Content
You can plant lemon to stimulate flowering and obtain a bountiful harvest at home, even with minimal skills in caring for garden trees. In this process, an important role is played by the quality of the tools used, the optimal timing of the procedure, and the correct preparation of the donor tree and the grafted seedling.
Goals and objectives of vaccination
Grafting home or garden trees is one of the ways to propagate and cultivate them. After a successful procedure, the lemon begins to bloom and bear fruit faster.
Proper vaccination:
- stimulates flowering and growth;
- significantly brings the date of the first harvest closer;
- preserves the characteristics of the variety;
- helps to get a strong, viable tree in a short time.
Is it necessary to graft a lemon grown from a seed?
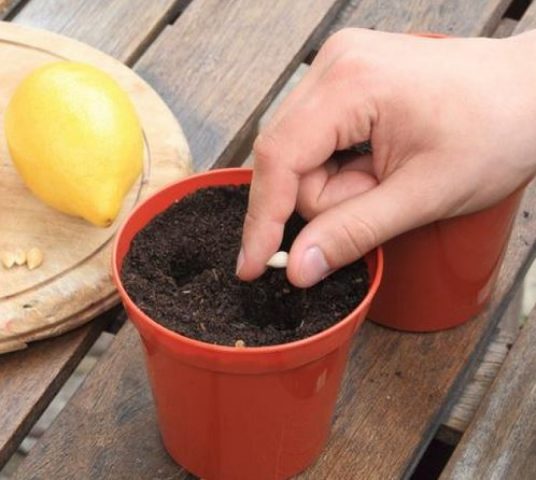
A strong, healthy, viable lemon can be grown at home from an ordinary seed. To do this, it is enough to place it in fertile soil, monitor timely watering, and occasionally apply complex fertilizers. Plant breeders call the resulting tree wild.
It is difficult to achieve a harvest from such a lemon. With careful care, the first flower ovaries will appear on it no earlier than 5–6 years later, and full-fledged fruits will appear 7–8 years after planting. In most cases, the wildflower begins to bloom only in the second decade of life. At the same time, it produces a meager harvest of small, sour fruits.
To stimulate budding and produce large fruits, a bud or cutting of a fruit-bearing indoor plant is grafted onto a lemon grown from a seed. After merging, the young shoot receives all the nutrients from the donor tree, is part of it, but retains its varietal characteristics and taste.
The grafted lemon begins to actively bear fruit already in the 2nd – 3rd year of growth.
Vaccination methods
Methods for grafting lemons at home differ in the methods of combining shoots of 2 different plants:
- scion – buds or cuttings of an indoor fruit-bearing tree;
- Pdouble – a young seedling selected for implantation of grafting material.
After examining them, the most suitable technology is determined at the preparatory stage:
- Budding - an easy and safe method for wood, with a high survival rate and low material consumption. The method is optimal if there is a dense, properly formed crown of the donor tree. For grafting, a young, strong bud of a varietal lemon is carefully placed under the bark of the rootstock. At the same time, the damage caused to plants is minimal.
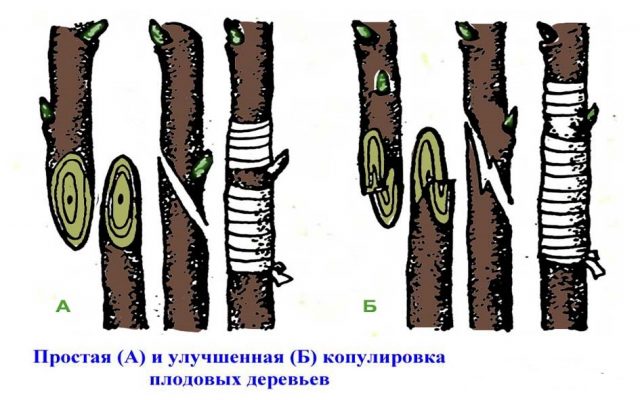
- Copulation - a common, but more traumatic method for the rootstock. The cuttings of the scion and the mother tree are cut at an acute angle, combined, and fixed. The diameter of the trunks should be approximately the same so that there is as little bare wood as possible.
