Content
On private farmsteads you rarely see beef cattle that were bought for the purpose of breeding. More often they buy bulls for fattening. Most often these are animals of the same breeds that are bred on the nearest dairy farm. If the farm is aimed at milk production, it is more profitable for the owner to sell the bulls without distracting staff to care for small calves. Therefore, even for fattening, owners of private farmsteads take dairy animals.
Specialized meat breeds of cows have a number of advantages: they grow quickly, give a large slaughter yield of meat from the carcass, and the quality of their meat is better than that of dairy cows. But to maintain a breeding herd you need to have a whole farm. And the second for raising young animals for meat.
General characteristics
Animals of beef cattle breeds look like powerful, muscular animals. They weigh more than dairy cattle, but their bone structure is quite graceful. Their muscles give them the impression of very large, massive animals. General standard for beef breed cows:
- small head;
- short powerful neck;
- well developed withers;
- long body;
- wide, flat back;
- wide lower back;
- elevated sacrum;
- tail set high;
- wide round chest;
- well developed dewlap;
- short legs.
The structure of meat animals is such that the amount of waste is as small as possible. Therefore, due to short legs (unnecessary tubular bones of the metacarpus and metatarsus), beef cattle breeds are not distinguished by impressive growth like Holstein dairy, but their weight is much greater.
Beef cows produce milk only for their calves and therefore their udders are very small, although regularly shaped.
Beef farming originated in England in the 18th century. It was then that cattle breeds were purposefully bred to actively gain muscle mass. Until today, the best breeds of beef cattle trace their ancestry to the cattle of the United Kingdom. Not only Great Britain tried to breed beef cattle, but the most popular beef cattle breeds in the world are Hereford and Aberdeen Angus. Both come from the islands.
Hereford
Due to its high adaptation to different climatic conditions, it is today distributed throughout the world, including Australia and South Africa. These are massive animals, already divided into three types:
- red horned;
- red polled;
- black.
Meat producers prefer polled cattle because they are easier to work with. Because of this, the original horned Hereford is becoming a thing of the past.
Black Hereford arose from the infusion of Aberdeen Angus or Holstein blood into red cattle.
This is an industrial cross that gives increased meat yield in the first generation. If you continue backcrossing, you can get a black Hereford. This is exactly how it was received.The black type is slightly larger than the red type, which is why it is preferred by industrialists. Besides, he is also polled.
The weight of Herefords ranges from 900-1200 kg, cows weigh up to 850 kg. The slaughter yield from the carcass reaches 62%.
Aberdeen Angus
An original Scottish breed of cattle. They have good adaptive abilities and can live even in northern regions. They are characterized by very rapid development. Bulls reach 1 ton in weight, cows are medium-sized, weighing an average of 550 kg. The Aberdeen Angus breed of beef cattle and their external characteristics are more reminiscent of dairy cattle. They have thin, loose skin and elegant bones. The structure of the uterus is more similar to a dairy cow, which is not milked and fattened for slaughter. The only thing that indicates their meat purpose is a well-developed dewlap.
These two English breeds are competed by two French ones.
Charolais
A very old French breed whose original purpose was yoke work. Draft animals must have significant muscle mass to transport heavy loads. This feature was fixed in Charolais cattle. Later, the ability to gain muscle rather than fat tissue made Charolais one of the most sought-after meat breeds. The current weight of adult Charolais bulls is 1.1 tons, cows - 0.9 tons.
Therefore, Charolais cows do not look muscular, unlike bulls that have been selected for the quality of their muscle mass for the last 100 years. The Charolais meat breed of cows brought to Russia is generally more reminiscent of an ordinary Russian cow. Including fatness. However, nothing surprising.Where will the energy and muscles come from if you drive cattle 20 km at the speed of a trotting horse, i.e., Charolais mothers with calves should cover 20 km, according to the shepherds, in 2 hours.
A serious disadvantage of Charolais is difficult calving, which is why it cannot be recommended for breeding in private farms. Hassle-free childbirth in animals is one of the main conditions for raising livestock. Only at first glance it seems that it is not at all difficult to spend several days a year near a giving birth animal. In fact, caring for livestock is very exhausting and the best option for the owner is “he came in the morning and was happy looking at the newborn,” the rest was done by the uterus. This approach is not suitable for Charolais.
Limousinskaya
It got its name from the French province of Limousin, where it was bred. Bulls have distinct features of a meat breed. Cows are more graceful. The weight of bulls is 1100 kg, cows 600 kg with a small height of animals about 125-130 cm.
Limousines consistently transmit their characteristics when crossed with other breeds. These are animals with thin, strong bones and a significant amount of muscle. They are in good health. Suitable for the Russian climate, as it can withstand frosts down to 30 degrees, provided there is plenty of roughage.
Limousines are characterized by easy, problem-free calving and high calf yield: up to 95%. The ease of calving is explained by the fact that calves are born large (32-34 kg), but not wide.
This is one of the “old” beef cattle breeds bred in Russia. It has been bred in Central Russia since 1961. The cattle are unpretentious to feed and are well suited for keeping in a private farmstead.
When analyzing what types of beef cattle there are, one cannot help but mention the Belgian Blue.
