Content
Milk appears in a cow as a result of complex chemical reactions occurring with the help of enzymes. The formation of milk is a coordinated work of the whole organism as a whole. The quantity and quality of milk is influenced not only by the breed of the animal, but also by many other factors.
When does a cow produce milk?
Lactation is the process of milk secretion, and the time when a cow can be milked is the lactation period. Specialists are able to correct the functioning of the animal’s mammary glands and increase the amount of cattle dairy products.
Milk production in all mammals is largely facilitated by prolactin, a hormone associated with reproduction. It is necessary for lactation, promotes the maturation of colostrum and turns it into mature milk. Accordingly, it appears immediately after the birth of the baby, so that it can fully feed. After each feeding and milking, the mammary gland fills up again. If a cow is not milked, milk ceases to be produced, and milk yield begins to decline.
This also happens in the natural habitat of mammals - as soon as the baby grows up, the need for feeding disappears, and lactation begins to decrease.
The cow begins to produce milk immediately after her first calving. You need to let the calf approach it to milk the swollen udder. Natural sucking will develop the mammary glands, which will allow for better milk production.
A cow produces the maximum amount of milk at 6 years of age, then milk production declines.
Does a cow give milk without calving?
Since the cow is a mammal, calves feed on their mother's milk for the first 3 months of life. They can feed on it for much longer, but on farms they are separated from their mother on the very first day, otherwise it will be much more difficult to do this later. For both the calf and the cow, separation will be severely stressful, which will affect health and productivity. The calf is placed in a specially equipped calf barn, and the cow is milked by hand and part of it is fed to the baby.
Mother's milk is necessary for the calf during this period, as it contains all the necessary nutrients for growth and development:
- proteins fats carbohydrates;
- some vitamins (A, B, D, K, E);
- minerals (iodine, potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc).
After 3 months he is transferred to adult food. The cow is milked until she becomes pregnant again. In this case, they stop milking her 2 months before the expected calving, so that during this time she gains strength.
In nature, the lactation period of cattle is shorter, since the baby does not eat all the milk, it gradually burns out. And on farms, cows are milked completely, and the body believes that the calf does not have enough milk, so it constantly comes.
On average, cows calve once a year, that is, milk will be produced within 10 months. This period, if the cow does not become pregnant again, can be extended to 2 years. True, the volume of dairy products will be significantly lower.
If a cow, after several matings, does not become pregnant for some reason, then she will no longer produce milk and must be culled.
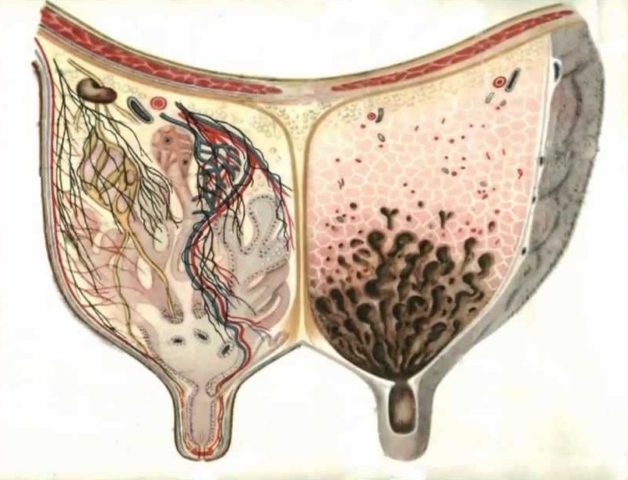
The process of milk formation in a cow
To understand how milk is produced, you need to know the structure of the udder. It consists of the following parts:
- adipose, muscle, glandular tissue;
- milk and teat tanks;
- nipple sphincter;
- alveoli;
- blood vessels and nerve endings;
- fascia.
The basis of the gland is parenchyma, connective tissue. It consists of alveoli, in which milk is formed. Connective and adipose tissue protects the gland from negative external influences.
The process of milk formation uses nutrients delivered to the udder through the blood from the digestive system. Those individuals that have a good blood supply are considered high-yielding, because a huge amount of nutrients enters the udder. It is known that to produce 1 liter of milk, up to 500 liters of blood passes through the udder.
However, in its basic composition, milk differs significantly from the composition of blood. Almost all of its components are transformed in the alveolar cells of the gland with the help of certain substances that enter there. Mineral elements and various vitamins come from the blood in prepared form. This occurs thanks to glandular cells. They are able to select certain substances and prevent others from entering.