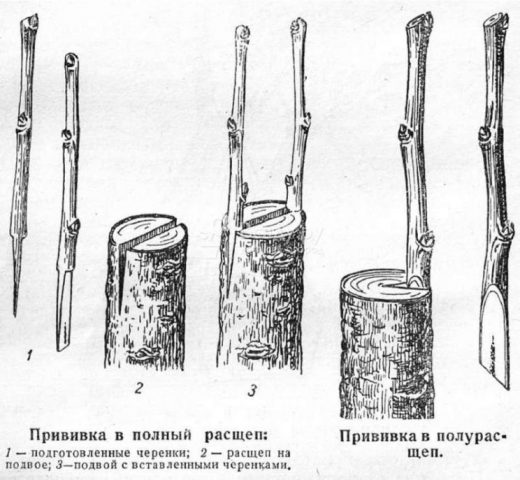
- Cuttings from the bark or into a split - one of the effective, but more complex methods. The trunk of the donor tree must be thick enough to withstand damage and increased stress. At the same time, the tree should not be older than 2.5 - 3 years. The advantage of the method is a large number of viable buds remaining on the scion. However, if the grafting is rejected, the donor tree usually dies.
What can you graft lemon onto?
The key to successful grafting of a lemon tree is the correct choice of rootstock. The plant must be strong, viable, disease-resistant, and have good taste.
For the rootstock, you should choose young seedlings of dwarf varieties of orange, grapefruit or lemon, grown independently from seeds. It is important that the diameter of the sprout trunk does not exceed 2–4 cm. The plant must be no older than 3 years and have a strong, developed root system.
If the mother tree is chosen correctly, young shoots grow actively. After a year, they are abundantly covered with flowers, and after another year, with proper care, they produce their first harvest.
Optimal time for lemon grafting
According to experienced plant growers, the optimal time for gardening is early spring. In March–early April, sap flow is intense, shoots and leaves are actively growing, and seedlings are susceptible to agricultural practices.
The timing of lemon grafting at home depends on the chosen method of the procedure:
- Budding takes place successfully in April–early May, when the plant actively begins to grow. It is permissible to graft a lemon in August, but at this time the tree is already “falling asleep”, the survival rate is reduced, and the formation of cuttings is slow.
- Copulation - carried out in winter or early spring before the first buds appear. Seedlings are most viable during this period.
- The best time for grafting into a cleft is March, when the lemon has many young and strong shoots.
To carry out grafting work, you should choose a rainy, cloudy day with the highest air humidity. This way the plant will tolerate manipulation more easily and adapt faster.
An incorrectly chosen period can lead to rejection of the grafting material, rotting, and drying out of the bud or main trunk.
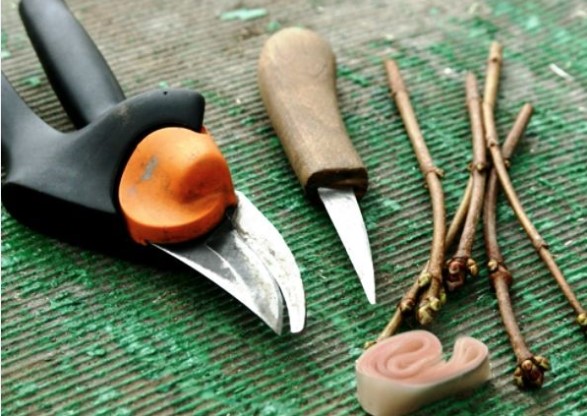
Preparation of tools and material
To successfully graft a lemon, you need to properly select and prepare gardening tools, materials, scion and rootstock.
The set of necessary tools includes:
- pruning shears for removing excess leaves and shoots;
- sharp knife or blade;
- special strapping material, electrical tape, narrow elastic or gauze bandage;
- garden varnish to protect the cut from infection and rotting;
- disinfectant solution, wet wipes.
Tools must be carefully sharpened and disinfected. The trunk, cuttings and hands are treated with antiseptic wet wipes.
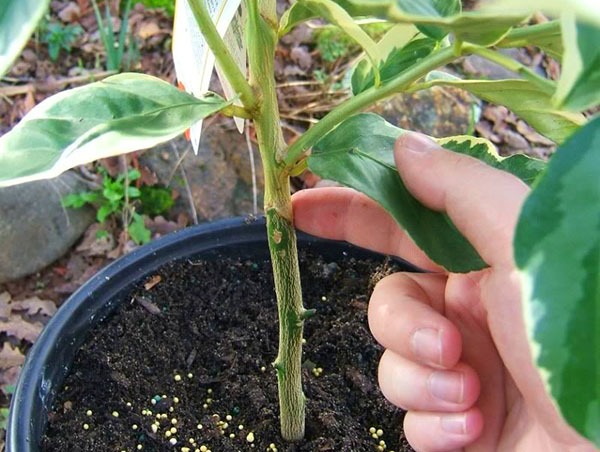
How to graft a lemon with a cutting
For wild animals with a strong, developed root system, grafting a lemon with a cutting will be optimal. The method involves cutting off the donor trunk and merging it with a scion seedling of similar diameter. As a result, a young shoot replaces the old branch: a tree with a varietal crown grows in its place.
