Content
If dill turns yellow, there are many possible reasons for this phenomenon - from poor-quality seed material and the wrong place for planting to lack of proper care and damage by diseases or pests. Timely identification of the problem and appropriate measures in most cases make the situation reversible.
Why does dill turn yellow and not grow?
Yellowing of dill is often associated with violations of agricultural practices. The cause can be identified by accompanying symptoms.
Poor quality seeds
Dill may turn yellow if low-quality seeds are used. Expiration date, storage conditions, and the source of the collected material are important.
Soil acidity
Soil with neutral acidity is recommended for growing dill. This is a pH level of 6.1-7. If the dill begins to turn yellow, then the soil may be too acidic (with an alkaline reaction, redness is observed).
The pH level is determined with a special device or indicator paper. The latter can be bought at a gardening store.The strip is placed in an earthen lump taken from a depth of 10 cm and squeezed tightly. To determine the level, the color of the indicator paper is checked against the control scale.
Planting density
Dill turns yellow when planted too thickly. The crop simply does not have enough nutrients that are important for its growth and development. Additionally, excessive planting density increases the risk of disease and pests. Plants weaken, becoming more vulnerable.
Another point is the amount of dill sown. If there is too much of it, then you simply may not have time to harvest in a timely manner. Then the greens will begin to turn yellow and wither - the cycle of full ripening will simply end.
Improper watering
Yellowing of dill is a consequence of improper watering. The cause may be either excess or deficiency of moisture. Too dry soil also causes leaves to curl. When the soil is often waterlogged, the root system rots, which is why dill turns yellow and withers.

Dill may turn yellow if cold water is used to water it.
Lack of light
In the garden and on the windowsill, dill is turning yellow due to lack of light. The culture prefers sunny areas. It is optimal if a 16-hour daylight hours is provided. When greens grow in the shade, they not only turn yellow, but also become thinner and dry out. Its taste also deteriorates and its characteristic aroma disappears.
Exposure to sunlight
In hot weather, the ripening process accelerates. Umbrellas may appear earlier, and the greenery also turns yellow before the due date.
The reason for the change in color of dill often lies in excessively intense lighting.Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause burns. As a result, the greens dry out and turn yellow, and their quality decreases. For dill, it is better when there is light partial shade at noon.
Nutrient deficiency
Dill may turn yellow if it lacks nutrients. The reason usually lies in excessive planting density or soil depletion. Dill often turns yellow when it lacks nitrogen. It is this element that stimulates the growth of green mass.
Pests
If the dill dries out and turns yellow, and its leaves curl, the reason may lie in aphids. The insect feeds on plant juices, disrupting the process of crop formation. Aphid infestation can be detected not only by the presence of insects, but also by a white sticky coating. Over time it turns black. The secretions accumulate, slowing down photosynthesis.
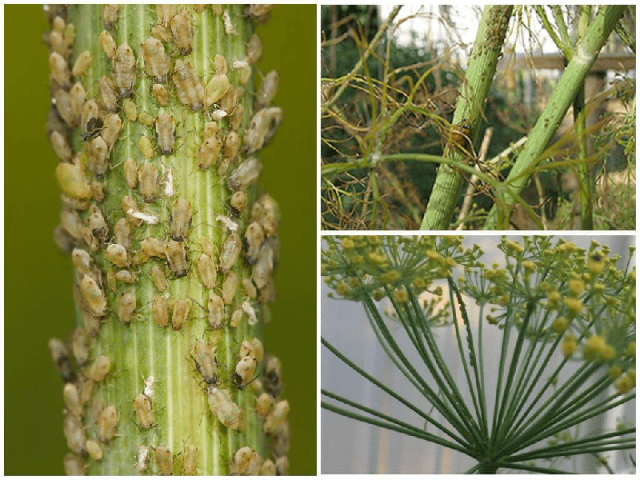
Aphids multiply quickly, transmit viruses and often cause developmental abnormalities in plants
Diseases
If the dill turns yellow on the bottom, it may be verticillium wilt. The reason lies in soil contaminated with a fungus or the use of unrotted manure or compost. The disease begins with yellowing of plants on sunny days. Then the dill withers, curls and turns brown.

The risk of verticillium wilt is higher for plants with damage to the root system and lower part of the stem
Yellowness of dill may also be the first sign of peronosporosis. It appears on the outer part of the leaves, which then turn brown. A white coating appears from below.
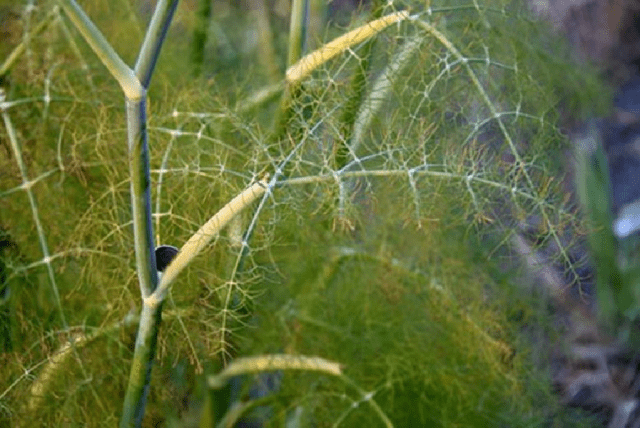

Optimal conditions for infection with peronosporosis are rainy weather and air temperatures up to 20 °C
Yellowness of dill is the initial sign of Fusarium wilt.It develops from the lower leaves. Then the greenery turns red and brown. After the defeat and the top leaves, the plant withers.

