Content
Common dogwood is a paradoxical plant. It is unpretentious and can grow on any soil, but this applies to adult dogwood or its cuttings/root offspring. The common dogwood can be grown from seeds, but at the beginning of its life it is a very capricious object.
Of the berry bushes, this plant is the first to bloom and the last to ripen. The berries look already ripe, but in fact they still have a long time to ripen. The fruits of this plant were considered medicinal. Now they are used in folk medicine.
Dogwood: description of the plant
A deciduous, medium-sized plant from the small dogwood family. The second name for dogwood is male dogwood. The root system of the tree is located close to the surface of the earth, fibrous. The leaves are large, 3.5-8 cm long. The location on the branch is opposite. The leaf shape is simple. The color is bright green. The leaf has 3-5 pairs of veins.
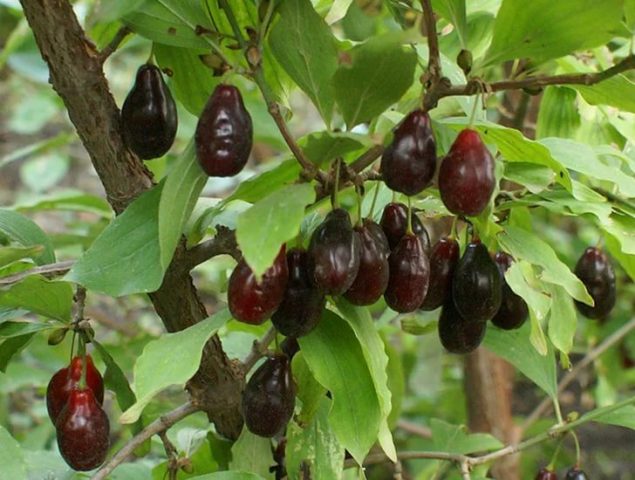
The fruit is an oval-shaped drupe of dark brown, almost black color. The berries of the common wild dogwood have relatively little pulp. It is less juicy and denser than the fruits of cultivated forms of deren.
The fruits of garden dogwood are very large and juicy. Can be of different shapes:
- pear-shaped;
- spherical;
- oval.
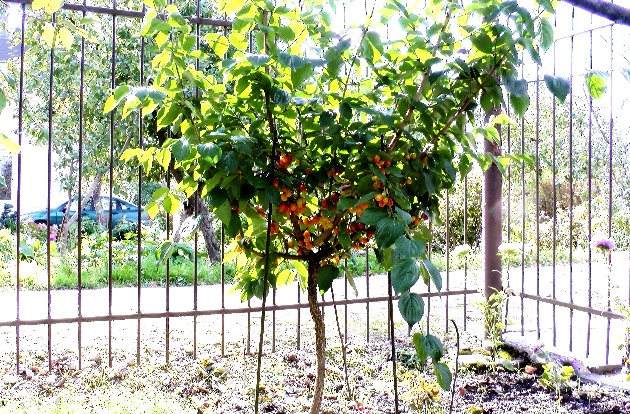
The color of the ripe berry is very dark. A more common belief is that dogwood berries are red. In fact, derain berries are collected very early, while the fruits are still hard. Ripe berries are dark brown, almost black in color and burst easily.
The surface of the berries of the male tree is shiny and smooth. The structure of the fruit may be incorrect, then the berry will look lumpy. Ripe dogwood berries in the photo below.
Depending on the variety of garden tree, the weight of the berry ranges from 2 to 6 g. The percentage of pulp to the total weight of the fruit: for wild 68%, for garden 88%.
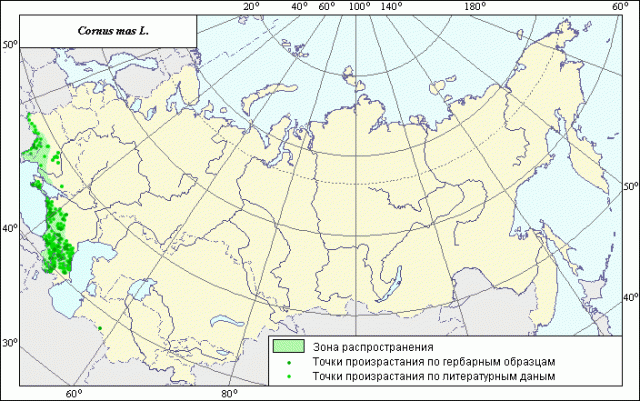
The natural habitat of the common wild dogwood is the southern regions. Thickets of the plant are found throughout the Southwestern part of Russia. The most favorable conditions for male deren are in the mountains and foothills of the Caucasus and Crimea.
