Content
- 1 Are there porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
- 2 Types of porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
- 3 When to pick porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
- 4 Where porcini mushrooms grow in the Leningrad region
- 5 Rules for collecting porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
- 6 How long does the porcini mushroom season last in the Leningrad region?
- 7 Advice from experienced mushroom pickers
- 8 Conclusion
The end of summer, the beginning of autumn is the time to harvest the forest harvest. Porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region begin to appear in July. You can find them in forest thickets and pine forests. Before going on a quiet hunt, it is important to study the places where boletus is especially common.
Are there porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
In 2019, the first boletus appeared in the vicinity of St. Petersburg in June, which could not but please lovers of quiet hunting. The forests located around the northern capital have long been famous for the abundance of edible mushrooms.
White fruiting usually peaks in August-September. In the deciduous forests of the Leningrad region, their numerous appearances are observed this season.
Types of porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
In the deciduous and mixed forests of the outskirts of the northern capital, the original boletus mushroom, porcini mushroom, and several of its varieties are found.They are easy to distinguish from each other by their appearance.
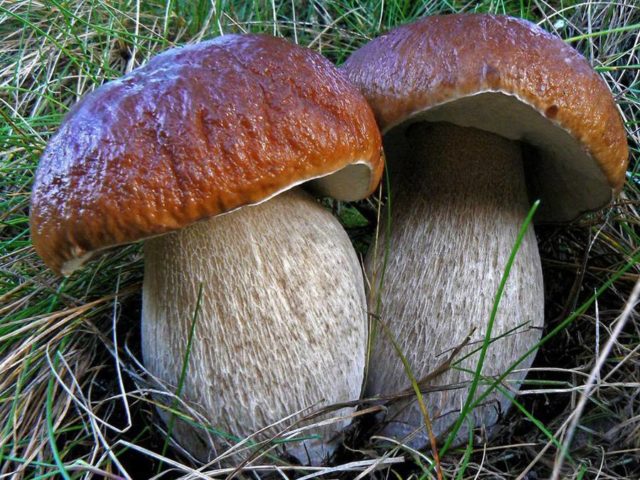
Boletus - white mushroom
This is a large, massive basidiomycete, the diameter of the cap can reach up to 30 cm. On average, its size does not exceed 10 cm. It is colored dark brown or burgundy. The shape is convex.
The leg is thick, barrel-shaped, fleshy, its length can reach up to 20 cm. The pulp is dense, juicy, fleshy, with a characteristic mushroom smell.
White oak mushroom
The large spherical cap grows up to 25 cm in diameter. Its color can take on any shade of brown - from light to dark. In dry weather, a characteristic mesh appears on the surface of the cap.
The leg is club-shaped or cylindrical, covered with a network of shallow cracks. Its color is light walnut.
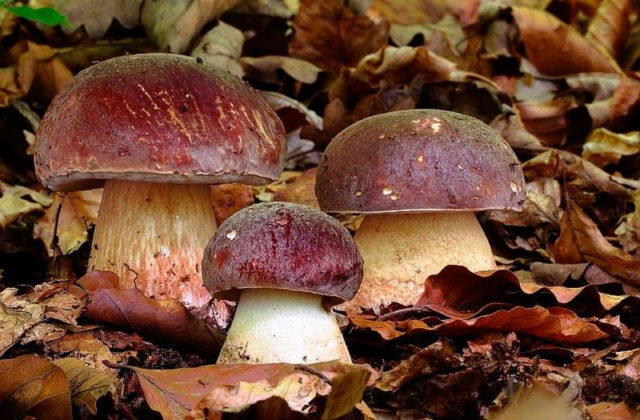
White pine mushroom
It differs from its older brother with a bright brown-red or dark, wine-colored cap. Its surface is loose and uneven.
The leg is thick, fleshy, much lighter than the cap. The skin is covered with a red mesh pattern.
Spruce porcini mushroom
It is distinguished by its large size and dark brown convex cap. Its diameter can exceed 25 cm. The weight of some specimens reaches 4 kg.
