Content
In the 2nd half of the 20th century, USSR breeders developed many varieties of edible honeysuckle. Many of them are still in demand and enjoy deserved popularity among gardeners. The following is a description of the variety, photos and reviews of honeysuckle Cinderella - an unpretentious and productive variety of this shrub, quite often found in household plots.
Description of honeysuckle variety Cinderella
Edible honeysuckle has always attracted the attention of breeders. Unlike ordinary berry bushes, the fruits of this plant are much healthier, and almost no care is required. However, in nature, edible honeysuckle has a very limited distribution area. To expand it as much as possible and increase quantitative and qualitative indicators, breeders from different countries have made a lot of efforts. Thanks to their work, many varieties of this amazing plant have appeared, suitable for cultivation even in the most unfavorable regions.

The fruits of honeysuckle Cinderella are quite large
The variety of edible honeysuckle (loniceraedulis) Cinderella was bred in 1974 by breeders of the Siberian Horticulture Research Institute named after. M. A. Lisavenko.The progenitor is Kamchatka honeysuckle No. 8 (later the Start variety), selected seedlings of which acquired the necessary properties as a result of free pollination. Variety testing was carried out from 1982 to 1990, and in 1991, Cinderella honeysuckle was included in the State Register as recommended for planting in the West Siberian and East Siberian districts. Subsequently, this territory was expanded to cover the entire country.
The main parameters and characteristics of the plant are shown in the table below:
Parameter | Meaning |
Plant type | Deciduous shrub. |
Crown | Compact, medium spreading, thickened, 0.6-0.7 m high. |
Escapes | Medium thickness, straight or slightly curved, green, hairless. |
Leaves | Large, oval-elongated, with a slight concavity, light green. |
Root system | Tree-like, branched, the bulk of the roots lie at a depth of up to 0.5 m. |
Flowers | White, large, flowering time - May |
Fruit | Oval-elongated, elongated, sometimes fusiform, dark, blue-violet, with a waxy bluish coating. Weight 0.7-1.4 g. |
Ripening period | 2nd half of June |
Productivity | Up to 5.5 kg from 1 adult bush |
Precociousness | The first fruits appear 3 and sometimes 2 years after planting. |
Taste | Sweet with a slight sourness and pronounced strawberry aroma. |
Purpose of fruits | Universal. |
A short overview video about how Cinderella honeysuckle bears fruit can be viewed at the link:
Planting and caring for honeysuckle Cinderella
Honeysuckle Cinderella, like most other edible varieties of this shrub, is self-sterile.Therefore, when deciding to plant this crop, it should be taken into account that it is necessary to plant not only the plant itself, but also the pollinator, which should be located in close proximity. Optimal for fruiting is a group of at least 4 bushes growing next to each other.

When choosing a seedling, you should give preference to planting material with ZKS
When choosing planting material, you should give preference to seedlings 2-3 years old, sold in special containers. A closed root system is more stable and tolerates planting much better. The honeysuckle seedling Cinderella should have a good appearance, there should be no mechanical damage or signs of disease. If the roots of the plant are open, be sure to inspect them for rot.
The best time to plant Cinderella honeysuckle seedlings in open ground is early spring or autumn. In areas with a temperate and warm climate, it is better to plant in the autumn, at the end of the growing season. There should be at least a month left before the onset of cold weather. During this time, the seedling will have time to take root and adapt to the new place, and after winter it will confidently begin to grow. In areas where winter comes early, Cinderella honeysuckle should be planted in early spring, as soon as the ground thaws.
Choosing the right place to plant Cinderella honeysuckle is very important. In order for the shrub to grow and bear fruit well, the area for planting it must be well lit. It is desirable that the place be protected from the north wind, so honeysuckle is often planted on the south side of a fence or building.The soil should be loose and breathable, fertile, loamy or sandy loam, with a close to neutral acidity level.

