Content
Calf houses are successfully used in individual farms and on large farms when raising young animals. In homemade construction, the structure is a small wooden box. Factory-made boxes are made of durable polymer.
What are calf houses for?
Previously, young animals were kept together with an adult herd. A calf near a cow gains weight faster. In addition, there is no need to equip additional premises. However, the outdated method has a huge disadvantage. Adults are carriers of pathogens. Cows have good immunity, but young calves are still weak. The young animals begin to get sick, lose weight, and some individuals even die.
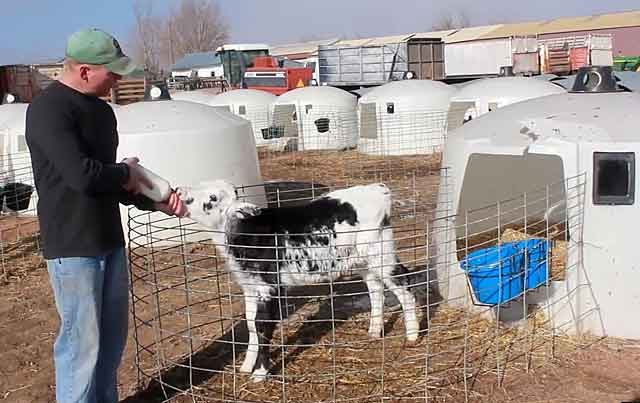
Due to the great competition in the agricultural market, farmers have become faced with a serious problem related to the need to improve the survival rate of young animals. To separate calves from the adult herd, houses were invented. The design resembles a box. Private livestock breeders knock down wooden houses.Boxes made of food-grade polymer are produced for farms. The material is durable and completely eliminates the possibility of injury to the animal.
Plastic boxes are lightweight and durable. The lower part has an expansion, which ensures the stability of the structure. The house is easy to wash and can be easily moved or carried by two people to another place. Install the box inside or outside the barn. On the entrance side, a metal fence is installed for walking animals, feeding troughs and drinking bowls are installed.
Advantages and disadvantages of raising calves in hutches
The technology of keeping calves in separate boxes has its positive and negative sides.
Advantages:
- Raising calves separately eliminates the possibility of contracting dangerous diseases from adult cows.
- It is easier to keep clean in the houses. Plastic boxes are easy to wash, making it convenient to change the bedding for calves more often.
- A box installed outside the barn allows calves to breathe clean air rather than ammonia fumes.
- When the box is installed outdoors, the young animals receive sunlight. Animals absorb vitamin D, which promotes health.
- The solid walls of the house protect the calf from drafts and cold winds. The likelihood of the animal developing a cold is reduced.
- Young animals reared separately are easier to monitor: assess their general condition, growth, and weight gain.
- Separate houses make it possible to provide individual nutrition to each calf and raise weak individuals to their feet.
Flaws:
- additional costs for purchasing boxes for calves;
- with the onset of cold weather, it is more difficult to heat the box, calves begin to consume more feed;
- In order for calves to set up separate boxes, free space is required.
However, due to the possibility of repeated use, the houses pay for themselves over time and begin to make a profit.
Types of houses for young cattle
The houses differ in the materials they are made from:
- wooden;
- plastic.
By design:
- individual;
- group.
An individual calf box contains only one animal. The calf grows from birth to 10 weeks. An animal isolated from the general herd develops faster and its immunity improves. The factory-made plastic individual box resembles a small hangar with a semicircular roof. Opposite the entrance doors is a metal fence that forms a calf walking area.
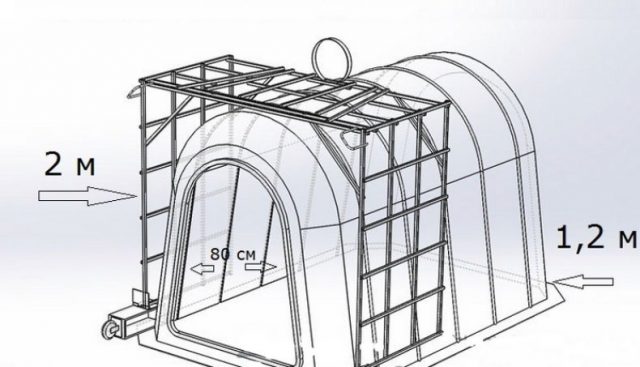
Young animals up to 4 weeks old, weighing up to 30 kg are given boxes measuring 150x130x130 cm. The dimensions of the house for calves over 4 weeks old, weighing 40 kg are 200x130x140 cm. The size of the doorway in the first case is 84x55 cm, in the second option - 94x57 cm.
Group boxes are in demand by farms with a large number of livestock. The young animals are transferred here after being kept in individual houses for ten weeks. In group pens, calves adapt to the herd lifestyle. The number of individuals for one house depends on their physique and weight:
- calf weight 150 kg – minimum area 1.5 m2;
- calf weight 200 kg – minimum area 1.7 m2;
- calf weight more than 200 kg – minimum area 1.8 m2.
It is optimal to create a herd of young animals of 5-20 individuals of the same age. Calves gathered in a group should not be sick. There should be free space inside the house. Young animals are kept in group boxes until they reach the age of 6 months. Depending on the model, the size of the factory-made structure reaches 43x21.8 m.