Fusarium wilt is promoted by high temperature and excessive soil moisture.
What to do if the dill turns yellow
When dill turns yellow, you need to act according to the cause of this problem. In most cases, eliminating it is sufficient.
If dill turns yellow due to an acidic soil reaction, dolomite flour or eggshells (crushed into powder) will help normalize it. It is not recommended to use lime and ash - the crop reacts poorly to them. Soil deoxidation should be done before sowing.
When dill turns yellow due to planting density, the problem is solved by thinning. A minimum of 2 cm is left between adjacent plants, and the rows are made at a distance of 5-6 cm. You should focus on the specific variety and the planting scheme recommended for it.
If yellowing is caused by a fungal disease, then fungicides are needed:
- Alirin-B;
- Gamair;
- Strobe;
- colloidal sulfur;
- copper sulfate;
- Bordeaux mixture.
Folk remedies are also used to combat fungal diseases at an early stage. Their advantage is that there is no need to wait until a safe time before harvesting. There are many options, including:
- infusion of onion and garlic;
- mustard powder solution;
- foam of green, laundry, tar soap;
- kefir or whey (diluted in ten parts of water) with the addition of iodine (a drop per 1 liter).
If dill turns yellow due to improper watering or too cold water, then the regime needs to be normalized. The crop requires moisture once a week.When the weather is dry and hot, watering is increased 2-3 times. Use warm water (from 18 °C). When growing in open ground, it is optimal to spend 10 liters per 1 m². In addition to the correct watering regime, regular loosening is important. It ensures air and moisture permeability of the soil.

If dill turns yellow due to excess moisture, then at first it is necessary to loosen the soil after each watering and precipitation.
When the reason for the yellowing of dill lies in excessive lighting, then you need to shade the plantings during the hottest hours. For this purpose, white covering material is used.
Nutrient deficiencies can be resolved by applying appropriate fertilizers. Urea can be used as a source of nitrogen - for foliar feeding 5-6 g per 1 liter of water. This volume is enough for 33 m². The lack of organic matter can be well compensated by an infusion of mullein and bird droppings. Other options are also effective:
- nettle infusion - the raw material is filled with water, left for a week, used for watering twice a month;
- ammonia – 1 ml per 1 liter of water, spraying twice a week;
- liquid fertilizer Biud on horse manure - diluted in 20 parts of water, watered the soil;
- Ideal concentrate – 9 ml per 1 liter of water, solution consumption 10 liters per 6 m².
To combat aphids on dill, you can use laundry or tar soap - dissolve the bar in 5 liters of water and leave for 7 hours. The resulting product is sprayed onto the stems and leaves. Other methods are also used against aphids:
- drugs – Biotlin, Fitoverm, Akarin, Tanrek, Aktara;
- folk remedies - soap and soda solution, infusions of tobacco, ash, zest, tomato tops, pine needles, horse sorrel;
- the neighborhood of repellent plants - marigolds, coriander, fennel, mint, garlic, onions, basil, mustard, lavender.
Is it possible to eat yellowed dill?
You can use yellowed dill for food if the color change is associated with improper agricultural practices or weather conditions. It should be taken into account that such reasons affect not only the color, but also the taste and juiciness.
Do not eat greens that have turned yellow due to disease or pests. This can be harmful to health and cause poisoning.
Prevention measures
It is easier to prevent any problems than to deal with the consequences. To prevent yellowing of dill, the following measures are important:
- choosing the right place for planting - a sunny and well-ventilated area, loose soil;
- proper preparation of beds - adding organic matter, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers;
- disinfection of seeds, usually using a solution of potassium permanganate (1 g per 100 ml of warm water, soaking for 20 minutes, rinsing);
- normalization of pH levels before sowing;
- correct predecessors - dill is not planted in a row in one place and after other umbrella crops, alternated with nightshade, legumes, and melons;
- compliance with the planting scheme and timely thinning;
- regular weeding and loosening;
- correct watering mode;
- selection of varieties that are resistant to fungal diseases and flowering.
Dill ripens quickly, therefore, with proper preparation of the site, it is enough to feed it with minerals once a season, and the rest of the time with organic matter. There will be no deficiency of nutrients if you add the following per 1 m² in the fall:
- 4-5 liters of humus;
- 15 g nitrogen;
- 20 g potassium;
- 30 g phosphorus.

To prevent damage to dill by aphids, which also harm most other plants, you need to fight ants
Conclusion
If dill turns yellow, the reasons can be very different. Most of them can be solved, especially at the beginning, when the plants have just begun to change. Preventive measures will help you avoid trouble in the future. Most of them are related to the rules of agricultural technology.