The size of the planting hole depends on the volume of the root system of the seedling
Before planting honeysuckle Cinderella, it is necessary to dig holes, the dimensions of which must correspond to the volume of the root system of the seedlings; this is at least 0.6 m in diameter and 0.5 m deep. The excavated soil is mixed in equal parts with humus; to increase fertility, a little potassium and phosphorus fertilizers, wood ash are added to it, and if the soil has high acidity, then additional lime or dolomite flour is added. The honeysuckle seedling Cinderella is installed in the planting hole strictly vertically. The root collar is not deepened when planting. The free space of the pit is filled with enriched soil, periodically compacting it. After filling the entire volume, abundant watering of the root zone is carried out, and then the surface is mulched with humus.

Honeysuckle needs regular watering
Further care of the shrub is simple. Cinderella honeysuckle needs regular watering, but excess moisture is harmful for this crop. If there is insufficient rainfall, honeysuckle is watered once a week, approximately 10 liters for each bush. During fruit ripening, watering can be done more often and more abundantly to avoid premature shedding of unripe berries. It is recommended to fertilize the bush starting from the 3rd year after planting. It is produced in several stages:
- Early spring. Foliar feeding with urea (20 g per 10 liters of water) or root fertilizing with ammonium nitrate (25-30 g per bush)
- Spring, after flowering.Rotted manure or compost is applied to the root zone in an amount of 10-15 kg for each honeysuckle bush.
- Autumn, September-October. Root feeding with superphosphate (25-30 g) and potassium sulfate (15-20 g) for each bush. It is better to apply in diluted form, dissolving the required amount of fertilizer in 10 liters of water.
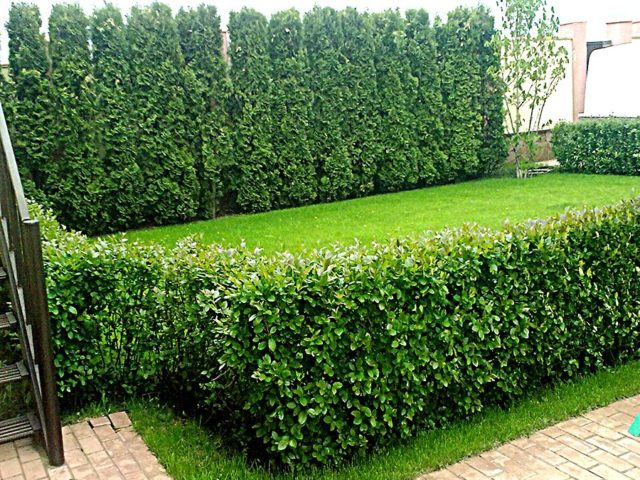

Low bushes of honeysuckle Cinderella can also be used as ornamental plants
Cinderella honeysuckle bushes are used not only for growing berries, but also as landscape plants, for example, for creating low hedges. In this case, formative pruning of the bush is performed to give it a more decorative appearance. In addition, it is necessary to thin out the crown, remove excess thickening, and remove side branches if they lie on the ground. Every year, in spring and autumn, it is necessary to clear the bushes of dry, broken and diseased shoots.
Pollinators of Honeysuckle Cinderella
The need for pollinators is one of the main disadvantages of Cinderella honeysuckle. If a plant is planted for the purpose of harvesting, then there must be other species nearby. The best pollinators for honeysuckle Cinderella are shown in the table:
Pollinator varieties | % pollination |
Azure | 76 |
Gerda | 55 |
Fiery | 36 |
Kamchadalka, Tomichka, Amphora | 25 |
Propagation of edible honeysuckle Cinderella
Reproduction of edible honeysuckle is possible both by seed and vegetative methods.Healthy seedlings can be obtained from seeds, but there is no guarantee that they will retain varietal characteristics. Therefore, gardeners propagate Cinderella honeysuckle vegetatively - by layering or cuttings.
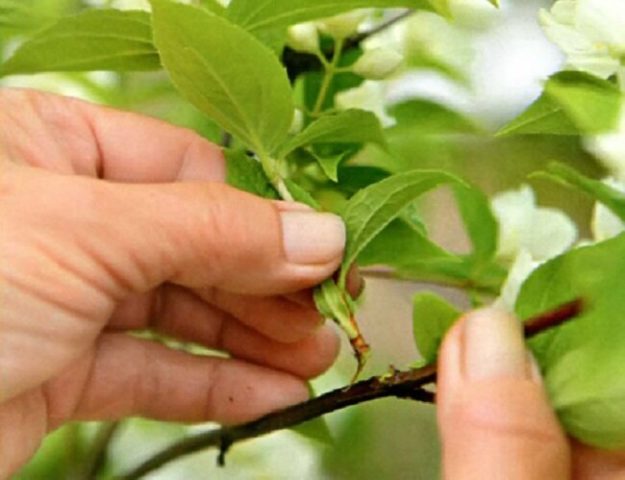

