it is enough to cut short cuttings up to 12 cm long with three internodes. The upper cut is made 5 mm higher from the bud at a right angle. The lower cut is oblique at a distance of 15 mm from the bud. Autumn cuttings are cut according to a similar principle, only their length is up to 20 cm, and there are five internodes.
How to root honeysuckle cuttings
To propagate the berry plant, two methods of rooting blanks are used. The easiest way is to germinate honeysuckle cuttings in water before planting them in the ground.

When germinating in water, you can see which branch has taken root and which one will not.
Immediately after cutting the green blanks with a lower oblique cut, they are placed in any container, for example, a jar. Pour in some water. To stimulate root growth, you can add “Kornevin”. As the liquid evaporates and is absorbed by the branches, add a little water. When roots about 2 cm long appear, the workpieces are transplanted into the ground.
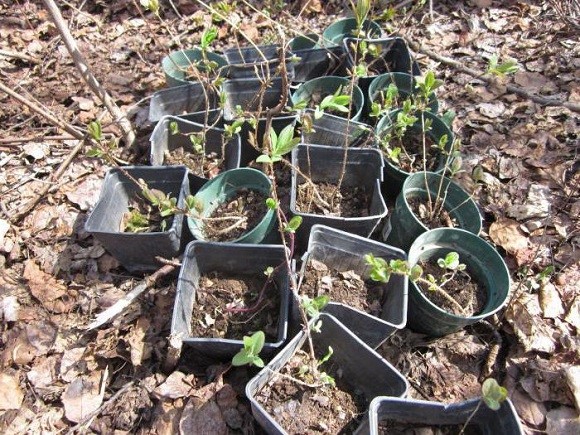

Germination in a substrate allows you to immediately obtain a ready-made seedling
The second rooting method is based on immersing the workpieces directly into the substrate. You can plant green shoots using this method, but most often it is used for lignified workpieces. Oblique cuts of cuttings are treated with Kornevin and immersed in the soil in a garden bed or in a nursery. Setting up a greenhouse. The soil is constantly kept moist. Droplets of condensation on the shelter indicate a good microclimate. After the sprouts appear, honeysuckle seedlings begin to harden, opening the shelter for a short time. Over time, the greenhouse is removed and the amount of watering is reduced.
Useful tips
Honeysuckle is considered an unpretentious berry crop. Even with its propagation, the gardener should not have problems. In order for the process to be successful and the berry plant to bear fruit well, it is important to listen to several recommendations:

Honeysuckle does not cause much trouble for the gardener
- With this method of propagation, it is necessary to harvest from shrubs of various varieties. Preferably at least 3 types. Without proximity to edible varieties, honeysuckle does not bear fruit.
- To plant rooted seedlings, choose a sunny place.
- It is better to plant seedlings not in rows, but in curtains. This arrangement better attracts pollinators.
- For cuttings, use healthy honeysuckle bushes without visible signs of disease or pest damage.
And what is also advisable to do is to harden the seedlings well before planting them in a permanent place.
Conclusion
The gardener chooses the method of propagating honeysuckle by cuttings that suits him best and is suitable for the climatic conditions of the region. The best survival rate of material harvested in spring or summer is observed. Some autumn branches may disappear over the winter if storage technology is violated.








