Content
Large cap-shaped inflorescences of hydrangeas do not leave anyone indifferent; both beginners and experienced gardeners strive to grow them. However, this garden plant may not always feel good on the site, which can be immediately noticed by some external signs. If the leaves of a hydrangea dry out at the edges, dark spots appear on them or yellowness appears, then urgent rescue measures must be taken.
Why do the tips of hydrangea leaves dry out?
Changes in the color or structure of hydrangea leaf blades are associated with various factors:
- Water balance disturbances (excess or lack of moisture, unsuitable water for irrigation).
- Lack of nutrition or deficiency of any specific micronutrients in the soil.
- Change in soil acidity.
- Reaction to solar activity.
- Sudden changes in air temperature, drafts.
- Mechanical damage to the plant.
- Disease or pests.
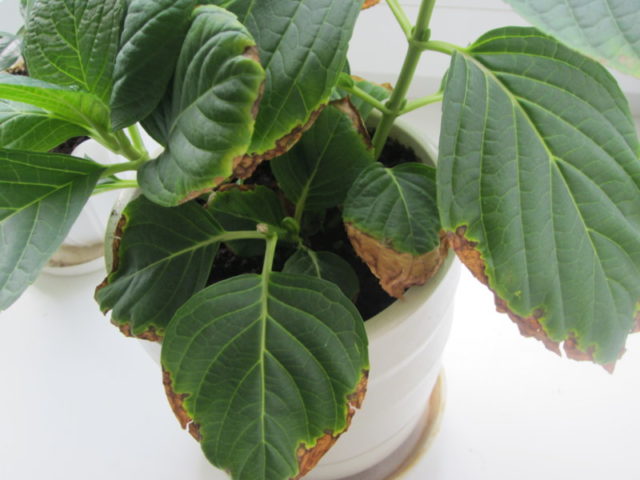

Drying of the edges of hydrangea leaves is a very common phenomenon.
Before taking any action, it is necessary to correctly assess all the factors that led to discoloration or drying of the edges of hydrangea leaves. After this, a set of special care measures can be carried out in order to normalize the situation. If this is not done, the consequences for the plant can be very sad.
Why do the leaves of home hydrangea dry out?
Indoor hydrangea is grown as a potted plant without transplanting it into open ground. However, it must be transplanted into another container annually. It is the consequences of this procedure that will be one of the reasons for the leaves drying out at the edges. This may be acclimatization to a new environment or mechanical damage received during work. A pot that is not the right size or a soil that does not meet the necessary properties can also affect the well-being of hydrangeas.
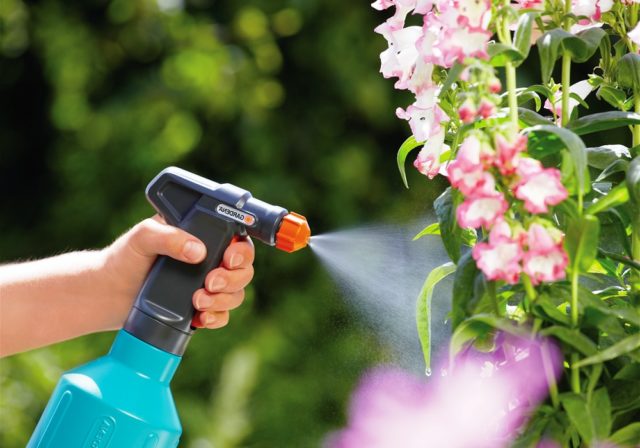

You can increase air humidity by spraying with a spray bottle.
The reason for drying of the leaf edges of hydrangeas growing indoors is often due to unsuitable climatic conditions. These may be the following factors:
- Humidity too low. It can be corrected by daily spraying the plants with water from a spray bottle.
- Changing soil properties and parameters. Excessive alkalization is removed by watering with a weak solution of citric acid, and the lack of nutrients is removed by fertilizing.
- Insufficient watering. The rate of moisture application needs to be increased.
- Sunlight too bright. In this case, the flower pot should be removed to a more shaded place.
Why do the leaves of garden hydrangea dry out?
Hydrangea grown in open ground is characterized by the same reasons for the leaves drying out at the edges or falling off as for a house plant. Here are some of them:
- Error with drop off or transfer location. If the new location is in direct sunlight, the plant may get burned.
- Damage to the root system during transplantation. In this case, the normal appearance of the hydrangea will be restored in 2-3 months.
- Alkalinization of the soil. Over time, the acidity of the soil gradually decreases. This happens mainly due to watering the bushes with tap or artesian water, which is characterized by increased hardness. Dissolved salts gradually react with the acid contained in the soil, and it becomes more and more alkaline, which is unacceptable for hydrangeas.
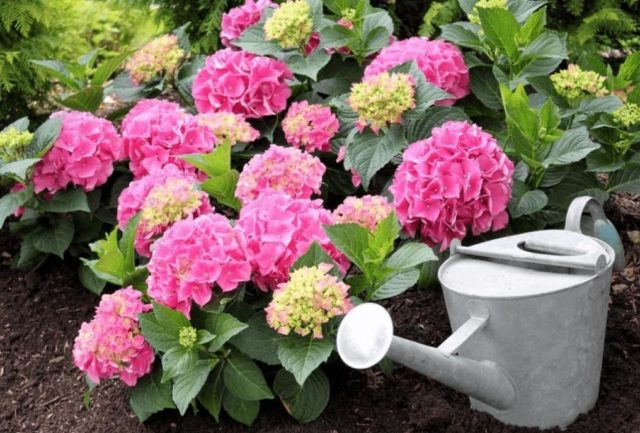