The common wild dogwood did not take root well in gardeners' summer cottages, since it is essentially undergrowth and requires forest soil for successful growth.Also, male turf could not be grown north of its natural habitats.
Dogwood is a tree or shrub
Botanists often like to make fun of non-specialists by asking a question about this or that representative of the flora: is it a shrub or a tree. To the amazement of ordinary people, a tree often turns out to be a bush, and a bush is actually a tree. You can also joke like this with an ordinary dogwood. Initially, dogwood is a shrub 3-5 meters high. But on soil rich in nutrients, the strongest shoot can grow and turn into a tree 5-6 m high.
Dogwood compatibility with other trees
Gardeners know that many trees do not tolerate proximity to each other. The main enemy of all fruit trees is the walnut. But other plants are not always friends. For example, a pear cannot be planted next to a cherry. Due to the fact that the dogwood is still a somewhat exotic inhabitant of the garden, there is almost no compatibility data on it.
It is guaranteed that you can plant different varieties of dogwood next to each other. The compatibility is perfect. According to unverified data, young dogwood can be planted under an adult apricot. Nobody knows what will happen in the opposite situation. According to other gardeners, dogwood can be planted under almost any fruit tree, since it even prefers shaded places. What those trees under which the owner planted the new plant “think” about this is not specified.
The statement that the dogwood bush is the only one that can grow under a walnut is very doubtful.In nature, walnut and turf do not come into contact.
Frost resistance of dogwood
The plant is distinguished not only by relatively good drought resistance, but also by high frost resistance. Common dogwood can withstand frosts down to -35°C, which makes it possible to grow garden varieties of dogwood in the northern regions. But it will not be possible to grow a dogwood tree in Siberia, since severe frosts often occur there. Because of this, only the shrub form of the tree is possible. When the ground part freezes, the plant recovers by sending out shoots from the roots.
Dogwood: from flowering to ripening
In addition to its official botanical names, the common dogwood has one more name: devil berry. There is a legend about the origin of the name associated with the timing of flowering and ripening of dogwood fruits.
When Allah created the world and decided to rest, during his sleep all living beings came running to the Gardens of Eden and began to divide the plants. There was a noise, a din, and a fight began. Allah did not like this, and he demanded that everyone choose only one plant. Among those who wanted to get something useful for themselves was the shaitan. And Shaitan asked for a dogwood, considering himself the most cunning. After all, the common dogwood blooms earlier than all other berry plants.
This is true. The flowering period for this plant is in April at an air temperature of 8-12°C. The flowers of the male dera are small and yellow. Umbrella inflorescences. The number of flowers in an umbrella is 15-25. Flowers have 4 stamens and a pistil, that is, they are bisexual. Petals 4. Flowering lasts 10-14 days. The common dogwood blooming in the photo is a specimen from the forest. Garden varieties of derain do not look so beautiful.
“Early flowering dogwood means early harvest,” thought the shaitan.The first berry is highly valued and you can make a lot of money from it. Why does Satan need money, the legend is silent. He sat down under a tree to wait for his harvest of early berries. Summer has passed, all the other fruits and berries have already ripened, but the dogwood is still green.
Shaitan decided to speed up the ripening of the fruit (that’s when this technology was born) and began to blow on the berries. The dogwood turned bright red but remained very sour and firm. Frustrated by the failure of a super-profitable business, the shaitan told people to take this crap for themselves and spat in frustration. So much so that the dogwood berries turned black.
And now in late autumn, after harvesting all the harvest in the gardens, people went into the forest for dogwood berries. They collected black but sweet berries and laughed at Satan.
In fact, the common dogwood does not ripen so late. The harvesting period for the fruits of the male tree is the end of August - September. And you can’t delay harvesting, as the berries fall to the ground.