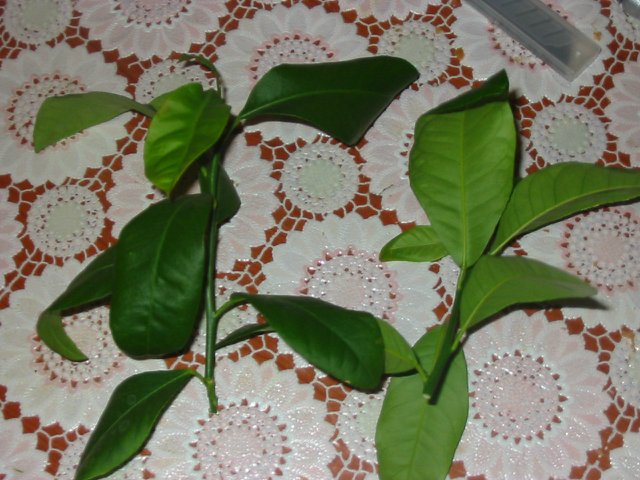
Where to get cuttings for lemon grafting
The success of implantation and fusion of shoots depends on the quality of the grafted material.
It is best to take a scion cutting from a 1-2 year old branch of a domestic fruit-bearing tree. For grafting, cut off 10–12 cm from a smooth, elastic shoot, leaving 2–3 viable green buds.
The rootstock for grafting indoor lemons is grown from an ordinary seed. It is not easy to obtain varietal scion material. You can find quality cuttings:
- at specialized points of sale;
- in a professional online store;
- through the private classifieds section on a local Internet portal;
- on the citrus growers forum.
The first option is the most reliable, guaranteeing that you will receive the desired lemon variety for grafting. Choosing other options involves a certain risk; you can purchase a hybrid or sterile plant.
Lemon grafting using copulation method
Copulation is a method of grafting a lemon by precisely combining sections of cuttings of the rootstock and scion. For successful engraftment, their diameter must be the same.
Procedure:
- A seedling no longer than 5 cm is cut from the mother plant.The crown is removed from the cuttings selected as the rootstock.
- Selected shoots are treated with antiseptic agents.
- On the cuttings, elongated oblique cuts of approximately the same size (3–4 cm) are made at an acute angle.
- Combine them with each other and secure them tightly with strapping material.
Improved lemon copulation involves an additional vertical cut-step for better fusion of shoots.
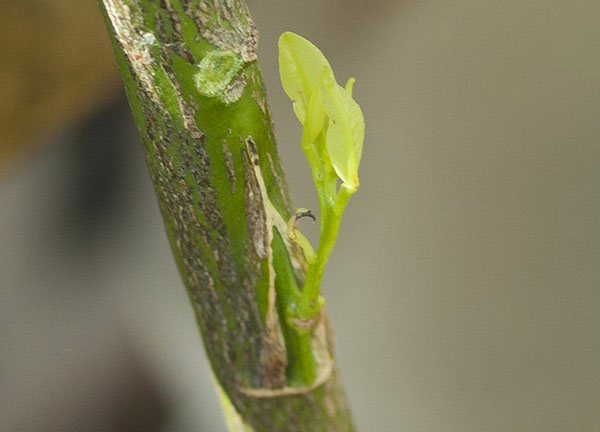
The result of the procedure can be assessed in approximately 3 weeks. After this period, the bandage is removed, regrown side shoots and shoots below the grafting site are removed.
Grafting a lemon into a cleft
Split grafting is convenient when it is necessary to grow cuttings of different diameters.
Algorithm of actions:
- The trunk of the donor tree is freed from leaves, growths, and small shoots.
- Wipe with an antiseptic composition and cut off at a height of 5–10 cm from the soil surface.
- In the remaining part, use a sharp knife and scalpel to a depth of 2.5 - 3 cm to make a vertical incision, carefully split it into 2 halves.
- In the lower part of the scion, cuts are made at an acute angle on both sides.
- The resulting wedge is carefully inserted into the split until it stops, aligning the boundaries of the bark.
- Bare areas of wood are smeared with garden varnish to protect against infection and rotting.
- The trunk is tightened with dressing material.
You can use 2 cuttings at the same time as a scion. The chances of survival in this case are higher.
The key to successful grafting is smooth, perfectly aligned sections. They are easy to make using a special pruner purchased from a gardening supply store.
The tool has a set of attachments suitable for any grafting method. This ensures the safety and ease of the procedure, rapid adaptation and healing of the shoots.