The leg is large and strong, barrel-shaped. Its circumference is at least 10 cm. The color is creamy brown, with a light reddish tint. The surface is covered with a mesh pattern.
White birch mushroom
The species is widespread in the forests of the Leningrad region, its popular name is spiker. It is a variety of white. The hat does not exceed 15 cm in diameter, its shape is flat and spread out. The color is white with a slight beige or yellow tint.
The leg grows in the shape of a barrel, the length does not exceed 10 cm.Its color is white with a slight brown tint; in the upper part you can see a fine mesh.
When to pick porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
Small caps of young boletus mushrooms of all types can be seen already at the end of May after the first heavy thunderstorm rains. But these are few, isolated specimens. Mushroom pickers observe their abundant fruiting already at the end of July. But for the real harvest of porcini mushrooms they go to the forest in August, early September. This period is the peak of their fruiting.
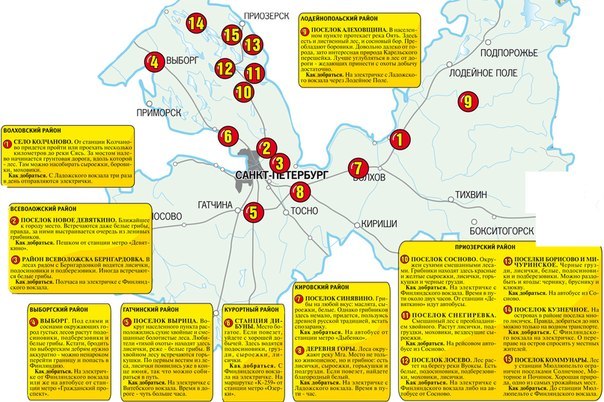
Where porcini mushrooms grow in the Leningrad region
The deciduous and mixed forests of the northern capital are rich in boletus mushrooms of all kinds. They prefer clay and sandy loose soils with good drainage. You can find them under deciduous trees: oaks, birches, aspens, and less often under pine trees. On the map, the presence of porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region is noted in its various districts.
Boletus growing areas:
- Volkhovsky;
- Luzhsky;
- Lyudeynopolsky district, Alekhovshchina village;
- Kirovsky;
- Lomonosovsky;
- Tosnensky;
- New Devyatkino;
- Sinyavino;
- Vyborg district;
- Gatchina.
Boletus is considered the most valuable find of a mushroom picker. Finding it will not be difficult, focusing on the supposed habitats of the species.
Rules for collecting porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region
Next to the boletus mushroom, gall and satanic mushrooms can grow - doubles that you should beware of. The latter is similar in shape to white and is its variety. You can recognize the poisonous species by the red color of the tubular layer and legs. When cut, the flesh of the satanic mushroom turns blue.

Satanic mushroom is one of the dangerous doubles of white
The gall mushroom (gorchak) is light brown in color, its tubular layer is initially white, later becoming gray.When damaged, the flesh turns pink.
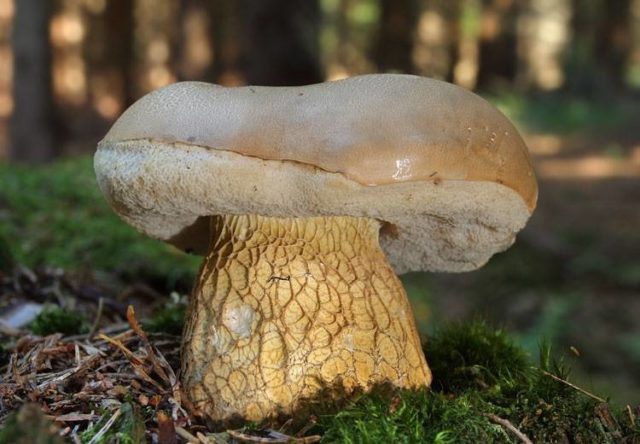

Gorchak is distinguished by its color and white tubular layer
It is better for novice mushroom pickers to take with them a more experienced friend who will teach them how to distinguish a toadstool from a valuable specimen.