Lack of watering is a common cause of drying edges of leaves in hydrangeas.
The most common cause of leaf edges drying out is insufficient watering. In this case, the water regime for the bushes must be reviewed and adjusted.
Causes of drying hydrangea leaves
Most often, there are several reasons for leaves drying at the edges of large-leaved and many other types of hydrangeas, since all the factors leading to this phenomenon have a noticeable impact on each other. Therefore, this problem needs to be considered holistically, weighing and eliminating possible care errors one by one.
Wrong choice of seedling
Errors in choosing a hydrangea variety for planting can also cause premature wilting of the plant. First of all, for this reason, the leaves of the most heat-loving species of this plant, large-leaved hydrangea, dry out.In regions with harsh winters, it is recommended to grow it only as a tub plant, without transplanting into open ground. Tree-like and paniculate varieties are more winter-hardy. In these hydrangeas, the wilting of leaves is most often associated with a seasonal factor, since it is still a deciduous shrub.
Improper care
Improper care can be understood as any erroneous or insufficient actions of the grower, starting from the moment of planting the hydrangea. These are, first of all, various violations of the irrigation regime:
- Using poor quality water.
- Too much or, conversely, insufficient watering.
- Sprinkling during periods of high solar activity, leading to burns.
Untimely or improper feeding or excessive pruning can lead to wilting of the leaves of these flowers.

Errors during replanting can lead to drying out of the leaf edges of hydrangeas.
For hydrangeas grown at home, risk factors include errors during transplantation, improper placement indoors, due to which the flowers receive too much direct sunlight, insufficient air humidity, and unsuitable soil for growing.
Adverse weather conditions
Heat-loving hydrangeas do not always do well in areas with cool climates and changeable weather. The following factors most often lead to drying of leaf edges in plants growing in open ground:
- Heavy rainfall.
- Prolonged drought.
- Constant cold wind.
- Sudden temperature fluctuations.
Diseases and pests
One of the common diseases of hydrangeas is chlorosis. It can be identified by a change in the color of the leaves; they become light green, with clearly visible dark veins. The cause of chlorosis is iron deficiency in the soil or a decrease in the plant’s ability to absorb this trace element. Too low soil acidity also favors the development of this disease. To get rid of chlorosis, hydrangea is sprayed with a solution of iron sulfate and citric acid (2 and 4 g of each component, respectively, diluted in 1 liter of water). You can also water the plant at the root with the same preparation.