And then everything was attributed to the shaitan, since he was very offended that he gave his berries to people. The next year, Shaitan managed to double the dogwood harvest. People were happy about this. But to ripen so many derain fruits, it also required twice as much solar heat. And the sun, which gave up all the heat during the summer, could not warm the earth in winter. Since then, there has been a sign that if the common dogwood has grown well, it means that the winter will be cold.
Dogwood pollination
Although the common dogwood has bisexual flowers, pollination does not occur on one plant. To produce a harvest, dogwood needs a pollinator.The wind acts as a pollinator for male deer at low temperatures, so it is necessary to plant at least two specimens of different varieties in the garden for cross-pollination to occur.
Common dogwood is a strict cross-pollinated plant, so you can plant two bushes of the same variety, but these seedlings must be from different mother bushes. The easiest way to guarantee a harvest from a plant is to plant a wild forest bush next to the garden variety of male dera.
When pollinated by wind, the yield will be low. Other pollinators of dogwood are honey bees. If they are available, the garden owner is guaranteed an annual rich harvest of derain berries.
How the garden dogwood blooms
The flowering of garden varieties of male dera is the same as that of the wild ancestor. Due to the fact that summer cottages are usually protected from cold winds and have their own microclimate, garden turf can bloom even earlier than wild plants. In northern regions, turf may begin to bloom too early and, as a result, fail to bear fruit.
When is dogwood harvested?
Cultivated dogwood can not only be of different colors and shapes, but also have early, mid and late ripening varieties. Early varieties of male dogwood begin to bear fruit in the second half of August, late varieties - in mid-October. Therefore, the timing of harvesting berries from male deer bushes in the garden can last for 2 months if you choose the varieties correctly.
The common dogwood does not ripen very smoothly and among the ripe berries there are unripe ones. When harvesting berries “for yourself,” you will have to pick the same plant several times.
The productivity of male tree depends on age.
Age, g | Productivity, kg |
5—10 | 8—25 |
15—20 | 40—60 |
25—40 | 80—100 |
How to propagate dogwood
Reproduction of common dogwood occurs in 5 ways:
- seeds;
- vaccination;
- cuttings;
- layering;
- basal offspring.
The first method is the most time-consuming and unreliable. The second fastest in terms of obtaining berries from a newly planted plant. The other 3 require minimal gardening skills.
Propagation by seeds
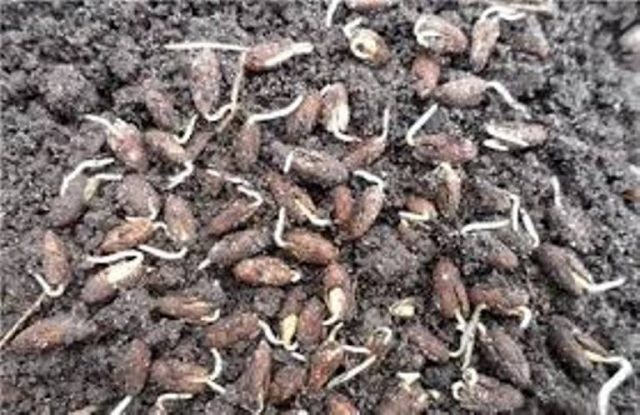
This method is the easiest way to grow male turf if the fruits are still green. The seeds and the pulp are buried in the ground, watered well and the hope is that in a few years the shell will rot and the seed will sprout.
The use of ripe dogwood berries involves some procedures that require a certain skill and accuracy, but allow you to speed up the germination of common dogwood. And still, the process of growing male dena will take several years:
- ripe fruits are poured with warm water and left for several days to ferment;
- after a few days, the seeds are removed from the softened pulp, washed with water and placed in sawdust in a cold place (refrigerator) for 1.5 years;
- in the second year, at the end of February, the seeds are taken out of the refrigerator and placed near the radiator to warm up for a week;
- during warming up, prepare the soil for planting: one part each of sand, compost and fertile soil (preferably forest soil from under wild dogwood);
- For accelerated germination, the seeds must be carefully cut, and this is where precision and accuracy are required;
- After planting, the soil is watered, the containers are covered with film and placed in a warm place.
When tree sprouts appear, the film is removed and the containers are placed so as to protect them from direct sunlight.
Male deer seedlings are planted in a permanent location after the onset of stable warm weather. And also in the shade or partial shade.
