Content
Vibriosis in cattle is a type of infectious disease that affects the genitals, as a result of which the animal may have an abortion or this will lead to infertility. If an infected cow gives birth to offspring, the fetus will not be viable. In their natural habitat, the disease can affect any cattle, regardless of breed.
The causative agent of bovine campylobacteriosis
The causative agent of vibriosis in cattle is a microorganism belonging to the genus Campylobacter fetus. This microorganism is polymorphic, its appearance resembles a comma, some compare it to a flying seagull. It is quite rare to find a pathogen in the form of a small spiral, which has 2-5 turns.
The bacterium has the following dimensions:
- length – 0.5 µm;
- width – 0.2-0.8 microns.
Microbes of the infectious disease campylobacteriosis are mobile; the formation of capsules and spores does not occur during reproduction. The causative agent of vibriosis is gram-negative, but can be gram-positive when old cultures are dissociated. It is also worth noting that when exposed to aniline dyes, coloring occurs.
For this you can use:
- fuchsin Tsilya;
- gentian violet;
- alcohol solution of blue;
- silvering method according to Morozov.
During microscopy, the pathogen can be detected in the hanging drop. As a rule, flagella can be seen in the short form of the pathogen, the length of which varies between 5-10 and 15-30 microns. Such flagella can be found at one or both ends of the body.
Fetus is an obligate species of parasite that causes abortions and infertility in animals. The pathogen is transmitted through sexual contact. As a rule, it is found in the vaginal mucus of an infected cow or in the seminal fluid of bulls.
Sources and routes of infection
As practice shows, in most cases the infectious agent is transmitted to a healthy individual through sexual contact - during artificial or natural mating. Up to 80% of cattle are infected this way. Immature calves and dairy calves are also exposed to infection when they come into contact with an animal that is already suffering from vibriosis.
In addition, it is worth taking into account the fact that there are other ways of transmitting vibriosis infection to healthy animals among cattle:
- through obstetric instruments that have not been disinfected - the most common option is rubber gloves;
- clothing for farm staff;
- through the litter.
Vibriosis actively develops in places where cattle live in crowded conditions, and when zoohygienic requirements were not met during mating or artificial insemination.
Symptoms and course of the disease
Vibriosis in cattle manifests itself clinically in the form of a complex of symptoms, among which there are associated pathologies:
- vaginitis;
- endometritis;
- salpingitis;
- oophoritis.
These phenomena contribute to the disruption of reproductive functions, as a result of which barrenness in cattle increases.
As a rule, abortion occurs regardless of the stage of pregnancy, but in most cases (more than 85%) at 4-7 months. There are cases when termination of pregnancy occurs at 2 months, but, as a rule, the service staff rarely notices this. Only when the 2nd heat begins after insemination can the first signs of vibriosis be noticed. If there was no termination of pregnancy, then weakened calves are born, which are exposed to the disease in the first few days and die within a week.
There are no signs of vibriosis in bulls. The only thing is that the mucous membrane, prepuce and penis turn red, and there is copious secretion of mucus. After some time, the symptoms disappear, and the bull becomes a lifelong carrier of the disease.
In aborted fetuses, you can see swelling in certain areas and hemorrhages in the chest area. The contents of the abomasum of the fetus are liquefied, cloudy, with a brown tint. Quite often the fruits are mummified.
Diagnosis of vibriosis in cattle
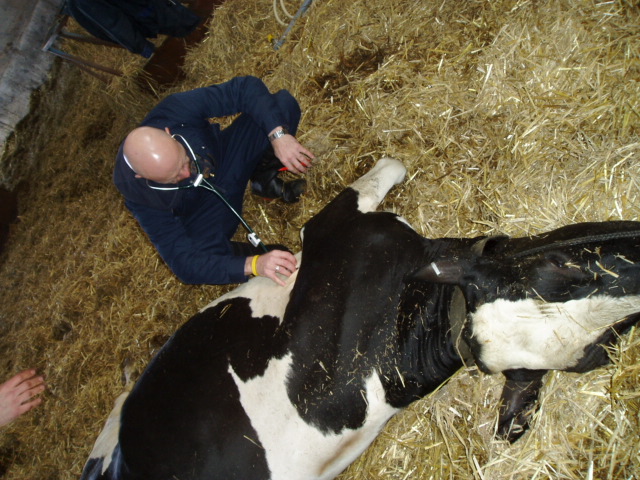
Diagnosis of campylobacteriosis in cattle can be based on clinical and epidemiological data and isolation of the pathogen.If a heifer is observed to have excessive overtime, barrenness, or the birth of a non-viable calf, this is only a suspicion of vibriosis. To clarify the diagnosis or refute it, laboratory tests, namely bacteriological tests, are required.
To conduct a bacteriological study, it is necessary to send the aborted fetus or part of it to the laboratory: head, stomach, liver, lung, placenta. Material for research must be provided no later than 24 hours after the abortion. Mucus is collected from the cow's cervix in the first few days after the abortion.
Only after all the necessary material for research has been obtained can an accurate diagnosis of the disease be made.
Treatment of bovine vibriosis
If vibriosis is detected or suspected, cattle are treated according to the instructions. After an abortion has occurred, infected animals must be injected into the uterine cavity with vegetable oil or fish oil in a volume of 30 to 50 ml, to which 1 g of penicillin is first added.
This mixture of oil and penicillin must be administered to cows up to 4 times, with an interval of 2-3 days between procedures. Together with this type of treatment, it is recommended to simultaneously administer penicillin intramuscularly about 3 times throughout the day, using the following dosage - 4000 units per 1 kg of cow weight.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out treatment according to clinical signs. Bulls are injected with antibiotics into the preputial sac. To do this, take 3 g of penicillin, 1 g of streptomycin, dissolve in 10 ml of clean water and mix with 40 ml of vegetable oil.
This mixture is injected through a catheter into the upper part of the prepuce, after which the insertion site is massaged from top to bottom. Treatment is continued for 4 days.At the same time, 4000 units of penicillin are administered for each kg of live weight of the bull.
Forecast
As a rule, the disease in cattle can occur in an acute or chronic form, and symptoms may not always appear. If you carefully examine the animals, you can detect redness of the mucous membrane of the genital organs in infected individuals.
In some individuals, after 5-15 days the following may be observed:
- increased body temperature;
- constant anxiety;
- copious secretion of mucus from the genitals.
In addition, the animal begins to move in a hunched position, the tail is constantly raised, and cloudy pus appears on the genitals.
Prevention of campylobacteriosis in cattle
Preventive measures to combat vibriosis in cattle must be carried out in accordance with sanitary and veterinary rules. In order to prevent the emergence of an infectious disease in cattle on a farm, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- cattle should not move around the farm freely, without accompaniment and permission from a veterinary specialist;
- veterinary and sanitary rules for feeding and keeping animals must be strictly observed;
- to replenish the herd, you should use only those individuals that are not susceptible to vibriosis;
- In the event that bulls are brought to the farm for breeding purposes, the animals must be quarantined for 1 month:
- breeding bulls must be tested for disease detection every 6 months - 3 times with an interval of 10 days.
In addition, vaccines are often used to prevent disease in cattle.
Conclusion
Vibriosis in cattle negatively affects future offspring, causing abortions and infertility in cows. The causative agent of the disease located in the external environment may die after 20 days if the temperature is +20°C or higher. At lower temperatures, the pathogen can live up to 1 month. If the temperature reaches +55°C, the microbes die in 10 minutes; when dried, in 2 hours. The causative agent of vibriosis can survive in frozen semen of cattle for up to 9 months.