How to graft a lemon with a bud so that it bears fruit
Grafting a lemon with a bud is called budding or “eye grafting.” The process involves transferring a bud and part of the bark from a lemon cutting to a depression on the main trunk or branch of the donor plant. This method is one of the safest and easiest to perform.
Before the procedure, you should carefully prepare the grafting material:
- A young, large, viable bud is selected from a varietal lemon.
- It is cut off along with the leaf petiole and part of the bark (scutellum).
- The leaf is removed completely or ¼ of the total area is left for nutrition.
- The scion is immersed in cool, preferably filtered or settled water, so that the bud does not dry out.
For the rootstock, choose a young (about 3 years old), strong plant with strong bark and active sap flow. The barrel must be wiped with a damp antiseptic wipe or treated with alcohol.
Algorithm of actions for grafting a lemon with a bud:
- A transverse incision 1 cm long is made on the trunk of the donor tree at a height of about 10–12 cm from the ground. Its depth should be such that the bark is easily separated from the wood, but the core remains intact.
- Another incision is made perpendicular to it, 2.5 - 3.5 cm long. A T-shaped cutout is obtained.
- The bark is slightly bent to allow access to the inner wood.
- A prepared shield with a bud of a cultivated lemon is inserted into the resulting recess.
- The trunk at the grafting site is tightly wrapped with bandaging material, elastic or gauze bandage, polyethylene or electrical tape. It is important to ensure that the “peephole” remains outside, and do not put a bandage on it.
- For tightness, garden varnish is applied over the binding.
To increase the chances of getting a varietal lemon, you can carry out a double grafting - implanting 2 buds on opposite sides of the trunk. You need to be confident in the strength and vitality of the mother tree: the load on its root system will be increased and a double amount of nutrients will be required.
The result of the procedure can be assessed in 15 – 25 days.
If the cutting turns yellow and falls off, the lemon grafting was successful. Soon a young shoot will appear and actively grow.
A month after germination, the strapping is removed, the trunk of the donor tree is cut off, retreating 10 - 15 cm from the place of implantation, and the cut is treated with garden varnish.
If the varietal bud has darkened, shriveled, and does not fall off when touched, the grafting has failed. The old cutting must be carefully removed, the cut must be disinfected, and the procedure repeated on another section of the bark.
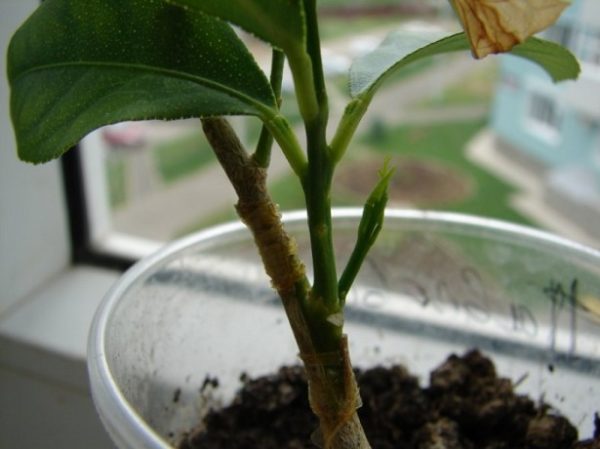
How to grow lemon grafted at home
After grafting, the lemon needs careful care and a set of restorative, healing and stimulating measures:
- Greenhouse conditions are created for the plant: covered with a glass jar, plastic bottle, or polyethylene.
- The resulting greenhouse is ventilated at least 2 times a day, opening the film slightly for 3 to 5 minutes.
- The pot of lemon is placed on a sunny, warm windowsill, providing enough light for growth and development.
- All leaves and lateral shoots are removed from the donor shoot.
- In an improvised greenhouse, a high level of humidity is maintained: a generously moistened napkin or a small container of water is placed under the film, and timely watering is ensured. In addition, experienced gardeners recommend mulching the soil with sawdust to avoid drying out.
- After 2–3 weeks, the condition of the scion is assessed. If the leaf cuttings turn black, the procedure was not successful; if they dry out and fall off, the operation was a success.
- After successful implantation of the varietal material, the donor trunk is cut off at a height of 10–15 cm from the grafting site, and the cut is treated with garden varnish.
- Carefully monitor the condition of the young lemon.
Caring attitude and careful care of the grafted shoot will help you get an excellent harvest of lemons 1 – 2 years after the procedure.
Conclusion
To graft a lemon at home, you need to carefully study the methods of carrying out such a procedure, choose a strong donor tree, and find high-quality grafting material. For beginners, it is better to use a special pruner that provides even, uniform cuts. For professionals, lemon grafting is a creative, exciting process that helps achieve an excellent varietal harvest in a short time.