You can simply plant derain seeds in May directly into the ground to a depth of 3 cm and wait for the shoots to appear. To create more favorable conditions, the planting site is covered with film.
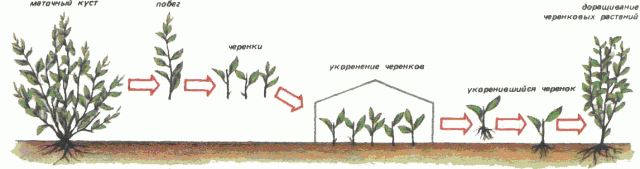
Cuttings
Annual shoots are cut from the mother plant in mid-summer. The lower leaves are removed by 1/3 and soaked in a stimulator for the growth of the root system for 5 hours. After this, they are planted in a shaded place. By autumn, approximately half of the male tree cuttings take root.
In the fall, cuttings are prepared from lignified shoots of the male tree, which are stored in the refrigerator until spring. In the spring, they are planted in a permanent place, having previously been soaked in a root system stimulator.
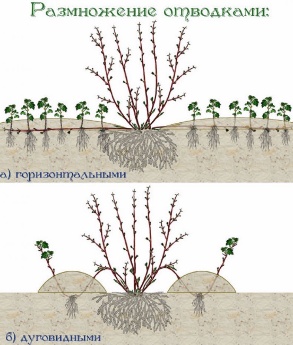
By layering
The method is suitable for a bush, since bending a young shoot from a tree is very difficult. Does not require any knowledge, special skills or fertilizers.
In the spring, one- and two-year-old shoots of the male tree are bent to the ground and covered with soil. There are two ways to propagate dogwood by layering:
- horizontal;
- arcuate.
With horizontal shoots, the plants are completely covered with soil. With an arcuate one, only the middle of the layer is sprinkled with soil, leaving the top outside. The procedure is carried out in the spring. By autumn, the tree shoots take root and can be separated from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place.
The difference between these methods is that from horizontal layering you can get many small seedlings, since the common dogwood takes root from each pair of buds. One “goes” to the roots, and the steam room produces a sprout.
With the arcuate method, only one seedling is obtained from each cutting of the tree. But this seedling will be older and will produce a harvest earlier.
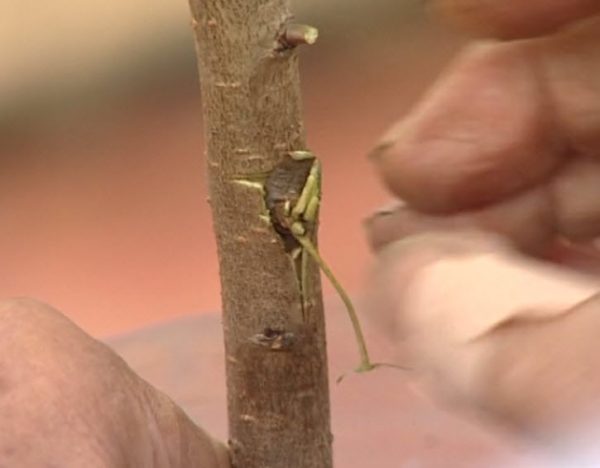
Vaccination
Suitable for the region where wild dogwood grows. It is used if you need to quickly grow a garden variety of male deer. With this method of propagation, only a tree is obtained, since all “wild” shoots of the male tree must be pruned annually. In this case, a standard plant is formed.
Budding is carried out in the autumn, since the spring grafting of the common dogwood does not take root well. The budding technique is the same as for other plants. If everything is done correctly, the leaf petiole will fall off only after 3-4 days. After 1.5 months, the harness is removed. In the spring, all new wild shoots of a grafted dogwood are pruned, leaving only the grafted one.
Planting and caring for dogwood in open ground
Common dogwood is one of the plants that prefer to grow in open ground, since its root system, although it does not go deep into the ground, grows widely near the surface.
Planting and caring for common dogwood is almost the same as for other fruit plants. The bush is cared for like a bush form. Seedlings are planted, making sure that the root system of the tree is preserved as best as possible. The more small roots the seedling has preserved, the better the male tree will take root and the sooner it will produce a harvest.
But if caring for an already established plant is not difficult, then planting is a very important moment, since at this time the common dogwood is very vulnerable to external factors and water shortages.