Requirements for houses
To successfully raise young cattle and comply with sanitary standards, strict requirements are imposed on the houses and the technology for keeping animals:
- The place for the boxes for young animals is chosen on a hill, where there is no likelihood of flooding with sewage. The wind rose is taken into account.
- The box is removed from residential buildings and sources of water intake.
- When making houses for calves on their own, they use safe, strong, durable materials. Hardwood is usually preferred. Wood also has high thermal insulation properties.
- The dimensions of the house must correspond to the age and physique of the animal.
- It is important to take care of additional heating of the young animals. Calves aged from 14 days to 6 months are maintained at an air temperature of +15OWITH.
- Ventilation is required. With the help of adjustable dampers inside the house, the air movement speed is ensured in winter - 0.3 m/s, in summer - 0.5 m/s.
- Ventilation maintains humidity from 40 to 75%. By ventilation, it is achieved that the maximum concentration of gases inside the box is: ammonia - 15 mg/m3, carbon – 0.25%, hydrogen sulfide – 5 mg/m3.
- Each house is assigned individual drinking bowls, feeders, equipment for maintenance, and special clothing for working personnel.
The inside of the boxes is kept constantly clean. After each cleaning, the floor is disinfected with bleach or formaldehyde.
How to make a custom calf house with your own hands
A homemade box for young cattle helps to save on the purchase of an expensive factory-made structure. If you have the materials, tools, and construction skills, create a suitable project and get to work.
Necessary tools and building materials
The base and floor of the house will be wooden. To work with the material you will need a saw, a screwdriver, and a plane. The roofing material chosen is corrugated sheeting. To cut sheets you need metal scissors. You will also need a marking tool: tape measure, pencil, level.
The frame of the box for calves is made of timber with a side size of 50x50 mm. A 40 mm thick board is suitable for the floor. The walls of the house are covered with OSB boards or 20 mm thick boards.
Creating a Project
Adhering to the recommended house sizes for a certain age of calves, a drawing is drawn up. The box diagram will help you roughly calculate the required amount of material. Separately, the project includes a fence for walking young animals. Its optimal dimensions are 150x130x100 cm (length, width, height, respectively).
Building a house
The step-by-step process consists of the following steps:
- Blanks are cut from timber. First, a rectangular frame is knocked down, forming the base of the box frame. The corner connection of the timber is made with cuts 25 mm deep. Nails or self-tapping screws are used for connections.
- The racks of the box frame are attached perpendicular to the frame. The elements are reinforced with mounting metal corners. The verticality of the racks is checked with a level.There are 4 of them installed in the corners and 2 additional ones, forming a doorway.
- The height of the rear pillars is cut so that they are 100 mm shorter than the front pillars.
- The racks are secured at the top with timber strapping. It is identical in size to the lower frame. Irregularities that arise at the joints are cleaned off with a plane.
- The finished calf box frame is covered with OSB boards. When using a board, it is laid end-to-end, and the joints are additionally closed by stuffing planks on top.
- Logs are attached to the bottom frame. The floor is laid from boards.
- Three slats are nailed to the top frame of the box: one in the center, and two closer to the edges. Sheets of corrugated sheets are fixed to the sheathing with self-tapping screws. A wind strip is installed along the perimeter of the roof to protect against drafts.
- The doorway of the box remains open. With the onset of cold weather, it is covered with a tarpaulin.
- The fencing for the calf's run is made of metal posts and mesh. It can be designed removable or stationary with a gate.
- If the house will be located outside in winter, the ceiling and walls will be insulated from the inside with foam plastic or basalt wool. The thermal insulation on top is covered with OSB sheathing.
- Ventilation holes are cut out in the ceiling and air ducts with adjustable dampers are inserted.
When the house is ready, we begin the interior arrangement. Install feeders and drinking bowls. The floor is covered with hay.
Rules for caring for calf houses
Individual housing allows you to better care for calves, pay more attention, prevent diseases in a timely manner, introduce useful additives into the diet of young animals, and prevent mold from forming in the feed. Caring for the houses is based on maintaining cleanliness.Plastic structures are equipped with a smooth floor. It cleans well of manure and dirty litter and is easy to clean. To remove calf waste, open the back cover. Some of the manure is thrown out through the doorway.
Beams must be laid on the threshold of the house. The element prevents animals from removing bedding, as well as from bringing in organic waste from the street. The inner surface of the walls and ceiling of the plastic structure is washed with a rag soaked in a disinfectant solution. Wooden houses are disinfected by whitewashing with lime or treating with special store-bought preparations.
For ease of maintenance, the fence is equipped with structural elements that allow you to close the calf inside the house or pen. It is optimal to have a removable or hinged fence. During maintenance without a pen, access to the house is simplified. A big plus is the removable canopy. It is placed for shade or to protect the animal from precipitation, and if necessary, it is removed.
Up to three feeders are installed on the fence of the pen for young animals. Each equipment is designed for a specific type of feed. Don't forget about the drinking bowl. To simplify the care of young animals, boxes are installed as close as possible to the farm. Maintenance personnel will have to travel a shorter distance. Productivity and quality of care will increase. In addition, calves will constantly see cows, which will improve their appetite.
Conclusion
Housing for calves accelerates the growth of animals and improves their physical condition. When keeping young livestock separately, you can resort to early fertilization of the heifer, which allows you to increase milk productivity.