Content
Iput cherries have been successfully grown by gardeners in our country for quite some time. This variety was bred specifically for the weather conditions of Central Russia. It is frost-resistant and partially self-fertile, which greatly simplifies the work of caring for plantings.
The combination of all these factors plus good yield - all this became the key to the successful distribution and cultivation of this cherry variety.
History of selection
The homeland of the Iput cherry is the village of Michurinsky, Bryansk region. The All-Russian Research Institute of Lupine, located here in the 80s of the last century (now a branch of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution “Federal Scientific Center for Forage Production and Agroecology named after V.R. Williams”), at that time was engaged not only in the selection of forage crops, but also by breeding new varieties of berry bushes.
The result of this painstaking work is more than 65 varieties of cherries, sweet cherries, black currants, raspberries and apple trees. One of them is the Iput cherry variety, named after the river of the same name flowing in the Bryansk region. Its authors are breeders Kanshina M.V. and Astakhov A.A. In 1993, the variety was included in the State Register.
Description of culture
The Iput cherry is a medium-sized tree with a fairly wide crown. It usually begins to bear fruit at 4-5 years of age. Productivity is average. This variety can be grown in many regions. Cherry Iput is considered an early variety.
Characteristics
The main characteristics of the Iput cherry variety are given in the table.
Parameter | Meaning |
Type of crop | Fruit stone fruit tree |
Height | On average 3.5, sometimes up to 4.5–5 m |
Bark | Reddish brown |
Crown | Wide, pyramidal |
Leaves | Dark green, matte, egg-shaped. The plate is slightly curved, the surface is without pubescence. Length up to 8 cm, width up to 5 cm |
foliage | Thick |
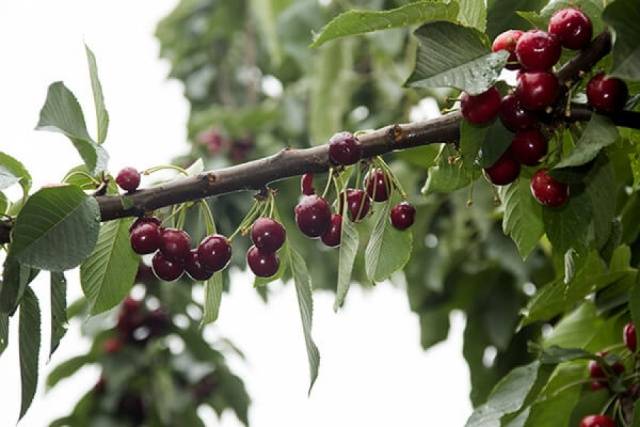
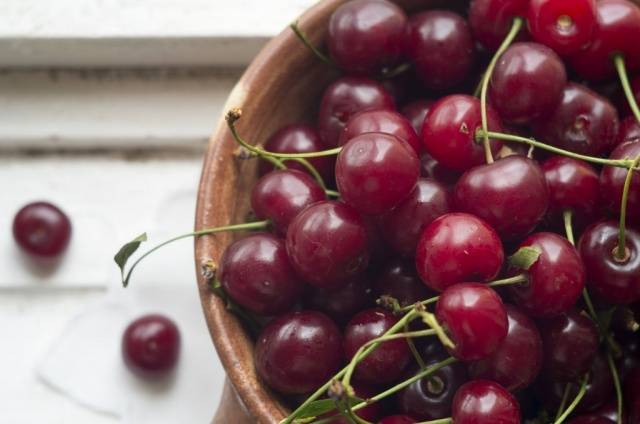
Fruit | Large, dark red, almost black. The average berry weight is 5–9 g. |
Pulp | Red, juicy |
Taste | Sweet, aftertaste with a slight bitterness |
Bone | Small, difficult to separate |
Purpose of the variety | Universal |
Transportability | Medium, weak for fruits with cracking |
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
Winter hardiness is one of the advantages of the Iput cherry variety. The trees will tolerate frosts down to -30 °C quite calmly. Thaws followed by a sharp cold snap are more destructive for cherries. After above-zero temperatures, frosts even down to -20°C are almost guaranteed to kill the tree.