Chlorosis is a common disease associated with iron deficiency.
Fungal diseases appear on hydrangea relatively rarely. Here are the main ones:
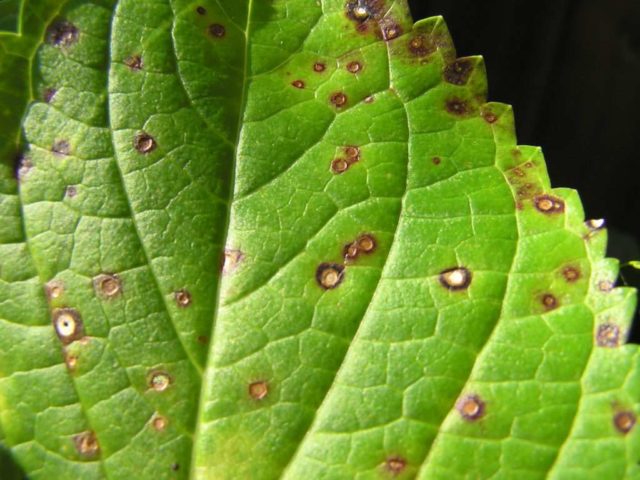
- Septoria. This disease can be recognized by small brown spots on the leaves. If the disease is not treated, hydrangea leaves begin to brown, dry out and fly off. At the first signs of septoria, the affected parts of the plant should be cut off and burned, and then the bushes should be treated with preparations containing copper: Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride or copper sulfate.
Hydrangea leaf affected by septoria
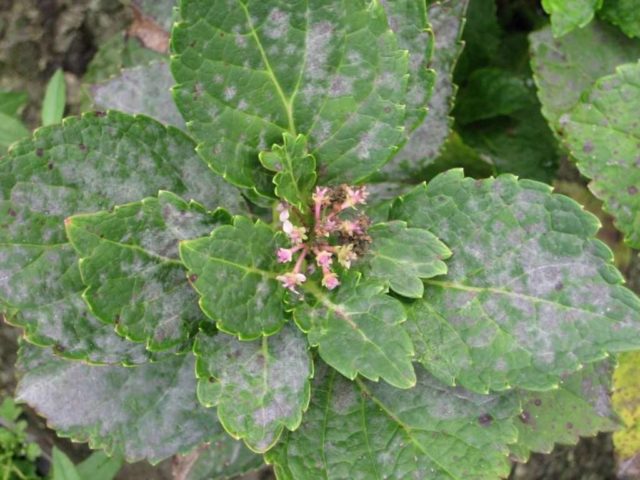
- Powdery mildew. It often appears on the leaves in the form of a light ash coating. Affected shoots quickly wither, become deformed and, as a rule, die in winter. They fight this disease by treating the bushes with various fungicides: Topaz, Chistotsvet, Fitosporin.
Light gray coating on the leaves is a sign of powdery mildew
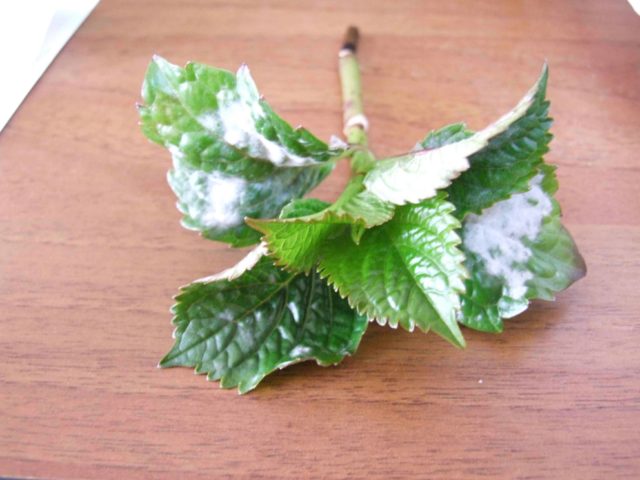
- White rot. A sign of the appearance of this disease is the darkening of the shoots, the presence of rot on their lower part, while a white fluffy coating becomes noticeable on the leaves. In most cases, the plant cannot be saved, so many gardeners, when white rot appears, destroy the hydrangea bush immediately, without waiting for the disease to spread to neighboring plantings. If it can be recognized at an early stage, then the affected parts of the bush are removed, the sections are burned with potassium permanganate, and then the plantings are treated with fungicides or special products against white rot.
White rot is a dangerous fungal disease
The following insect pests pose a danger to hydrangeas:
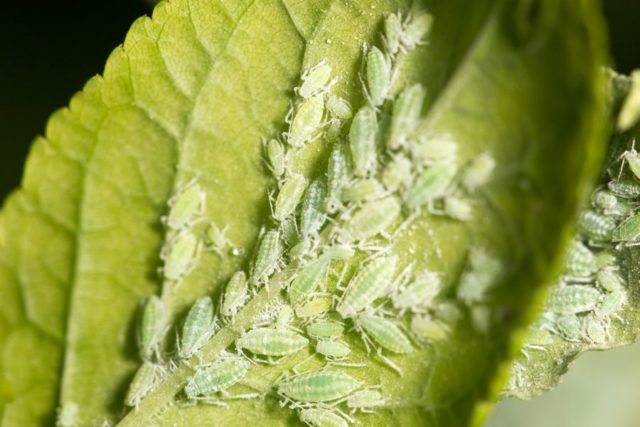
- Aphid. In small quantities, this small sucking insect does not pose a danger, but large colonies of it can seriously weaken or even kill the plant. The situation is aggravated by the fact that aphids reproduce very quickly, so their numbers can increase tens or hundreds of times in a short time. Due to the loss of nutrients, hydrangea leaves darken and dry, and the shoots wither. They fight aphids by treating the bushes with various insecticides, but if you notice small pockets of insects in time, you can simply wash them off with soapy water.
Aphids are dangerous because of their numbers
- Spider mite. Refers to sucking parasitic insects that suck juices from leaves and young shoots. It is found not only on hydrangeas, but also on many other garden plants. The appearance of this insect can be recognized by the presence of a thin cobweb entangling the nests with the pest. The affected leaves curl and dry out. The fight against this pest is carried out by treating plants with special means - acaricides.If the damage is not widespread, then the spider nests are torn off and burned, and the leaves are washed with a soap solution.
A thin web entangling the leaves is a sign of spider mites
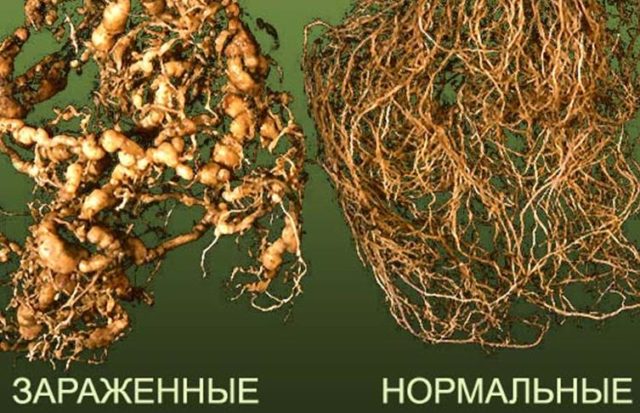
- Root nematode. This insect lives in the ground and is a microscopic worm that can live both in the roots and in the stem of a plant, gradually poisoning it with its waste products. The presence of the parasite can be determined by the characteristic reddish swellings at the base of the stem - galls. In these places, the process of rotting gradually begins, which is why the plant dies. To prevent the appearance of nematodes, the soil before planting hydrangeas is treated with Actofit or Fitoverm.
A plant infected with a root-knot nematode usually dies
What to do if the edges of hydrangea leaves dry out
Before you begin to take any action to correct the situation, you need to determine the cause of its occurrence. First of all, you need to carefully examine the plant, identify changes that have occurred with the leaves or shoots, and determine whether there are signs of diseases and pests on the hydrangea. After this, it is advisable to do a chemical analysis of the soil to determine its acidity, restore the water balance, and fertilize.
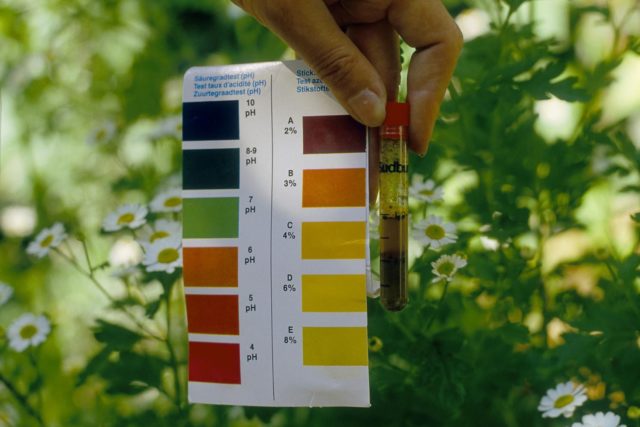