After a rain and thunderstorm, on a foggy morning they set off to collect the forest harvest. During periods of high humidity, boletus mushrooms are found not under trees, but in clearings and well-lit clearings.
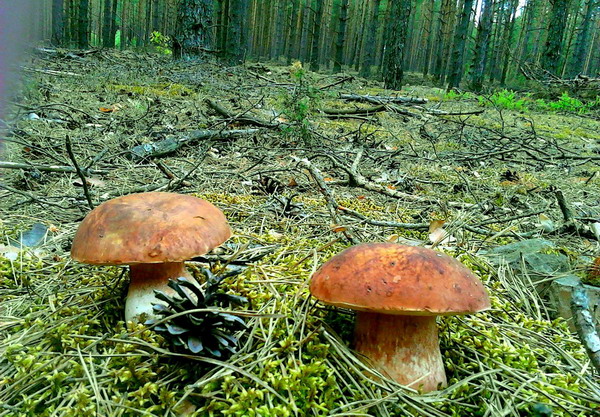

During periods of drought, the porcini mushroom hides under the spreading crown of an oak tree in the thick grass.
The first frosts are not scary for boletus, it retains its aroma and pleasant taste.
Other recommendations for collecting boletus mushrooms in the Leningrad region:
- Porcini mushrooms begin to hatch during the ripening period of the rye.
- The mushroom in the Leningrad region often grows next to morels; when collecting, they are guided by this feature.
- They come to the forest before sunrise - the caps of porcini mushrooms are clearly visible at the first rays of sunlight.
- It’s good to take a long, strong stick with you so that you can rake leaves with it without bending over again.
- They move slowly through the forest, carefully examining the soil under their feet.
- They look especially well into sandy soil and loams - this is the habitat of the boletus.
- The porcini mushroom is cut off at the mycelium itself or twisted out, and the cut is cleaned of leaves and soil.
- The fruit body is placed in the basket with the cap down.
- Specimens with a long stem are turned on their side.
- Only mature specimens without worms and foulbrood are collected.
How long does the porcini mushroom season last in the Leningrad region?
Mushroom season may not always arrive within the clearly allotted time. It all depends on weather conditions in the Leningrad region.If the spring is warm and rainy, harvesting begins in early June. The season ends at the end of September or beginning of October. On average, the mushroom season in the Leningrad region lasts 3-4 months.
The fruiting body of the porcini mushroom grows from 6 to 9 days in summer, and from 9 to 15 in autumn. In the autumn, there is a greater chance of collecting fresh, not overripe specimens.
Advice from experienced mushroom pickers
The first and main recommendation is to take only the mushroom in which you have 100% confidence. Unknown species that are encountered for the first time are left where they grow.
Other useful tips:
- Ideal for collecting and eating is a specimen whose cap diameter does not exceed 4 cm.
Young boletus
- The upper part of the fruiting body is especially carefully examined; this is where the worms appear.
- If you come across a large, beautiful, but wormy porcini mushroom, it is left in the forest. Eating such specimens is strictly prohibited. This rule also applies to overripe, spoiled fruiting bodies.
- Tasting raw mushroom pulp is prohibited.
- The fruiting body, the stem of which is thickened at the base but hollow inside, is not eaten. To do this, it is cut as close to the ground as possible to check for voids.
- The collected fruiting bodies are cleaned and processed on the same day (within 10 hours), since they are not stored for a long time at room temperature, and in the refrigerator they lose most of their beneficial properties.
It is important for beginning lovers of quiet hunting in the Leningrad region to listen to the advice of experienced mushroom pickers. This way, harvesting the forest harvest will not cause trouble, and only valuable and tasty specimens will end up in the mushroom basket.
Conclusion
Porcini mushrooms in the Leningrad region are common in deciduous, mixed and coniferous forests.Some areas of the region are especially rich in these valuable representatives of the forest kingdom. 2019 was distinguished by a rich early harvest of boletus mushrooms, which can be harvested before the onset of the first frost.