The drought resistance of the Iput cherry variety is good. Even in severe drought, it is recommended to water it no more than once a week.Excess moisture primarily affects the berries, which begin to crack.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening time
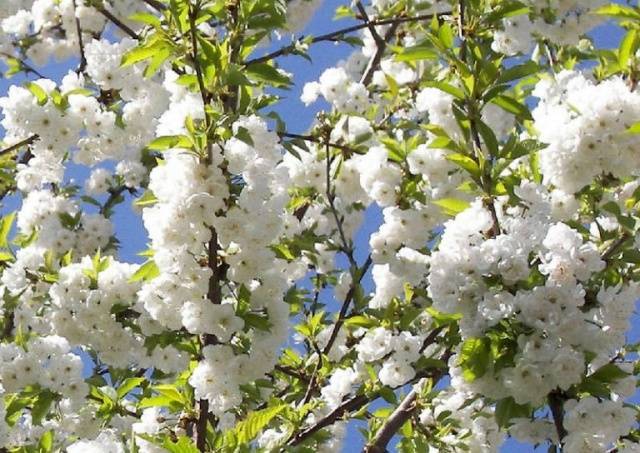
The flowering time of the Iput cherry depends on the region of growth. In the middle zone this is mid-May, in more southern regions the dates are earlier. The tree blooms very beautifully, in dense white clusters.
The cherry variety Iput is considered partially self-fertile, i.e. self-pollinating. However, in reality, the percentage of self-pollinated flowers is quite small (as a rule, no more than 5–7% are self-pollinated). Therefore, to obtain a good harvest, it is necessary to plant pollinator plants nearby. For Iput cherries, the Revna, Tyutchevka or Ovstuzhenka varieties are suitable for this purpose. The berries are fully ripe by the end of June.
Productivity, fruiting
Starting from the fifth year of life (less often from the fourth), fruiting of the Iput cherry becomes regular. Its harvest ripens every year and averages 30 kg per tree. However, with proper care and compliance with all rules of agricultural technology, the yield can be doubled.
Area of application of berries
The versatility of the Iput cherry variety allows the fruits to be used both fresh and processed. It makes excellent compotes, preserves, and jams. Among all varieties of cherries, Iput has the highest content of vitamin C, so its berries are not only tasty, but also very healthy.
Resistance to diseases and pests
Iput cherry has good immunity to pests and diseases. Most often, trees suffer from fungal diseases in conditions of high humidity or due to improper pruning. Of the pests, aphids are the most dangerous.
Advantages and disadvantages
Iput cherries have quite a lot of advantages. Here are the main ones:
- frost resistance;
- stable annual yield;
- early ripening;
- resistance to diseases and pests;
- the tree is not very tall, it is convenient to pick berries;
- the variety is universal in purpose;
- good berry taste (tasting rating 4.4 out of 5).
The disadvantages of the variety include the following:
- late entry into fruiting (4-5 years);
- the tendency of fruits to crack when there is excess moisture;
- poor separation of the stone from the pulp.
Landing Features
When planting Iput cherries in your garden plot, you should immediately take care of pollinators, otherwise you may not get a harvest. Seedlings are almost always planted in groups (an exception can be made if the neighbors also have a cherry tree growing next to the fence).
In addition, there are several other factors to consider.
Recommended timing
The timing of planting Iput cherry seedlings greatly depends on the region. In the south, in climate zones with mild winters, this can be done both in spring and autumn. Moreover, autumn planting is considered more preferable, since a tree planted in the spring will constantly suffer from a lack of water and sunburn. In more northern territories, autumn planting is completely excluded. The seedling simply does not have time to take root and will die.
A prerequisite for planting Iput cherries is that the seedlings must be at rest. In the spring, this is the time before the movement of juices and the swelling of the buds, and in the fall - after the leaves fall.