Controlling soil acidity is an important part of hydrangea care.
It is very important to assess the parameters of the microclimate: measure the temperature and humidity of the air, control the level of illumination. If the values of all these values are brought into line with the recommended ones, then, most likely, the hydrangea will recover very soon.
How to feed hydrangea when the leaves dry out
If hydrangeas were fertilized regularly, in the required volumes and at the recommended time, then additional stimulation is unlikely to improve their well-being. Fertilizer application is indicated if there is a clear lag in shoot growth and pale foliage color. In this case, it is more advisable to use special fertilizers for hydrangeas, azaleas and rhododendrons.

Many complex fertilizers are developed specifically for hydrangeas.
They contain a complete set of microelements necessary for the plant. They are used in accordance with the instructions.
Advice from experienced gardeners
Here are some tips from experienced gardeners regarding caring for hydrangeas when the edges of the leaves dry out:
- When transplanting hydrangeas, you can use Zircon along with watering. Thanks to it, the plant adapts faster to a new place.
- In extreme heat, even with intensive watering and mulching, hydrangeas may not have enough moisture, which leads to yellowing and drying of the leaves around the edges. You can increase the plant’s immunity if you treat it with a solution of a mixture of Epin and Cytovit.
- Artesian and tap water should not be used for watering hydrangeas without special softening. It contains a large amount of magnesium and calcium salts, which, when watered, will reduce the acidity of the soil more and more each time. Hydrangeas should only be watered with settled rainwater.
A short video on this topic can be viewed at the link below.
Conclusion
If the leaves of a hydrangea dry out around the edges, then this is not a reason to panic. In many cases, an unpleasant phenomenon occurs due to the vagaries of the weather. For example, prolonged heat in July may cause the leaves on the hydrangea to begin to dry out in August.In this case, natural regulation of the plant occurs, the root system of which cannot cope with the nutrition and water supply of a large amount of green mass. In addition, there may be several reasons, each of them needs to be dealt with in detail and the sooner the better.