The formation process occurs constantly, especially between milkings. That is why it is recommended to adhere to a certain regime for keeping cattle, so that milking is carried out after a certain period of time.
The animal’s nervous system plays a huge role in milk production. Secretion depends on its condition. When the maintenance regime changes, worsens, or stress, the process of milk formation is inhibited.
As it forms, milk fills the cavities of the alveoli, all ducts, canals, and then cisterns. Accumulating in the udder, the tone of smooth muscles decreases and muscle tissue weakens. This prevents strong pressure and promotes milk accumulation. If the interval between milkings is more than 12 hours, then too much product accumulates and some inhibition of the activity of the alveoli occurs, accordingly, milk production decreases. The rate of milk formation directly depends on the quality and complete milking.
Complex processes also include lactation and milk ejection, which precede milking.
Milk excretion is the release of milk into the cavity of the alveoli and its entry into the ducts and cisterns in the intervals between milkings.
Milk ejection is the reaction of the mammary gland to the milking process, during which milk passes from the alveolar part to the cisternal part. This happens under the influence of conditioned and unconditioned reflexes.
Lactation periods in cattle
Lactation is divided into 3 periods, in each of them the milk differs in composition, and the animal requires a different feeding ration.
- The colostrum period lasts on average about a week. Colostrum is rich in fats, very thick in consistency and is undesirable for human consumption. But the calf needs it in the first days of its life.At this time, the baby’s digestive and immune systems are developing and colostrum will be a useful nutrition for him.
- The period during which the cow produces normal, mature milk lasts a little less than 300 days.
- The period of transitional milk lasts 5-10 days. At this time, the protein level in the product increases, and the lactose content and acidity decrease. The animal is in the process of recovery and carbohydrates in the feed should be reduced to a minimum.
Lactation periods are individual for each animal and depend on the state of health, nervous system, feeding and housing conditions.
What affects the quantity and quality of milk yield
A cow's productivity is influenced by many factors. If you want to increase milk yield, you should make sure that the animal belongs to a dairy breed. In any case, after the first calving, the cow will not produce more than 10 liters, and with each subsequent pregnancy, the production of the product should increase. To improve the quality and quantity of the product it is necessary:
- Maintain a certain temperature in the barn, preventing the animal from freezing, so that energy and nutrients do not go to generating heat.
- Milking needs to be done at a certain time, as the cow gets used to the routine. This mode allows you to collect 10-15% more.
- It is better to milk a cow 3 times a day. With this approach, annual production increases by 20%.
- You should arrange daily active exercise in nature. Cows have an increased appetite after walking.
- 2 months before the next calving, you need to start the cow to give her the opportunity to rest and gain strength for the next lactation.
Proper balanced nutrition is necessary. Feeding should also be done at certain hours.The diet is made taking into account the weight, age, and physiological state of the animal.
The most appropriate diet for high-quality milk production should include:
- hay, straw, green food in summer;
- wheat bran, barley;
- mineral and vitamin supplements.
It is also necessary to add beets, zucchini, carrots, boiled potatoes and pieces of white bread. In this case, the daily diet should be about 20 kg.
Conclusion
A cow produces milk solely for feeding her offspring - this is how nature works. How long the lactation period will last and what the milk yield will be in terms of quality and quantity depends on a person’s actions.










The cow separated prematurely, the calf is dead, there is no milk, will there be milk and what should I do?
In case of premature stillbirth, milk production CANNOT be stimulated!
One of the characteristic and most clearly manifested symptoms of brucellosis in cows is the abortion of the fetus at 5-8 months of pregnancy or the birth of a dead calf. The remaining clinical signs of brucellosis appear later, since these are diseases with a long period of development. An apparently healthy cow can be a source of infection.
Brucellosis is transmitted to humans and the main route of infection for people is through drinking milk from a sick cow.
Veterinary rules require that in the event of a miscarriage in a cow, the aborted fetus must be taken to a laboratory to establish a diagnosis of the disease.Abortion is not only caused by brucellosis.
There are several other contagious diseases with a similar symptom. Moreover, abortion is often observed during the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Since the calf’s corpse has most likely already been disposed of, in your case it is best to invite a veterinarian who will collect material for laboratory testing and examine the cow.