Choosing a suitable location
For good growth and high productivity, the place for growing Iput cherries must meet the following conditions:
- There should be no other trees between the planted seedlings so as not to interfere with cross-pollination.
- The place should be sunny and protected from cold winds.
- The soil should be light, fertile, sandy loam or loamy, with neutral acidity.
- Groundwater should not be higher than 2 m.
- The landing site should not be located in a lowland or any other place where water stagnation is possible.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to cherries?
The Iput cherry is not a pronounced aggressive plant like, for example, a nut. However, you should not plant an apple, pear or plum tree next to it. It is better when another cherry tree (which is useful for pollination) or a sour cherry grows nearby. Grapes grow well next to cherries. Black elderberry is often planted nearby; it perfectly protects the plantings from aphids.
Flowers grow surprisingly well under the Iput cherry tree: daffodils, tulips, primula. But it is better to avoid planting tomatoes or potatoes in the root zone.
Selection and preparation of planting material
For planting Iput cherries, it is better to use two-year-old seedlings. By this time, the tree should have the following parameters (in the table).
Parameter | Meaning |
Barrel diameter, mm | At least 15 |
Number of branches, pcs | At least 3 |
Branch length, m | Not less than 0.3 |
Root system | Well developed. The cut root is clean, without rot, the cut color is cream |
Bark | Clean, smooth, without damage or new growths |
You should pay attention to the difference in the thickness of the rootstock and scion. It is clearly visible on grafted seedlings.
Landing algorithm
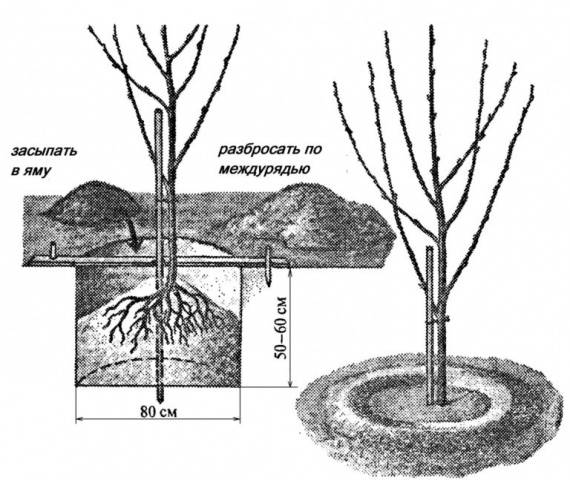
Iput cherry seedlings are planted at a distance of at least 3 m from each other. Planting holes must be prepared in advance; for example, for spring planting they are prepared in the fall. The size of the pit should be 1 m by 1 m and the depth should be at least 0.8 m.The excavated soil must be preserved; a nutrient substrate will subsequently be made from it. To do this, mix it with 3 buckets of humus and add 0.25 kg of superphosphate.
Before planting, the seedling is inspected again, and damaged roots are cut off if necessary. A stake is driven in a little to the side of the center of the hole, which will initially serve as a support for the young tree. A mound of soil is poured into the bottom of the hole, on which the seedling is placed so that its root collar is at ground level. After which the roots are gradually covered with nutritious soil, compacting it to prevent the formation of voids.
An earthen bank is poured around the seedling, which will prevent water from spreading. The planted tree is tied to a support and watered with 3-4 buckets of water. Then the tree trunk circle must be mulched with straw or sawdust.
Subsequent care of the crop
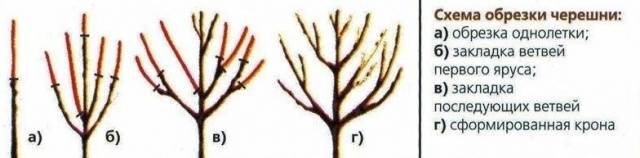
To have a good harvest, you need to correctly form the crown of the future tree. To do this, formative pruning is used, making the tree crown multi-tiered.
- The first pruning is done in the second spring after the habit. At this time, the first tier of 3-4 main branches is formed, located at a distance of 0.5–0.6 m from the ground. All other shoots are cut in half or completely cut out.