Belgian
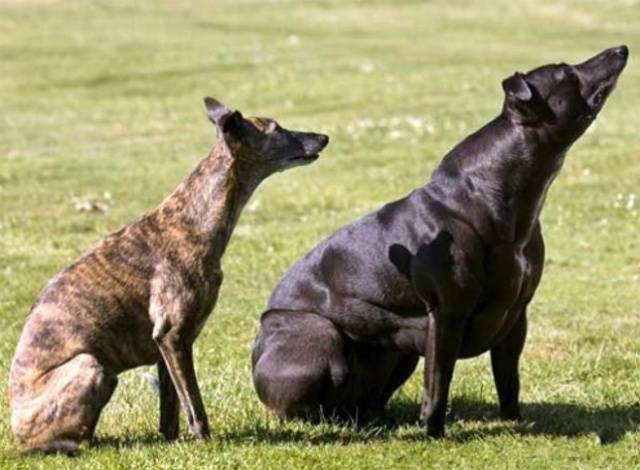
This best beef breed of cows was actually created by accident. In the genotype of ordinary cattle, as a result of a mutation, the gene responsible for limiting the growth of muscle mass has been “broken.” No genetic engineering was used. A similar phenomenon exists in dogs.
Both dogs are whippets, but the black one lacks a gene that limits muscle growth.
The exact same mutation occurred with Belgian cattle. But if Wendy the whippet was culled from breeding, then the opposite happened with cattle. Livestock farmers seized on this golden opportunity and secured the mutation.
Photos of the Belgian beef cattle breed are impressive.
The question arises as to how these cattle can reproduce. But in livestock farming, only artificial insemination has long been practiced. The uteruses of this breed are not able to calve on their own and they undergo a caesarean section. One uterus can withstand 6-10 operations.
These bulls require special conditions to be kept. They cannot gain weight on pastures like normal animals. They are kept in boxes that have access to a small pen.
But the advantage of this breed is its dietary meat with a low fat content. Living organisms are designed in such a way that it is more profitable for them to accumulate fat than to build muscle. In the case of a “broken” gene, the body, on the contrary, “refuses” to accumulate fat, “giving preference” to muscles.
But it is unlikely that Belgian cattle will ever appear on private farms due to difficulties with breeding.
Soviet breeds
They did not breed beef cattle in Rus'.All domestic beef breeds date back to the times of the Soviet Union and, in fact, are a cross between local national breeds and foreign beef cattle.
Cattle for meat production in Russia are represented mainly Kazakh white-headed a breed developed on the basis of Herefords.
Kazakh white-headed
This unpretentious breed weighs less than its parent, the Hereford. Kazakh white-headed bulls weigh up to 850 kg, cows 500. But Kazakh cattle are able to survive and gain weight where no European breed can survive. Cattle are adapted not only to poor nutrition, but also to wintering in the cold steppes. From a household point of view, the Kazakh Whitehead is more profitable than other beef cattle, since it does not require special care, and its fertility is 96%.
Selection work is being carried out on the breed in order to improve its milk productivity. Already today there are two lines. If the milk yield of a pure meat line is 1-1.5 tons of milk per lactation, then a dairy line is capable of producing 2.5 tons of milk. If you purchase the Kazakh White-headed dairy line, the owner will be able to not only provide himself with meat, but also get some milk for his daily needs.
If for some reason you are not satisfied with Kazakh cattle, you can consider Ukrainian beef breeds.
Ukrainian meat
The main composition of the parent breeds is three-quarters foreign. Charolais, Simmentals and Kiansi took part in the breeding of Ukrainian beef cattle. Among the locals there were only gray Ukrainian cattle.
The cattle are unpretentious to living conditions and are able to survive on pasture. True, these animals eat almost any plant, which creates a danger for fruit crops.
The animals are tall. Bulls can reach 150 cm at the withers and weigh 1.2 tons.Cows grow up to 130 cm and weigh 550 kg. Their meat yield is above average: 50-64%. But the main advantage of this breed is its thick skin, which is used to make leather shoes and other household items. The downside is that the breed is relatively new. Approved in 1993. Although the total number of livestock today reaches 10 thousand, few have heard of it and even fewer have seen it.
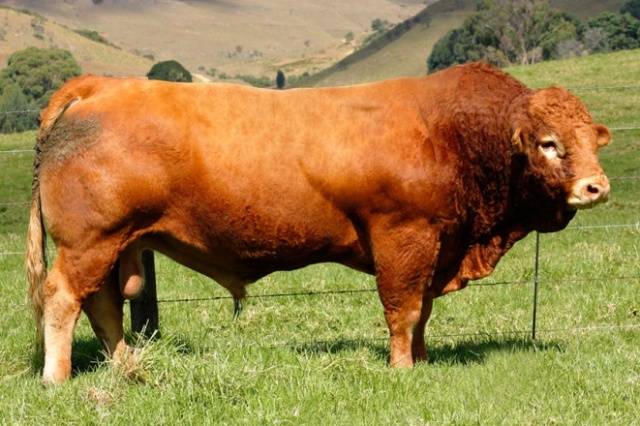
Volynskaya
Another Ukrainian breed is almost the same age as the previous one. Difference between Volyn and Ukrainian meat year. Volynskaya was bred in 1994. But the genetic base used to breed this cattle is slightly different:
- limousine;
- Aberdeen Angus;
- Hereford;
- Polish red;
- black-and-white.
The result was a red color of all shades: from cherry to light red.
The average weight of bulls is 1 ton, cows - 500-550 kg. The slaughter yield from the carcass is higher than that of Ukrainian meat and ranges from 60 to 66%.
Animals of a strong constitution with a powerful bone structure, uncharacteristic for beef cattle. The head is small, the neck is short and powerful. The withers and dewlap are well developed. The body is shorter than that of other meat breeds, wide in the back, with a round chest. Also, unlike other beef cattle, the muscles are not very visible under the skin. Although the skin of Volyn meat is of medium thickness.
Conclusion
Before choosing a beef breed of cow for your farmstead, it is better to familiarize yourself with the photo and description of the cattle, since not all of them have an easy-going disposition and will be safe for the owner.