Where to plant dogwood
For planting, choose an area in partial shade. Wild dogwood can grow in direct sunlight, but prefers shaded areas. For young shoots of male deer grown from seeds, sunlight is contraindicated.
The site is chosen in the southwest. Preferably with a slight slope of 5-10° to drain excess rainwater. Groundwater should be at a depth of 1.5-2 m.
You need several bushes and the planting area for this plant should be large. The average for one bush is 6x6 m. On rich soils with watering, the feeding area for one plant can be 5x4 m. For poor soils without watering - 7x7 m.
What kind of soil does dogwood like?
Common dogwood requires light soils with good water permeability. Sandy loam soil is good. If you focus on natural conditions, then you need soil with a large amount of half-rotten plant debris, which allows water to pass through well and supply the bushes with nutrients.
How to plant dogwood
Having found a suitable area, they dig a hole under the seedling, 0.6 m deep. The plants are quite small, but the hole is needed to fill it with soil suitable for common dogwood.
Since the plant needs specific microflora, bacteria can multiply in the fertile soil with which the hole is filled.
When planting, the root collar is slightly buried, since after watering the soil will settle and the collar will rise level with the ground.After planting, the seedling is watered abundantly, compacting the soil. If the neck comes out of the ground too high, add additional soil.
When does dogwood begin to bear fruit after planting?
Fruiting time directly depends on the method of plant propagation. When growing from seeds, the first harvest should be waited no earlier than 8 years after the sprouts appear. In the first years, the root system develops and young shoots are not ready to bear fruit.
A grafted tree may produce the first berries the very next year after planting, but the harvest will be small.
With vegetative propagation by offspring, everything depends on how old the seedling is. The harvest may be either next year or 3-4 years later. When propagated by cuttings, the harvest will occur after 3-4 years.
Dogwood transplant
Since the common dogwood grows only in the open air and lives for 150 years, the best option would be to plant it in a permanent place where it will not interfere with other plants for a long time. And leave him alone. But if there is a serious need to replant the plant, then it should be dug up with a large lump of earth in order to damage the root system as little as possible. The plant is large and you will have to use a winch or crane to move it to a new location.
The dug plant is carefully transferred to a newly prepared hole and covered with new soil, taking the same precautions as when planting young seedlings. Replanting is carried out in the fall, when the plant goes into hibernation.
How to care for dogwood
Caring for an established plant consists of timely removal weed, loosening the soil and fertilizing the plant if necessary.
There are more worries with young and immature shoots. Before wintering, the soil under the first-year seedlings is mulched to protect the roots from freezing. Later, after the plants go into hibernation, they are covered with spruce branches. In the spring, the insulation is removed in stages. First, the seedlings are freed from the spruce branches. You don’t have to remove the mulch, but mix it with the soil when loosening it.
Natural materials are used for mulching:
- sawdust;
- fallen leaves;
- grass;
- peat.
Organic matter, rotting, will provide the dogwood with nutrients.
How to feed dogwood
The common dogwood has adapted to grow in rather poor soil. On the one hand, areas close to the seas are not rich in nutrients. These substances simply have nowhere to come from where there was a sea relatively recently. But these same areas are rich in calcium deposits. Although the common dogwood is a forest shrub, the forest floor is of little nutrition if it has not already turned into black soil.
In summer cottages, fallen leaves are removed to avoid contamination of plants with pathogenic microflora. No matter how poor the soil on which the common wild dogwood normally grows is, it will lack nutrients in the country. Therefore, in spring and autumn, fertilizers are added to the soil around the plant. Although in small quantities:
- phosphorus 30 g per square meter. m in autumn;
- potassium at 12 g per sq.m. and nitrogen at 18 g per sq.m. in the fall.
Organics are added at the rate of 2-3 kg per square meter. m. The soil is dug up to a depth of 10 cm.
How to water dogwood
Young seedlings are watered relatively often in the first year, since after transplantation the bushes often suffer from a lack of moisture. An established adult plant usually does not need watering, except during particularly dry and hot summers.
How to prune dogwood
In a grafted dogwood seedling, the crown is formed in the first few years of its life. The trunk is made about 70 cm in height, leaving 5-7 main branches. The shoots below are completely cut off. Later, only sanitary pruning of the crown is carried out, removing damaged and dry branches, as well as excess branches that thicken the crown.