- The next spring, a second tier is laid, leaving 2 branches at a distance of 0.5 m from the first. The rest are cut out.
- The next year, 1 branch is left above the second tier, and the main trunk is cut off.
- In subsequent years, all annual shoots are shortened by half.
In addition to formative pruning, every year you need to carry out sanitary pruning, cutting out diseased, dried or broken branches. In addition, shoots that grow incorrectly and thicken the crown are pruned.
Iput cherry is a moisture-loving crop, but excess water is detrimental to it. Therefore, watering is only necessary during dry periods.
Iput cherry fertilizing is carried out throughout the season. In spring, fertilizers are applied three times:
- Before the tree blooms, add 20 g of ammonium nitrate per 1 square meter to the tree trunk. m.
- During the flowering period, add a urea solution of 20 g per 10 liters of water.
- At the end of flowering, chicken manure is added to the root zone in the form of a solution at the rate of 1.5–2 liters of concentrate per bucket of water.
In the summer, foliar feeding of Iput cherries is carried out with potassium monophosphate or nitrophoska. In the fall, they use organic matter, adding humus to the tree trunk.
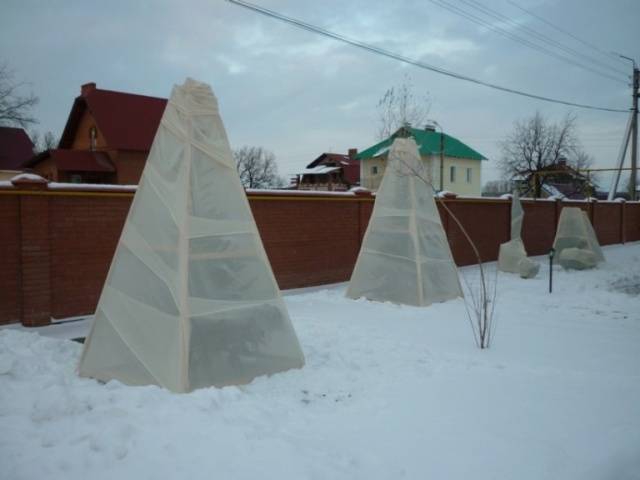
Iput cherries do not require shelter for the winter. However, some careful gardeners in regions with cool climates cover young trees using special covering materials.
The trunks of mature Iput cherry trees need to be whitened to prevent sunburn and damage by pests that hibernate in the folds of the tree bark.
Diseases and pests, methods of control and prevention
Cherry Iput gets sick relatively rarely. Most often, diseases appear from excess moisture or poor tree care. The main diseases of cherries are shown in the table.
Disease | Signs of appearance, consequences | Prevention and treatment |
Rust | Brown spots on leaves. Affected leaves die and fall off. | Treatment with Hom before flowering. After harvesting, re-treatment with Bordeaux mixture 1%. Affected shoots should be pruned and burned. |
Clusterosporiasis (hole spotting) | Brown spots on the leaves; holes subsequently form at the places where they appear. The shape of the fruit changes. | Three times per season (before flowering, after flowering and after 2 weeks) treat plants with a solution of copper-containing preparations or 1% Bordeaux mixture. Affected leaves should be torn off and burned. |
Coccomycosis | Purple spots on the leaves, which soon dry out and fall off. | After flowering and after picking the berries, you need to treat with Bordeaux mixture 1% or copper oxychloride. |
Of the pests, the greatest danger to Iput cherries is the cherry weevil and cherry aphid. They are fought with the help of various insecticides (Decis, B-58) or folk remedies (soap solutions, infusions of tobacco, celandine, wormwood).
Conclusion
Iput cherry has long and deservedly taken its place among horticultural crops in many regions of the country. However, most gardeners agree that it lacks a certain zest that makes it worth holding on to. However, there are so many people, so many opinions. Therefore, the gardener himself will decide whether or not to plant this variety or replace it with another. And Iput cherries are definitely a good choice.