Green cuttings give the highest percentage of rooting
The most effective method of propagation is green cuttings. When using them, approximately half of the planting material takes root. The best time for cuttings is the period of fruit ripening. The procedure is as follows:
- A branch of annual growth 20-40 cm long must be torn off from the mother branch with a piece of cambium (heel).
- Place the cuttings in a root formation stimulator (heteroauxin) for 12-16 hours.
- Plant the cuttings at an angle of 45° towards the sun in a special bed. A mixture of peat and perlite is used as a nutrient soil. The location for the bed should provide shade for the cuttings at midday and light in the morning.
- Regularly moisten the bed with cuttings. After 2-3 weeks, the shoot will begin to form its own root system.
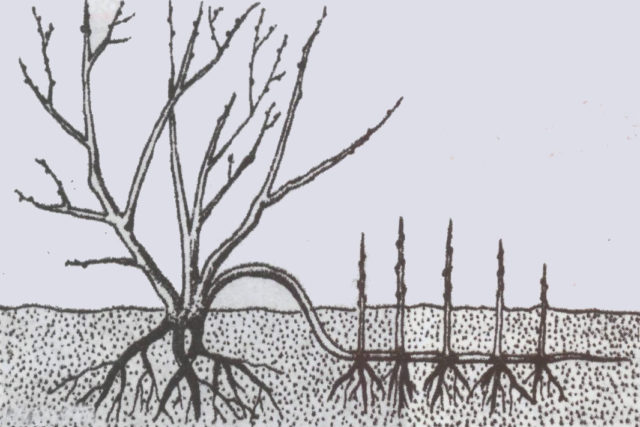
Reproduction scheme for honeysuckle Cinderella by layering
Another simple way to propagate Cinderella honeysuckle is to create air layering. To do this, a strongly inclined side shoot is fixed to the ground and dug in. In the process of regular moistening, roots and independent shoots will begin to form in the internodes of the shoot. The cuttings overwinter together with the mother bush, and in the spring they can be cut off from the parent branch and transplanted to another place.
Diseases and pests
The originator of the variety notes that there are no cases of diseases or pests on the Cinderella honeysuckle, and this is also evidenced by reviews from gardeners. The shrub is highly resistant to viruses and fungi, however, for prevention in early spring, it is advisable to treat the shrub with a solution of Bordeaux mixture.

For prevention, it is advisable to treat the bushes with a fungicide in early spring.
It is also necessary to regularly remove dry and broken branches from the crown, which can become a source of infection, and remove fallen leaves.
Conclusion
Description of the variety, photos and reviews of honeysuckle Cinderella are confirmation that this shrub can easily replace traditional berry bushes, especially in regions with harsh climates. The plant really has many positive qualities, and even such nuances as the need for pollinators, a slight prolongation of fruiting and a tendency to shed berries do not detract from all its advantages. In addition, the agricultural technology for growing honeysuckle Cinderella is extremely simple, the crop is unpretentious and resistant to many unfavorable factors, which is very important for gardeners who are not able to devote sufficient time to plantings.