The bush is thinned out as needed. Ordinary scheduled pruning of dogwood is carried out in the fall, after the start of the dormant period. Also, after 20 years, the berry garden is rejuvenated. But even here, in order to properly prune the common dogwood for rejuvenation, it is enough to just cut off 4-year-old shoots. In this case, many new shoots are formed.
To maintain a decorative appearance, pruning will have to be done every year, without worrying about the harvest.
The nuances of growing dogwood in the regions
If growing and caring for dogwood in its habitat does not present any particular difficulties, then in more northern regions it is not so simple. Garden varieties are now grown even in the St. Petersburg region, and there it is not enough to simply plant a dogwood seedling and care for it. In other regions, not only does the climate not match that usual for dogwood, but the soil often lacks the necessary microelements.
In central Russia
Planting and caring for dogwood in the central zone differs from the southern regions in that in this area you need to choose a sunny place, not blown by winds and well warmed by the sun. But even in this case, the bush does not grow higher than 1.5 m and usually does not bear fruit.The latter is due to flowering too early.
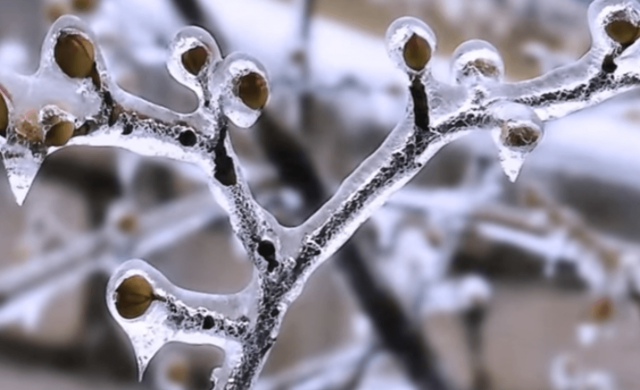
The common dogwood has a protective mechanism: when the temperature drops, the flowers curl back into buds. But this only works with small and short-term frosts. In addition, pollinating bees do not yet fly at this time.
Photo of how the common dogwood blooms during frosts with icing of the branches.
In outskirts of Moscow
There are no special varieties for the Moscow region. To grow dogwood in the Moscow region, you can use frost-resistant varieties of dogwood bred in Ukraine, applying to them the agricultural technology of the Middle Zone:
- Evgenia;
- Coral Brand;
- Nikolka;
- Vladimirsky;
- Grenadier;
- Elena;
- Lukyanovsky.
You can take the long route and invest your life in breeding your own version of the frost-resistant dogwood.
To do this, it is enough to grow several generations of dogwood bushes from seeds. The first generation is grown from purchased seed material, the subsequent ones will be homegrown. After a few generations, it will be possible to obtain specimens that will not be afraid of frosts near Moscow. And such copies already exist. Such a man's tree was grown by Vladimir Vasilyevich, a resident of Moscow region Nikolaev, an experienced gardener who became interested in the issue of adaptation of the common dogwood to the north. The flower buds of the dogwood near Moscow bloom 10-20 days later than those of its southern ancestor.
In the Leningrad region
The Leningrad region is characterized by an excess of groundwater, and the common dogwood does not tolerate waterlogging. When planting dogwood in the Leningrad region, they will first equip a well-drained area where water will not linger.
The second feature of agricultural technology: providing daylight hours in the spring that will be longer than natural. Otherwise, the flower buds may not bloom. The probability of getting a harvest is very low due to the absence of bees at this time.
Otherwise, agricultural technology in the Leningrad region is the same as in the Middle Zone.
In the Urals
Due to the harsh winters for the southern bush, the common dogwood can freeze to death. Even if the roots survive the winter, new shoots will not produce a harvest. Therefore, turf in the Urals must be covered for the winter.
Even if the bush does not grow higher than 1-1.5 m, these are already long enough lashes for shelter in winter. And the tree, in general, will be impossible to close.
They close the dogwood for the winter, bending the shoots to the ground. After which they are covered with any heat-preserving material, since before the snow cover is stable, the soil in the open space may be even colder than the air. To save space, the bushes are bent to one side, although if there is sufficient space, the shoots can be arranged even in a circle. It is difficult to bend down old woody trunks, so such branches are periodically pruned, leaving younger and more flexible shoots.
Just like central Russia, the Ural soil is poor in surface calcium deposits. Before planting seedlings and subsequently in the soil where dogwood grows, lime must be periodically added. In this area, common dogwood is planted only on southern, southeastern and southwestern slopes, which are well illuminated by the sun. Unlike the southern regions, in the Urals derain does not grow in shaded areas.
In Siberia
Planting and caring for dogwood in Siberia is carried out in the same way as in the Urals, but frost-resistant garden varieties are chosen for breeding:
- Elegant;
- Pink;
- Vavilovets;
- Firefly;
- Joy.
Since it takes 2 years for seeds to germinate, it is better to plant dogwood seedlings.
Why doesn't dogwood bear fruit?
Common dogwood does not bear fruit for many reasons:
- the planted bushes are clones, that is, they come from one mother plant;
- lack of pollinating bees during flowering;
- lack of nutrients in the soil (very rare);
- waterlogging;
- overdrying of the soil
- insufficient growing season.
If the summer is dry, then you cannot overdo it with fertilizers. Due to the lack of water in the soil, the concentration of salts there is already increased. Additionally, applying fertilizer will cause moisture to be “sucked out” from the roots, which will only worsen the problem.
Dogwood diseases
It is believed that male derain is not susceptible to disease. At least in the northern regions. In fact, there are no living organisms that are not susceptible to certain diseases. Fungal diseases and pests of dogwood are the same as those of other fruit trees.
Fungal diseases that affect male turf:
- scab (Ventura cerasi);
- fruit rot (Monilia fructigena). It often affects fruits during long-term storage;
- powdery mildew (Erysiphales);
- leaf spotting, which is caused by three types of fungi: Ascochuta cornicola, Cercospora cornicola, Septoria cornicola;
- brown edged spot (Ramularia angustissima);
- dark brown spot (Fusicladium pyracanthae);
- fruit rot (Colletotrichum corni);
- rust (fungus Fungosporangium chavarieformae).
Below in the photo is what rust looks like on a sheet of male wood.
Methods of combating fungi are common for all plants: spraying leaves with fungicides.
In addition to fungi, the plant can infect such a large organism as the false polypore (Fomes igniarius), which causes rot of healthy parts of the plant. The only way to get rid of tinder fungus is to completely cut down all infected plants and burn them. Since male turf can grow from the root, all root systems of affected plants will also have to be removed.
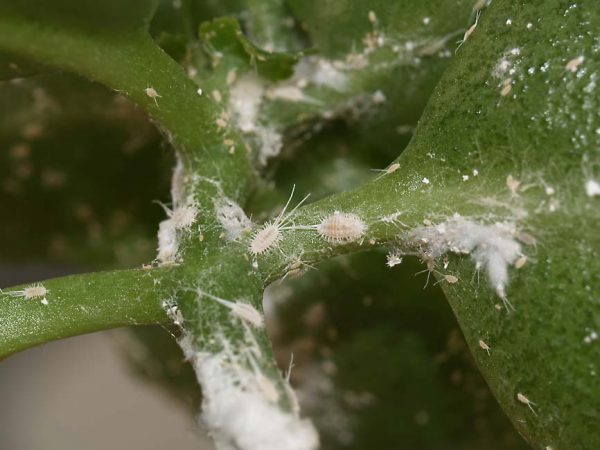
Of the insects, the male dera plant is eaten by:
- cochlear scale insect;
- microcodling moth;
- multicolor caterpillar.
Conventional methods of exterminating insect pests in gardens will protect the male turf from them. Insects are natural enemies of dogwood and may indeed not be found in northern regions.
The leaves of the common dogwood curl not because of disease, but because of drought and on hot days. If by evening the foliage of the male tree has unfurled, then everything is in order. If not, the plant needs to be watered.
Conclusion
Common dogwood in the northern regions is a very beautiful ornamental plant, even if it is impossible to get a harvest from it. To the south, the man's derain not only decorates the garden, but also the opportunity to get delicious, healthy berries. Taking into account the modern variety of colors of berries, the dogwood plantation will also look very elegant.